LSTM解读
1、LSTM
1.1、LSTM理解
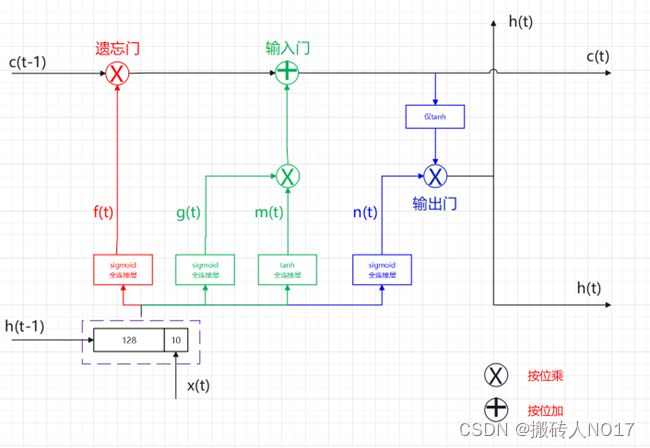
LSTM是一种循环神经网络,它可以处理和预测时间序列中间隔和延迟相对较长的重要事件。LSTM通过使用门控单元来控制信息的流动,从而解决传统RNN中的梯度消失和梯度爆炸的问题。LSTM的核心是三个门:输入门、遗忘门和输出门。输入门控制新信息的输入,遗忘门控制旧信息的保留,输出门控制输出的信息。在自然语言处理、语音识别、图像处理等领域应用广泛。
结构图如下:
通过遗忘门、输入门、输出门可以让LSTM有能力去学会衡量长短期记忆的能力。
涉及到的公式如下:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
长期信息记忆流,一直会存在,每个时间步后会更新:![]()
本时刻输出 h(t),会传给下一时刻,作为下一时刻的输入之一:![]()
1.2、单层LSTM
调用PyTorch框架中torch.nn.LSTM函数实现如下:
net = torch.nn.LSTM(input_size=20, hidden _size=100, num layers=1, batch_first=Ture)
解读:
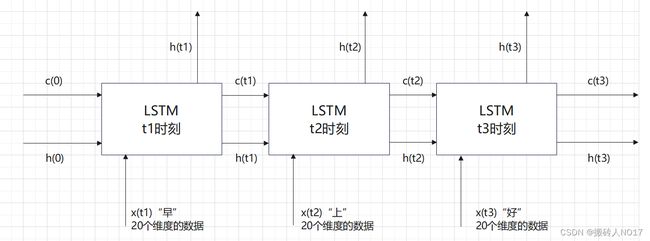
(1)设定有3个字的序列【“早”“上”“好”】要经过LSTM处理,每个序列由20个元素组成的列向量构成,所以input size就为20。
(2)设定全连接层中有100个隐藏单元,LSTM的层数为1。
(3)因为是3个字的序列,所以LSTM需要3个时间步(即会自循环3次)才能处理完这个序列。
(4)nn.LSTM()每层也可以拆开写,这样每层的隐藏单元个数就可以分别设定。
LSTM单元包含三个输入参数x、c、h;首先t1时刻作为第一个时间步,输入到第一个LSTM单元中,此时输入的初始从c(0)和h(0)都是0矩阵,计算完成后,第一个LSTM单元输出一组h(t1)\c(t1),作为本层LSTM的第二个时间步的输入参数;因此第二个时间步的输入就是h(t1),c(t1),x(t2),而输出是h(t2),c(t2);因此第三个时间步的输入就是h(t2),c(t2),x(t3),而输出是h(t3),c(t3)。
函数torch.nn.LSTM()的参数列表:
input_size:输入数据的特征维数,通常就是embedding_dim(词向量的维度)。
hidden_size:LSTM中隐层的维度。
num_layers:循环神经网络的层数。
bias:用不用偏置,default=True。
batch_first:这个要注意,通常我们输入的数据维度是shape = (batch_size, seq_length, embedding_dim),而batch_first默认是False,所以我们的输入数据最好在送进LSTM之前将batch_size与seq_length这两个维度调换。
dropout:默认是0,代表不用dropout。
bidirectional:默认是false,代表不用双向LSTM。
proj_size:如果大于 0,将使用具有相应大小的投影的 LSTM。默认值:0。
1.3、双层LSTM
调用PyTorch框架中torch.nn.LSTM函数实现如下:
net = torch.nn.LSTM(input_size=20, hidden _size=100, num layers=2, batch_first=Ture)
解读:
(1)设定有3个字的序列【“早”“上”“好”】要经过LSTM处理,每个序列由20个元素组成的列向量构成,所以input size就为20。
(2)设定全连接层中有100个隐藏单元,LSTM的层数为2。
(3)因为是3个字的序列,所以LSTM需要3个时间步(即会自循环3次)才能处理完这个序列。
(4)nn.LSTM()每层也可以拆开写,这样每层的隐藏单元个数就可以分别设定。
第二层LSTM没有输入参数x(t1)、x(t2)、x(t3);所以我们将第一层LSTM输出的h(t1)、h(t2)、h(t3)作为第二层LSTM的输入x(t1)、x(t2)、x(t3)。第一个时间步输入的初始c(0)和h(0)都为0矩阵,计算完成后,第一个时间步输出新的一组h(t1)、c(t1),作为本层LSTM的第二个时间步的输入参数;因此第二个时间步的输入就是h(t1),c(t1),x(t2),而输出是h(t2),c(t2);因此第三个时间步的输入就是h(t2),c(t2),x(t3),而输出是h(t3),c(t3)。
1.4、LSTM分类
(1)BiLSTM:双向长短期记忆网络。
单层的BiLSTM其实就是2个LSTM,一个正向去处理序列,一个反向去处理序列,处理完后,两个LSTM的输出会拼接起来。
(2)LSTMP:压缩LSTM。
LSTMP是一种基于LSTM的模型,它在LSTM的基础上增加了一个projection layer,用于将LSTM的输出映射到一个更小的维度。
2、代码
参考来自知乎。
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义LSTM网络
class LstmRNN(torch.nn.Module):
"""
Parameters:
- input_size: feature size
- hidden_size: number of hidden units
- output_size: number of output
- num_layers: layers of LSTM to stack
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, num_layers):
super().__init__()
self.LstmLayer = torch.nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
self.LinearLayer = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, _x):
# x size (seq_len, batch, hidden_size)
x, _ = self.LstmLayer(_x)
s, b, h = x.shape
x = x.view(s * b, h)
x = self.LinearLayer(x)
x = x.view(s, b, -1)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建数据集
data_len = 3000 # 数据集总量
data_input_dim = 20 # 输入数据集维度
data_output_dim = 8 # 输出数据集维度
t = np.linspace(0, 1000 * np.pi, data_len * (data_input_dim + data_output_dim))
dataset = np.sin(t)
dataset = dataset.reshape((data_len, -1))
np.random.shuffle(dataset)
dataset = dataset.astype('float32')
# 选择训练数据和测试数据
train_data_len = int(data_len * 0.8)
# 训练数据
train_x = dataset[0:train_data_len, 0:data_input_dim]
train_y = dataset[0:train_data_len, data_input_dim:(data_input_dim + data_output_dim)]
print("train data: ", train_x.shape, train_y.shape)
# 测试数据
test_x = dataset[train_data_len:, 0:data_input_dim]
test_y = dataset[train_data_len:, data_input_dim:(data_input_dim + data_output_dim)]
print("test data: ", test_x.shape, test_y.shape)
INPUT_FEATURES_NUM = 20
OUTPUT_FEATURES_NUM = 8
# ----------------- train -------------------
train_x_tensor = train_x.reshape(-1, 8, INPUT_FEATURES_NUM) # 设置batch=8
train_y_tensor = train_y.reshape(-1, 8, OUTPUT_FEATURES_NUM) # 设置batch=8
# 将数据转成tensor格式
train_x_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_x_tensor)
train_y_tensor = torch.from_numpy(train_y_tensor)
print("train data shape: ", train_x_tensor.shape, train_y_tensor.shape)
lstm_model = LstmRNN(INPUT_FEATURES_NUM, 150, OUTPUT_FEATURES_NUM, 3)
print('LSTM model:', lstm_model)
print('model.parameters:', lstm_model.parameters)
# 损失函数
loss_function = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# 优化器;lr为学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(lstm_model.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
# 训练的epoch数量
max_epochs = 10000
for epoch in range(max_epochs):
output = lstm_model(train_x_tensor)
loss = loss_function(output, train_y_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if loss.item() < 1e-5:
print('Epoch [{}/{}], Loss: {:.5f}'.format(epoch + 1, max_epochs, loss.item()))
print("The loss value is reached")
break
elif (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch: [{}/{}], Loss:{:.5f}'.format(epoch + 1, max_epochs, loss.item()))
# 用训练数据进行预测
predictive_y_for_training = lstm_model(train_x_tensor)
predictive_y_for_training = predictive_y_for_training.view(-1, OUTPUT_FEATURES_NUM).data.numpy()
# ----------------- test -------------------
lstm_model = lstm_model.eval()
# 用测试数据进行预测
test_x_tensor = test_x.reshape(-1, 5, INPUT_FEATURES_NUM) # 设置batch为5;和训练集一致
test_x_tensor = torch.from_numpy(test_x_tensor)
predictive_y_for_testing = lstm_model(test_x_tensor)
predictive_y_for_testing = predictive_y_for_testing.view(-1, OUTPUT_FEATURES_NUM).data.numpy()
结果:
train data: (2400, 20) (2400, 8)
test data: (600, 20) (600, 8)
train data shape: torch.Size([300, 8, 20]) torch.Size([300, 8, 8])
LSTM model: LstmRNN(
(LstmLayer): LSTM(20, 150, num_layers=3)
(LinearLayer): Linear(in_features=150, out_features=8, bias=True)
)
model.parameters:(LstmLayer): LSTM(20, 150, num_layers=3)
(LinearLayer): Linear(in_features=150, out_features=8, bias=True)
)>
Epoch: [100/10000], Loss:0.00040
Epoch: [200/10000], Loss:0.00004
Epoch: [300/10000], Loss:0.00002
Epoch: [400/10000], Loss:0.00002
Epoch: [500/10000], Loss:0.00001
Epoch [544/10000], Loss: 0.00001
The loss value is reachedProcess finished with exit code 0