20.云原生之GitLab CICD实战
云原生专栏大纲
文章目录
- GitLab Runner
-
- GitLab Runner 介绍
- Gitlab Runner工作流程
- Gitlab集成Gitlab Runner
-
- GitLab Runner 版本选择
- Gitlab Runner部署
-
- docker-compose方式安装
- kubesphere中可视化方式安装
- helm方式安装
- 配置gitlab-runner
- 配置gitlab-ci.yml
-
- gitlab-ci.yml 介绍
- 编写gitlab-ci.yml 测试
- GitLab CICD 【待补充】
GitLab Runner
GitLab Runner 介绍
GitLab Runner 是一个开源的持续集成/持续交付(CI/CD)工具,用于在 GitLab CI/CD 环境中执行自动化构建、测试和部署任务。它是 GitLab CI/CD 的一部分,负责管理和执行 CI/CD 作业。
以下是 GitLab Runner 的一些关键特点和功能:
- 多平台支持:GitLab Runner 可以在多种操作系统上运行,包括 Linux、macOS 和 Windows。这使得它非常灵活,可以适应不同的开发环境。
- 并行执行:GitLab Runner 支持并行执行作业,可以同时运行多个作业,提高构建和测试的效率。
- 多种执行器:GitLab Runner 提供了不同类型的执行器,包括 Shell、SSH、Docker、Kubernetes 等。这些执行器可以根据需要选择,以便在不同的环境中执行作业。
- 可扩展性:GitLab Runner 可以通过添加自定义执行器来扩展其功能。这使得它可以与各种不同的工具和服务集成,以满足特定的需求。
- 安全性:GitLab Runner 提供了各种安全功能,包括作业隔离、安全沙盒和访问控制。这些功能可以确保作业的安全性和可靠性。
- 配置灵活:GitLab Runner 的配置非常灵活,可以通过配置文件或命令行参数进行配置。你可以根据需要自定义执行器的行为和设置。
使用 GitLab Runner,你可以轻松地将 CI/CD 流程集成到 GitLab 中,实现自动化构建、测试和部署。它提供了强大的功能和灵活的配置选项,使得开发团队能够更高效地交付软件。无论是小型项目还是大型企业级项目,GitLab Runner 都是一个强大而可靠的 CI/CD 工具。
Gitlab Runner工作流程
GitLab Runner 的工作流程如下:
- 注册 Runner:首先,你需要在 GitLab 中注册一个 Runner。这可以通过在 GitLab 项目设置中创建一个新的 Runner 配置来完成。在注册过程中,你将为 Runner 分配一个唯一的 token,用于与 GitLab 服务器进行身份验证。
- 安装和配置 Runner:在你的执行环境中安装 GitLab Runner,并使用注册时获得的 token 进行身份验证。安装过程可能因操作系统而异,请按照官方文档提供的说明进行安装。安装完成后,你需要通过配置文件或命令行参数对 Runner 进行配置,包括指定 Runner 的名称、token、执行器类型等信息。
- 运行和监听:启动 GitLab Runner 后,它会连接到 GitLab 服务器,并开始监听作业的出现。Runner 会定期向 GitLab 服务器发送心跳信号,以保持连接。当有新的作业出现时,GitLab 服务器会将作业分配给可用的 Runner。
- 下载代码:当 Runner 接收到作业时,它会从 GitLab 服务器上获取项目的代码。这通常是通过克隆 Git 存储库或者拉取最新的代码变更来完成的。
- 执行作业:一旦代码下载完成,Runner 将根据作业的定义执行相应的操作。这可以是构建项目、运行测试、生成文档、打包应用程序等等。Runner 可以使用预定义的执行器(如 Shell、Docker、Kubernetes)来运行作业。
- 提交结果:当作业执行完成后,Runner 将结果提交回 GitLab 服务器。这包括构建日志、测试报告、生成的文件等。这些结果可以在 GitLab 的界面中查看和分析。
- 清理和释放资源:完成作业后,Runner 将清理执行环境,并释放使用的资源。这可以包括删除临时文件、停止容器、释放服务器资源等。
整个过程是自动化的,GitLab Runner 负责管理作业的执行和结果的提交。它可以与 GitLab CI/CD 配合使用,为开发团队提供一个强大的持续集成和持续交付平台。通过配置不同的执行器和作业定义,你可以根据项目的需求和特定的环境设置来灵活地定义和执行作业。
Gitlab集成Gitlab Runner
GitLab Runner 版本选择
https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/
出于兼容性原因,GitLab Runner major.minor 版本 应与 GitLab 主要和次要版本保持同步。年长的跑步者可能仍然可以工作 使用较新的 GitLab 版本,反之亦然。但是,功能可能不可用或无法正常工作 如果存在版本差异。
次要版本更新之间保证向后兼容性。然而,有时轻微 GitLab 的版本更新可以引入需要 GitLab Runner 在同一个次要版本上的新功能 版本。
GitLab Runner 15.0 对 注册 API 请求格式。它可以防止 GitLab Runner 与低于 14.8 的 GitLab 版本进行通信。 您必须使用适合 GitLab 版本的 Runner 版本,或者升级 GitLab 应用程序。
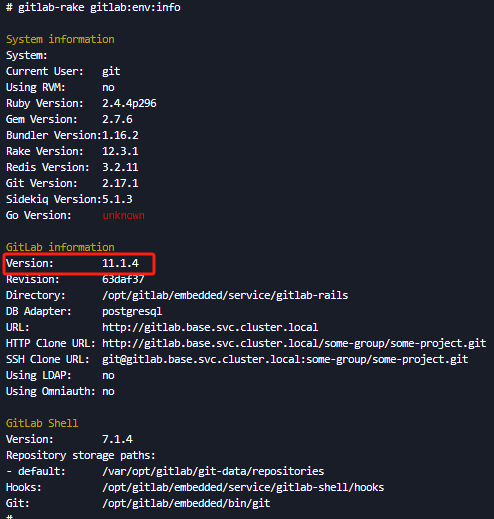
查看gitlab版本:
gitlab-rake gitlab:env:info
https://hub.docker.com/r/gitlab/gitlab-runner/tags查找跟gitlab版本对应的runner版本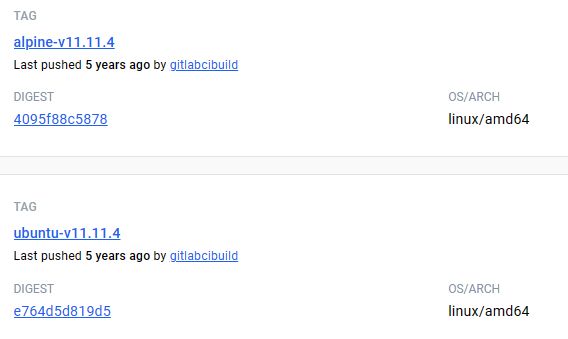
lpine Linux 和 Ubuntu 是两种常见的 Linux 发行版,它们在一些方面有所不同。
- 大小和资源消耗:Alpine Linux 是一个轻量级的发行版,以小巧和高效而闻名。它的基本安装映像非常小,通常只有几十兆字节,因此占用的磁盘空间和内存消耗相对较少。这使得它在容器化环境中非常受欢迎,因为它可以快速启动和部署。相比之下,Ubuntu 是一个功能更全面的发行版,提供了更多的软件包和功能。它的基本安装映像较大,通常几个几百兆字节,占用的磁盘空间和内存消耗也更高一些。
- 软件包管理:Alpine Linux 使用 apk 包管理器来管理软件包。它的软件包库相对较小,但它专注于提供核心软件包和常用工具,以满足大多数基本需求。Ubuntu 使用 apt 包管理器来管理软件包。它的软件包库非常庞大,包含了广泛的软件选择,包括开发工具、服务器应用、桌面环境等。
- 默认配置和用户友好性:Ubuntu 在默认配置和用户友好性方面更加注重。它提供了易于使用的图形界面和友好的安装程序,适合桌面和服务器使用。Alpine Linux 更加精简,更注重定制和自定义。它的默认配置较为简单,适合专注于特定用途的部署,如容器化环境或嵌入式系统。
选择使用 Alpine Linux 还是 Ubuntu 取决于你的具体需求。如果你需要一个轻量级、高效的发行版,适用于容器化环境或资源受限的系统,那么 Alpine Linux 是一个不错的选择。如果你需要更广泛的软件选择、更丰富的功能和更友好的用户体验,那么 Ubuntu 可能更适合你。
Gitlab Runner部署
docker-compose方式安装
version: '3.8'
services:
gitlab-runner:
image: gitlab/gitlab-runner:alpine-v11.11.4
container_name: gitlab-runner
restart: always
volumes:
- ./config:/etc/gitlab-runner
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock # 这一行是固定写法 不要随便改
kubesphere中可视化方式安装
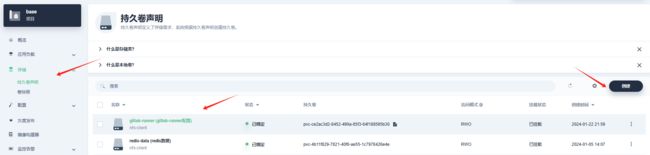
- 创建PVC
- 配置镜像地址
- 挂载配置
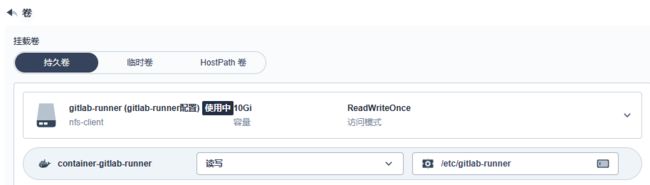
注意:/var/run/docker.sock挂载使用HostPath卷
helm方式安装
https://www.jianshu.com/p/2eb12252e4ee
注意:helm仓库中维护的版本都大于11,若想使用helm部署请升级gitlab
- 添加仓库
# 添加 chart 存储库
$ helm repo add gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
# 查看存储库
$ helm repo list
NAME URL
gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
- 在kubesphere应用仓库中部署
- 修改values.yaml 文件
#以下两个在gitlab页面获取
gitlabUrl: http://gitlab.base.svc.cluster.local # 使用k8s内部gitlab svc地址
runnerRegistrationToken: "gitlab-runner-tocken" #gitlab-runner注册用到的tocken
concurrent: 10 #最大作业并发数
checkInterval: 30 #新作业检查间隔
tags: "k8s-runner" #runner的标签
#rbac权限打开
rbac:
create: true
## Define specific rbac permissions.
## DEPRECATED: see .Values.rbac.rules
resources: ["pods", "pods/exec", "secrets","configmaps"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "patch", "delete","update"]
配置gitlab-runner
注册-gitlab-runner官网参考
- 查看gitlab中token和地址
- 进入gitlab-runner容器命令行,执行:
/ # gitlab-runner register
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=33 revision=e828d3bc version=11.11.4
Running in system-mode.
# gitlab地址
Please enter the gitlab-ci coordinator URL (e.g. https://gitlab.com/):
https://xxx.xxx.shop:99/
# 项目token
Please enter the gitlab-ci token for this runner:
cp6KwLn3KDTLWN8SD3ax
Please enter the gitlab-ci description for this runner:
[gitlab-runner-8575578f55-d8bfh]: ci
Please enter the gitlab-ci tags for this runner (comma separated):
ci
Registering runner... succeeded runner=cp6KwLn3
# 选择执行器,从给出列表选择
Please enter the executor: parallels, shell, kubernetes, docker, docker-ssh, ssh, virtualbox, docker+machine, docker-ssh+machine:
[ci]: shell
Runner registered successfully. Feel free to start it, but if it's running already the config should be automatically reloaded!
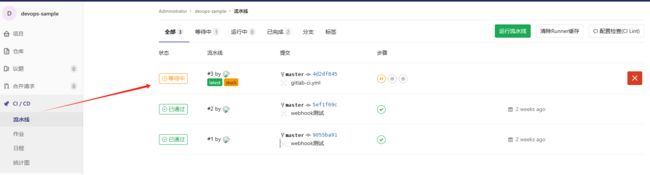
- 验证runner配置
登录gitlab项目中CI/CD面板,出现绿色可用runner表示配置生效: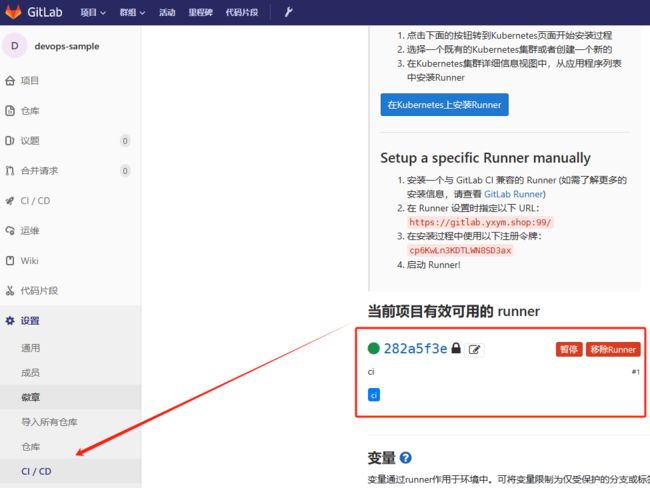
配置gitlab-ci.yml
gitlab-ci.yml 介绍
gitlab-ci.yml 是 GitLab CI/CD 的配置文件,用于定义项目的持续集成和持续交付流程。它采用 YAML 格式,位于项目的根目录或指定的目录中。
gitlab-ci.yml 文件包含了一系列的作业(jobs)和阶段(stages),定义了项目在不同情况下的构建、测试、部署等操作。以下是一些常见的 gitlab-ci.yml 配置项:
- image:指定用于作业执行的 Docker 镜像。可以选择现有的镜像,也可以自定义镜像。
- stages:定义项目的阶段顺序。每个阶段包含一组作业。
- before_script:在每个作业执行之前运行的脚本命令。可以用于设置环境、安装依赖等操作。
- after_script:在每个作业执行之后运行的脚本命令。可以用于清理环境、收集结果等操作。
- variables:定义作业的环境变量。可以在作业的脚本中使用这些变量。
- jobs:定义项目的作业。每个作业包含一个或多个脚本命令,用于执行具体的操作。
- script:指定作业要执行的脚本命令。可以是单个命令或多个命令的序列。
- artifacts:定义作业产生的构建产物,可以在后续的作业中使用。
- only 和 except:指定作业执行的条件。可以基于分支、标签、变量等进行条件判断。
gitlab-ci.yml 文件的配置可以根据项目的需求进行自定义。你可以定义多个作业和阶段,根据需要设置依赖关系,以及在不同的条件下执行不同的操作。这使得你能够构建灵活、可扩展的 CI/CD 流程,提高开发效率和软件质量。
需要注意的是,一旦 gitlab-ci.yml 文件发生变化,GitLab 会自动检测并开始执行新的 CI/CD 流程。执行结果和日志可以在 GitLab 的界面中查看和分析。
编写gitlab-ci.yml 测试
- 编写gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
build_job:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Building the project... "
test_job:
stage: test
script:
- echo "Running tests..."
deploy_job:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploying the project..."
- 登录gitlab查看流水线
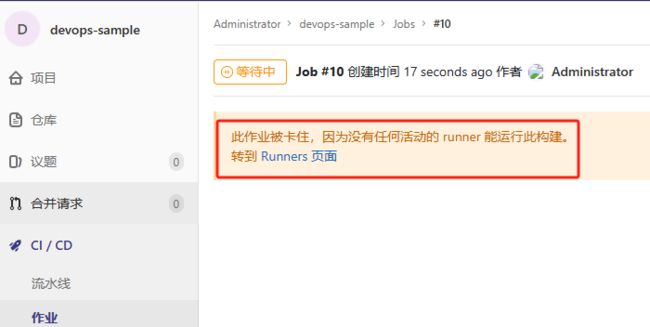
- 解决作业卡住问
登录gitlab点击runner下图按钮进入编辑
勾选运行没有标签的作业:
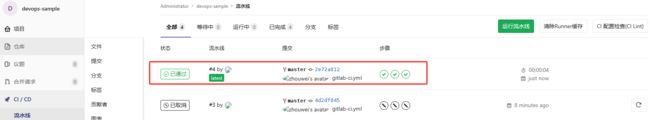
- 再次查看流水线,流水线运行完成
GitLab CICD 【待补充】
重新注册gitlab runner,执行器选择kubernetes,使用参考Kubernetes executor官网
runner 的 k8s 执行器工作流程:
- runner 会通过 RBAC 认证获取到调用 k8s 集群 API 的权限。
- runner 会监听 gitlab,当有合适的 job 时,runner 会自动抓取任务执行。
请注意,一个流水线中可以有很多个 stage,这些 stage 是串行执行的,而一个 stage 中又可以有多个并行的 job,runner 抓取的任务是以 job 为单位,而不是 stage,更不是 pipline。
- 随后,runner 会调用 k8s API,创建一个用于执行该 job 的 pod。
通常来说,runner 创建的所有 pod 有一个通用模板,我们需要在 runner 的 config.toml 配置文件中配置这个模板。但 pod 中具体使用什么镜像、在 pod 中执行什么命令,这些都是在后续的 .gitlab-ci.yml 文件中配置,并且随着 job 的不同而不同。
- 在完成了 job 内的工作后,runner 会将这个临时 pod 删除。