opencv图片倾斜度检测(一)对图片进行检测
改进篇opencv图片倾斜度检测(二)利用摄像头进行实时检测
利用opencv检测图片倾斜度
1.利用最小矩阵函数minAreaRect得到旋转角度
import cv2
import numpy as np
import imutils
def show(img):#显示函数
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def bianyuan(img):#边缘处理
img_ = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#转换为灰度
img_ = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_,(5,5),0)#高斯滤波去噪点
img__ = cv2.Canny(img_,75,200)#Canny边缘检测
return img__
def resize(img):#尺寸缩小
height, width = img.shape[0:2]
return cv2.resize(img1, (int(width/4), int(height / 4)), cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
def order_points(pts):#得到最大轮廓的四个坐标点
# 一共4个坐标点
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32")
# 按顺序找到对应坐标0123分别是 左上,右上,右下,左下
# 计算左上,右下
s = pts.sum(axis = 1)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
# 计算右上和左下
diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
img1_path = r'C:\Users\11054\Desktop\Scan\images\page.jpg'
img1 = cv2.imread(img1_path)
img1 = resize(img1)
img1_ = bianyuan(img1)
show(img1)
# 轮廓检测
cnts = cv2.findContours(img1_.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)#检测出所有轮廓
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]#opencv4写法
cnts = sorted(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)[:5]#排序得到前五个轮廓 可以根据图片自己设定
# 遍历轮廓
for c in cnts:
# 计算轮廓近似
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
# C表示输入的点集
# epsilon表示从原始轮廓到近似轮廓的最大距离,它是一个准确度参数
# True表示封闭的
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
# 4个点的时候就拿出来 因为物品是矩阵形状
if len(approx) == 4:
screenCnt = approx#保存下来
break
#在图片上描绘出来
cv2.drawContours(img1, [screenCnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
show(img1)
rect = order_points(screenCnt.reshape(4, 2))#得到坐标点
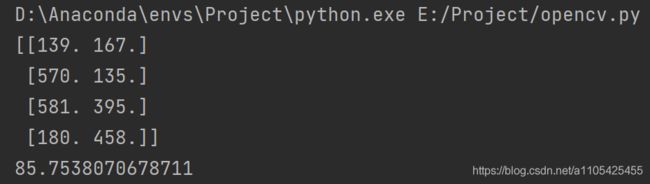
print(rect)
rangle = cv2.minAreaRect(rect)[2]#minAreaRect()函数返回角度 是最低的边到x水平坐标轴的角度
print(rangle)
2.算出最大边缘轮廓的四个坐标点计算斜率
import cv2
import numpy as np
import imutils
def show(img):
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def bianyuan(img):
img_ = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_ = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_,(5,5),0)#去噪点
img__ = cv2.Canny(img_,75,200)
return img__
def resize(img):
height, width = img.shape[0:2]
return cv2.resize(img1, (int(width/4), int(height / 4)), cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
def order_points(pts):
# 一共4个坐标点
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32")
# 按顺序找到对应坐标0123分别是 左上,右上,右下,左下
# 计算左上,右下
s = pts.sum(axis = 1)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
# 计算右上和左下
diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
img1_path = r'C:\Users\11054\Desktop\Scan\images\page.jpg'
img2_path = r'C:\Users\11054\Desktop\Scan\images\receipt.jpg'
img1 = cv2.imread(img2_path)
img2 = cv2.imread(img2_path)
img1 = resize(img1)
img1_ = bianyuan(img1)
show(img1)
# 轮廓检测
cnts = cv2.findContours(img1_.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]
cnts = sorted(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)[:5]
# 遍历轮廓
for c in cnts:
# 计算轮廓近似
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
# C表示输入的点集
# epsilon表示从原始轮廓到近似轮廓的最大距离,它是一个准确度参数
# True表示封闭的
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
# 4个点的时候就拿出来
if len(approx) == 4:
screenCnt = approx
break
cv2.drawContours(img1, [screenCnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
show(img1)
rect = order_points(screenCnt.reshape(4, 2))
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect
print(rect)
print('rangle:',np.arctan((br[1]-tr[1])/(br[0]-tr[0]))*57.3)