第四课:GPT2
文章目录
- 第四课:GPT2
-
- 1、学习总结:
-
- GPT2的学习目标和概念
-
- 任务调节
- 零样本学习和零短任务迁移
- 模型结构
- GPT-2 自注意力掩码实现
-
- 1- 创建qkv
- 2- 评分
- 3- 合并注意力头
- 4- Projecting
- 课程ppt及代码地址
- 2、学习心得:
- 3、经验分享:
- 4、课程反馈:
- 5、使用MindSpore昇思的体验和反馈:
- 6、未来展望:
第四课:GPT2
1、学习总结:
GPT2的学习目标和概念
任务调节
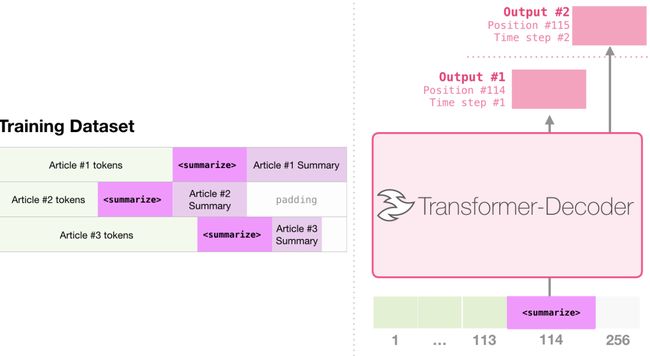
任务调节(Task Conditioning)就是GPT-2模型在学习多个任务时如何修改学习目标
- 原始语言模型学习目标:
- 在普通的语言模型中,学习目标通常被表示为 P(output|input),即在给定输入(input)的情况下,模型要学习生成正确的输出(output)。这是一种无监督学习的形式。
- GPT-2学习多任务的目标:
- GPT-2的目标是通过同一个无监督模型学习多个任务。为了实现这一目标,学习目标需要进行修改。修改后的目标被表述为 P(output|input, task),即在给定输入和任务的情况下,模型需要学习生成正确的输出。这就是所谓的任务调节。
- 任务调节的含义:
- **任务调节是指模型被期望在同一输入下,针对不同的任务生成不同的输出。**这样,模型可以适应多个任务而不需要重新训练。这对于提高模型的通用性和迁移能力非常有帮助。
- 任务调节的实现方式:
- 有些模型在架构层面上实现了任务调节。**这意味着模型的架构被设计成同时接收输入、任务信息,然后生成相应任务的输出。**在语言模型中,输出、输入和任务都是自然语言序列。
总的来说,任务调节是一种技术策略,通过修改语言模型的学习目标,使其能够适应并执行多个任务,而无需为每个任务重新训练一个独立的模型。这有助于提高模型的灵活性和泛化能力。
零样本学习和零短任务迁移
-
零样本学习(Zero Shot Learning):
- **零样本学习是指在没有提供任何样本的情况下,模型能够理解并执行新任务的能力。**通常情况下,模型需要通过示例进行训练,但在零样本学习中,模型从未见过与新任务相关的样本,而是通过给定的说明(instruction)来理解任务。这意味着模型可以在没有具体训练样本的情况下执行任务。
-
零样本任务迁移(Zero Shot Task Transfer):
- **零样本任务迁移是零样本学习的一种特殊情况,其中没有提供任何示例,而是提供了任务的描述或指示。**在这种情况下,模型被期望理解任务的性质,并根据指示执行任务。这是一种非常灵活的学习方式,使得模型能够在没有显式训练的情况下适应新任务。
-
GPT-2的零样本任务迁移能力:
- **GPT-2具有零样本任务迁移的能力,其中模型不需要事先看到特定任务的训练示例。**与GPT-1不同,GPT-2的输入格式被设计成期望模型理解任务的性质并提供答案,而不是通过对序列进行重新排列来进行微调。这是为了模拟零样本任务迁移的行为。
-
示例:
- 下图是一个英语到法语的翻译任务。对于这个任务,模型接收一个英语句子,后面跟着单词"French"和一个提示符(。模型需要理解这是一个翻译任务,并给出英语句子的法语对应部分。
总体而言,GPT-2通过设计输入格式,使模型在没有看到具体任务样本的情况下能够理解任务要求,这展示了其在零样本学习和任务迁移方面的强大能力。
模型结构
-
模型层数和词嵌入维度:
- **GPT-2采用了深层的模型结构,具体来说,模型包含了48个层(layers)。**每一层都参与对输入数据的处理和特征提取。**此外,GPT-2使用了1600维的词嵌入向量(word embedding vectors)。**这些词嵌入向量用于表示模型对词汇中每个单词的理解,使得模型能够学习丰富的语义信息。
-
更大的词汇表:
- **GPT-2采用了更大的词汇表,其中包含了50,257个不同的标记(tokens)。**这意味着模型可以处理更广泛和更丰富的语言表达,从而提高了模型的语言理解和生成能力。
-
更大的批处理大小和上下文窗口:
- **GPT-2使用了更大的批处理大小(batch size),具体为512。**批处理大小是指在一次训练迭代中同时处理的样本数量。较大的批处理大小可以带来一些训练效率和性能的优势。
- **此外,GPT-2使用了更大的上下文窗口(context window),包含1024个标记。**上下文窗口定义了模型在处理输入数据时所考虑的上下文范围。较大的上下文窗口有助于模型更好地理解文本中的长期依赖关系和语境。
**这些特征使得GPT-2成为一个非常强大的语言模型,能够处理大规模的语料库,捕捉丰富的语义信息,并生成高质量的文本。**然而,也需要注意到这样的大型模型在训练和推理时需要更多的计算资源。
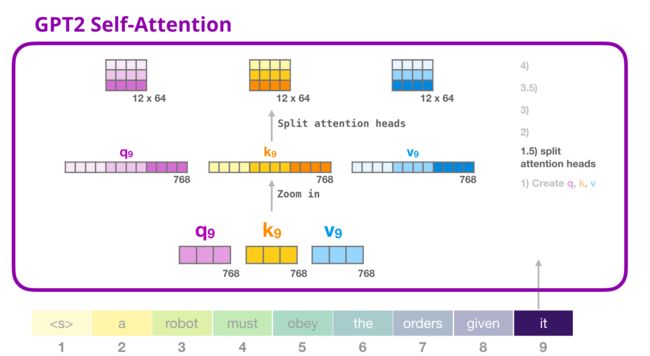
GPT-2 自注意力掩码实现
1- 创建qkv
import numpy as np
import mindspore
from mindspore import nn, ops, Tensor
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 10
embed_dim = 768
x = Tensor(np.random.randn(batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim), mindspore.float32)
from mindnlp._legacy.functional import split
from mindnlp.models.utils.utils import Conv1D
c_attn = Conv1D(3 * embed_dim, embed_dim)
query, key, value = split(c_attn(x), embed_dim, axis=2)
query.shape, key.shape, value.shape
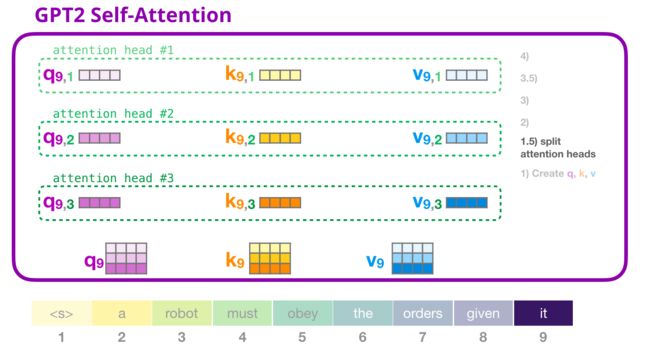
def split_heads(tensor, num_heads, attn_head_size):
"""
Splits hidden_size dim into attn_head_size and num_heads
"""
new_shape = tensor.shape[:-1] + (num_heads, attn_head_size)
tensor = tensor.view(new_shape)
return ops.transpose(tensor, (0, 2, 1, 3)) # (batch, head, seq_length, head_features)
num_heads = 12
head_dim = embed_dim // num_heads
query = split_heads(query, num_heads, head_dim)
key = split_heads(key, num_heads, head_dim)
value = split_heads(value, num_heads, head_dim)
query.shape, key.shape, value.shape
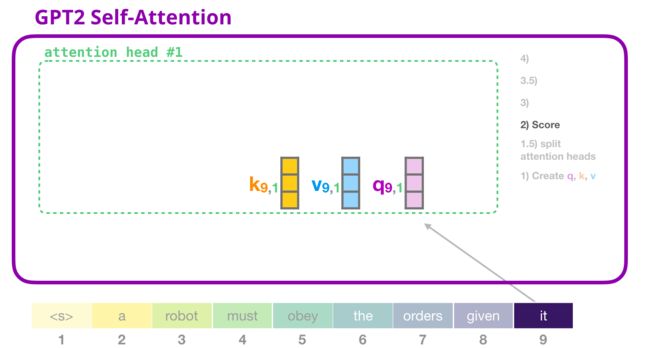
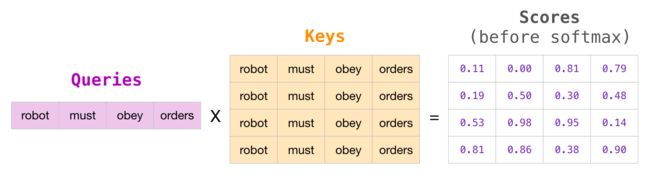
2- 评分
attn_weights = ops.matmul(query, key.swapaxes(-1, -2))
attn_weights.shape
max_positions = seq_len
bias = Tensor(np.tril(np.ones((max_positions, max_positions))).reshape(
(1, 1, max_positions, max_positions)), mindspore.bool_)
bias
from mindnlp._legacy.functional import where, softmax
attn_weights = attn_weights / ops.sqrt(ops.scalar_to_tensor(value.shape[-1]))
query_length, key_length = query.shape[-2], key.shape[-2]
causal_mask = bias[:, :, key_length - query_length: key_length, :key_length].bool()
mask_value = Tensor(np.finfo(np.float32).min, dtype=attn_weights.dtype)
attn_weights = where(causal_mask, attn_weights, mask_value)
np.finfo(np.float32).min
attn_weights[0, 0]
attn_weights = softmax(attn_weights, axis=-1)
attn_weights.shape
attn_weights[0, 0]
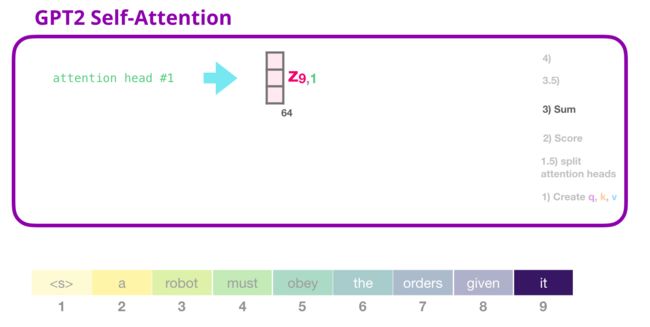
attn_output = ops.matmul(attn_weights, value)
attn_output.shape
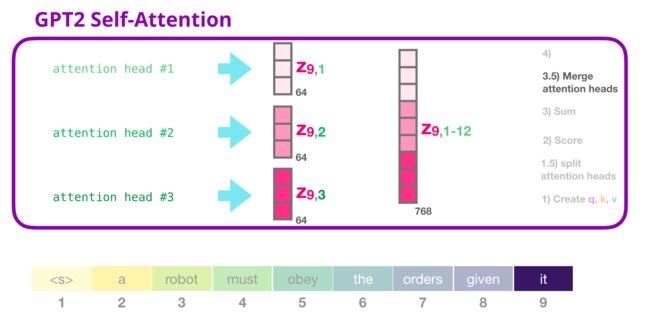
3- 合并注意力头
def merge_heads(tensor, num_heads, attn_head_size):
"""
Merges attn_head_size dim and num_attn_heads dim into hidden_size
"""
tensor = ops.transpose(tensor, (0, 2, 1, 3))
new_shape = tensor.shape[:-2] + (num_heads * attn_head_size,)
return tensor.view(new_shape)
attn_output = merge_heads(attn_output, num_heads, head_dim)
attn_output.shape
4- Projecting
c_proj = Conv1D(embed_dim, embed_dim)
attn_output = c_proj(attn_output)
attn_output.shape
课程ppt及代码地址
-
github地址(网络不好的可以访问下面我克隆到gitee上的地址):GPT2
-
gitee地址:GPT2
2、学习心得:
通过本次学习,熟悉了华为Mindspore这个国产深度学习框架,也对GPT2的基本技术原理有所了解,同时也学会了如何通过微调GPT2完成一个文本生成的任务,还是比较有成就感的!!!另外就是峰哥讲课的互动也比较多,还介绍了许多课程之外的一些知识,让人眼前一亮,受益匪浅!
3、经验分享:
在启智openI上的npu跑时记得使用mindspore1.7的镜像,同时安装对应mindnlp的版本,不然可能会因为版本不兼容而报错。另外就是微调GPT2完成一个文本生成的练习一定要做,这样能比较get到整个微调的全流程是怎样的,后面再去学习llama等其他大模型的微调时就会更加得心应手。
4、课程反馈:
本次课程中的代码串讲我觉得是做的最好的地方,没有照着ppt一直念,而是在jupyter lab上把代码和原理结合到一块进行讲解,让学习者对代码的理解更加深入。我觉得内容的最后可以稍微推荐一下与Mindspore大模型相关的套件,让学习者在相关套件上可以开发出更多好玩和有趣的东西!
5、使用MindSpore昇思的体验和反馈:
MindSpore昇思的优点和喜欢的方面:
- 灵活性和可扩展性: MindSpore提供了灵活的编程模型,支持静态计算图和动态计算图。这种设计使得它适用于多种类型的机器学习和深度学习任务,并且具有一定的可扩展性。
- 跨平台支持: MindSpore支持多种硬件平台,包括CPU、GPU和NPU等,这使得它具有在不同设备上运行的能力,并能充分利用各种硬件加速。
- 自动并行和分布式训练: MindSpore提供了自动并行和分布式训练的功能,使得用户可以更轻松地处理大规模数据和模型,并更高效地进行训练。
- 生态系统和社区支持: MindSpore致力于建立开放的生态系统,并鼓励社区贡献,这对于一个开源框架来说非常重要,能够帮助用户更好地学习和解决问题。
一些建议和改进方面:
- 文档和教程的改进: 文档和教程并不是很详细,希望能够提供更多实用的示例、详细的文档和教程,以帮助用户更快速地上手和解决问题。
- 更多的应用场景示例: 提供更多真实场景的示例代码和应用案例,可以帮助用户更好地了解如何在实际项目中应用MindSpore。
6、未来展望:
大模型的内容还是很多的,希望自己能坚持打卡,将后面的内容都学习完,并做出一些有趣好玩的东西来!