React
React基础
1 组件通讯
1.1 props
子组件
import React from "react";
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
import { Button } from "antd";
export default class EightteenChildOne extends React.Component {
static propTypes = { //propTypes校验传入类型,详情在技巧11
name: PropTypes.string
};
click = () => {
// 通过触发方法由子组件调用父组件方法并传参
this.props.eightteenChildOneToFather("这是 props 改变父元素的值");
};
render() {
return (
<div>
{/*this.props.name由父组件传递过来*/}
<div>这是通过 props 传入的值{this.props.name}</div>
<Button type="primary" onClick={this.click}>
点击改变父元素值
</Button>
</div>
);
}
}
父组件
{/*父组件定义eightteenChildOneToFather监听子组件方法调用*/}
<EightteenChildOne name={'props 传入的 name 值'} eightteenChildOneToFather={(mode)=>this.eightteenChildOneToFather(mode)}></EightteenChildOne>
// 或者
<EightteenChildOne name={'props 传入的 name 值'} eightteenChildOneToFather={this.eightteenChildOneToFather.bind(this)}></EightteenChildOne>
props 传多个值时:
传统写法
const {dataOne,dataTwo,dataThree} = this.state
<Com dataOne={dataOne} dataTwo={dataTwo} dataThree={dataThree}>
升级写法
<Com {...{dataOne,dataTwo,dataThree}}>
1.2 props 升级版
原理:子组件里面利用 props 获取父组件方法直接调用,从而改变父组件的值
注意: 此方法和 props 大同小异,都是 props 的应用,所以在源码中没有举例
调用父组件方法改变该值
// 父组件
state = {
count: {}
}
changeParentState = obj => {
this.setState(obj);
}
// 子组件
onClick = () => {
this.props.changeParentState({ count: 2 });
}
1.3 Provider,Consumer和Context
1.Context在 16.x 之前是定义一个全局的对象,类似 vue 的 eventBus,如果组件要使用到该值直接通过this.context获取
//根组件
class MessageList extends React.Component {
getChildContext() {
return {color: "purple",text: "item text"};
}
render() {
const {messages} = this.props || {}
const children = messages && messages.map((message) =>
<Message text={message.text} />
);
return <div>{children}</div>;
}
}
MessageList.childContextTypes = {
color: React.PropTypes.string
text: React.PropTypes.string
};
//中间组件
class Message extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<MessageItem />
<Button>Delete</Button>
</div>
);
}
}
//孙组件(接收组件)
class MessageItem extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.context.text}
</div>
);
}
}
MessageItem.contextTypes = {
text: React.PropTypes.string //React.PropTypes在 15.5 版本被废弃,看项目实际的 React 版本
};
class Button extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<button style={{background: this.context.color}}>
{this.props.children}
</button>
);
}
}
Button.contextTypes = {
color: React.PropTypes.string
};
2.16.x 之后的Context使用了Provider和Customer模式,在顶层的Provider中传入value,在子孙级的Consumer中获取该值,并且能够传递函数,用来修改context 声明一个全局的 context 定义,context.js
import React from 'react'
let { Consumer, Provider } = React.createContext();//创建 context 并暴露Consumer和Provider模式
export {
Consumer,
Provider
}
父组件导入
// 导入 Provider
import {Provider} from "../../utils/context"
<Provider value={name}>
<div style={{border:'1px solid red',width:'30%',margin:'50px auto',textAlign:'center'}}>
<p>父组件定义的值:{name}</p>
<EightteenChildTwo></EightteenChildTwo>
</div>
</Provider>
子组件
// 导入Consumer
import { Consumer } from "../../utils/context"
function Son(props) {
return (
//Consumer容器,可以拿到上文传递下来的name属性,并可以展示对应的值
<Consumer>
{name => (
<div
style={{
border: "1px solid blue",
width: "60%",
margin: "20px auto",
textAlign: "center"
}}
>
// 在 Consumer 中可以直接通过 name 获取父组件的值
<p>子组件。获取父组件的值:{name}</p>
</div>
)}
</Consumer>
);
}
export default Son;
1.4 EventEmitter
EventEmiter 传送门 使用 events 插件定义一个全局的事件机制
1.5 路由传参
1.params
<Route path='/path/:name' component={Path}/>
<link to="/path/2">xxx</Link>
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/path/" + name});
读取参数用:this.props.match.params.name
2.query
<Route path='/query' component={Query}/>
<Link to={{ pathname : '/query' , query : { name : 'sunny' }}}>
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/query",query: { name : 'sunny' }});
读取参数用: this.props.location.query.name
3.state
this.props.history.push({pathname:"/sort ",state : { name : 'sunny' }});
读取参数用: this.props.location.query.state
4.search
xxx
this.props.history.push({pathname:`/web/search?id ${row.id}`});
读取参数用: this.props.location.search
这个在 react-router-dom: v4.2.2有 bug,传参跳转页面会空白,刷新才会加载出来
5.优缺点
1.params在HashRouter和BrowserRouter路由中刷新页面参数都不会丢失
2.state在BrowserRouter中刷新页面参数不会丢失,在HashRouter路由中刷新页面会丢失
3.query:在HashRouter和BrowserRouter路由中刷新页面参数都会丢失
4.query和 state 可以传对象
1.6 onRef
原理:onRef 通讯原理就是通过 props 的事件机制将组件的 this(组件实例)当做参数传到父组件,父组件就可以操作子组件的 state 和方法
EightteenChildFour.jsx
export default class EightteenChildFour extends React.Component {
state={
name:'这是组件EightteenChildFour的name 值'
placeholder: '请输入'
}
componentDidMount(){
this.props.onRef(this) // 将EightteenChildFour传递给父组件
console.log(this)
// this.props.onRef()方法
}
click = () => {
this.setState({name:'这是组件click 方法改变EightteenChildFour改变的name 值'})
};
handleChange = (e) => {
console.log(e.target.value)
this.setState({
name: '这是组件EightteenChildFour的Input 值'+ e.target.value
})
}
render() {
return (
{this.state.name}
);
}
}
eighteen.jsx
state = {
eightteenChildFour: '',
}
{/*触发handleClickEightteenChildFourFunc方法调用EightteenChildFour 子组件click方法*/}
1.7 ref
原理:就是通过 React 的 ref 属性获取到整个子组件实例,再进行操作
EightteenChildFive.jsx
// 常用的组件定义方法
export default class EightteenChildFive extends React.Component {
state={
name:'这是组件EightteenChildFive的name 值'
}
click = () => {
this.setState({name:'这是组件click 方法改变EightteenChildFive改变的name 值'})
};
render() {
return (
{this.state.name}
);
}
}
eighteen.jsx
// 钩子获取实例
componentDidMount(){
console.log('eightteenChildFive的Ref值为')
// 获取的 ref 里面包括整个组件实例,同样可以拿到子组件的实例
console.log(this.refs["eightteenChildFiveRef"])
}
// 组件定义 ref 属性
1.8 redux
redux 是一个独立的事件通讯插件,这里就不做过多的叙述 请戳传送门:
1.9 MobX
MobX 也是一个独立的事件通讯插件,这里就不做过多的叙述
请戳传送门:
1.10 flux
flux 也是一个独立的事件通讯插件,这里就不做过多的叙述
请戳传送门:
1.11 hooks
1.hooks 是利用 userReducer 和 context 实现通讯,下面模拟实现一个简单的 redux
2.核心文件分为 action,reducer,types
action.js
import * as Types from './types';
export const onChangeCount = count => ({
type: Types.EXAMPLE_TEST,
count: count + 1
})
reducer.js
import * as Types from "./types";
export const defaultState = {
count: 0
};
export default (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case Types.EXAMPLE_TEST:
return {
...state,
count: action.count
};
default: {
return state;
}
}
};
types.js
export const EXAMPLE_TEST = 'EXAMPLE_TEST';
eightteen.jsx
export const ExampleContext = React.createContext(null);//创建createContext上下文
// 定义组件
function ReducerCom() {
const [exampleState, exampleDispatch] = useReducer(example, defaultState);
return (
);
}
EightteenChildThree.jsx // 组件
import React, { useEffect, useContext } from 'react';
import {Button} from 'antd'
import {onChangeCount} from '../../pages/TwoTen/store/action';
import { ExampleContext } from '../../pages/TwoTen/eighteen';
const Example = () => {
const exampleContext = useContext(ExampleContext);
useEffect(() => { // 监听变化
console.log('变化执行啦')
}, [exampleContext.exampleState.count]);
return (
值为{exampleContext.exampleState.count}
)
}
export default Example;
3.hooks其实就是对原有React 的 API 进行了封装,暴露比较方便使用的钩子;
4.钩子有:
| 钩子名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| useState | 初始化和设置状态 |
| useEffect | componentDidMount,componentDidUpdate和componentWillUnmount和结合体,所以可以监听useState定义值的变化 |
| useContext | 定义一个全局的对象,类似 context |
| useReducer | 可以增强函数提供类似 Redux 的功能 |
| useCallback | 记忆作用,共有两个参数,第一个参数为一个匿名函数,就是我们想要创建的函数体。第二参数为一个数组,里面的每一项是用来判断是否需要重新创建函数体的变量,如果传入的变量值保持不变,返回记忆结果。如果任何一项改变,则返回新的结果 |
| useMemo | 作用和传入参数与 useCallback 一致,useCallback返回函数,useDemo 返回值 |
| useRef | 获取 ref 属性对应的 dom |
| useImperativeMethods | 自定义使用ref时公开给父组件的实例值 |
| useMutationEffect | 作用与useEffect相同,但在更新兄弟组件之前,它在React执行其DOM改变的同一阶段同步触发 |
| useLayoutEffect | 作用与useEffect相同,但在所有DOM改变后同步触发 |
5.useImperativeMethods
function FancyInput(props, ref) {
const inputRef = useRef();
useImperativeMethods(ref, () => ({
focus: () => {
inputRef.current.focus();
}
}));
return ;
}
FancyInput = forwardRef(FancyInput);
1.12 slot
slot 就是将父组件的标签传给子组件,类似vue 的 v-slot
场景:有些组件只是共用部分dom 逻辑,里面有部分逻辑是独立的
// 父组件文件
import SlotChild from 'SlotChild'
这是父组件的 slot 1.13 对比
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| props | 不需要引入外部插件 | 兄弟组件通讯需要建立共同父级组件,麻烦 |
| props 升级版 | 不需要引入外部插件,子传父,不需要在父组件用方法接收 | 同 props |
| Provider,Consumer和Context | 不需要引入外部插件,跨多级组件或者兄弟组件通讯利器 | 状态数据状态追踪麻烦 |
| EventEmitter | 可支持兄弟,父子组件通讯 | 要引入外部插件 |
| 路由传参 | 可支持兄弟组件传值,页面简单数据传递非常方便 | 父子组件通讯无能为力 |
| onRef | 可以在获取整个子组件实例,使用简单 | 兄弟组件通讯麻烦,官方不建议使用 |
| ref | 同 onRef | 同 onRef |
| redux | 建立了全局的状态管理器,兄弟父子通讯都可解决 | 引入了外部插件 |
| mobx | 建立了全局的状态管理器,兄弟父子通讯都可解决 | 引入了外部插件 |
| flux | 建立了全局的状态管理器,兄弟父子通讯都可解决 | 引入了外部插件 |
| hooks | 16.x 新的属性,可支持兄弟,父子组件通讯 | 需要结合 context 一起使用 |
| slot | 支持父向子传标签 |
redux , mobx和flux对比
| 方法 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| redux | 1.核心模块:Action,Reducer,Store;2. Store 和更改逻辑是分开的;3. 只有一个 Store;4. 带有分层 reducer 的单一 Store;5. 没有调度器的概念;6. 容器组件是有联系的;7. 状态是不可改变的;8.更多的是遵循函数式编程思想 |
| mobx | 1.核心模块:Action,Reducer,Derivation;2.有多个 store;3.设计更多偏向于面向对象编程和响应式编程,通常将状态包装成可观察对象,一旦状态对象变更,就能自动获得更新 |
| flux | 1.核心模块:Store,ReduceStore,Container;2.有多个 store; |
2.require.context()
这个是 webpack 的 api,这个在 vue 技巧中有介绍,因为 Vue 和 React 工程都是基于 webpack打包,所以在 react 也可以使用
const path = require('path')
const files = require.context('@/components/home', false, /\.vue$/)
const modules = {}
files.keys().forEach(key => {
const name = path.basename(key, '.vue')
modules[name] = files(key).default || files(key)
})
3.Decorator
定义:decorator是ES7的一个新特性,可以修改class的属性
import React from 'react'
import Test from '../../utils/decorators'
@Test
//只要Decorator后面是Class,默认就已经把Class当成参数隐形传进Decorator了。
class TwentyNine extends React.Component{
componentDidMount(){
console.log(this,'decorator.js') // 这里的this是类的一个实例
console.log(this.testable)
}
render(){
return (
这是技巧23
)
}
}
export default TwentyNine
decorators.js
function testable(target) {
console.log(target)
target.isTestable = true;
target.prototype.getDate = ()=>{
console.log( new Date() )
}
}
export default testable
很多中间件,像 redux 里面就封装了Decorator的使用
4.使用 if…else
场景:有些时候需要根据不同状态值页面显示不同内容
import React from "react";
export default class Four extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1
};
render() {
let info
if(this.state.count===0){
info=(
这是数量为 0 显示
)
} else if(this.state.count===1){
info=(
这是数量为 1 显示
)
}
return (
{info}
);
}
}
5.state 值改变的五种方式
方式 1
let {count} = this.state
this.setState({count:2})
方式 2:callBack
this.setState(({count})=>({count:count+2}))
方式 3:接收 state 和 props 参数
this.setState((state, props) => {
return { count: state.count + props.step };
});
方式 4:hooks
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
// 设置值
setCount(count+2)
方式 5:state 值改变后调用
this.setState(
{count:3},()=>{
//得到结果做某种事
}
)
6.监听states 变化
1.16.x 之前使用componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillReceiveProps (nextProps){
if(this.props.visible !== nextProps.visible){
//props 值改变做的事
}
}
注意:有些时候componentWillReceiveProps在 props 值未变化也会触发,因为在生命周期的第一次render后不会被调用,但是会在之后的每次render中被调用 = 当父组件再次传送props
2.16.x 之后使用getDerivedStateFromProps,16.x 以后componentWillReveiveProps也未移除
export default class Six extends React.Component {
state = {
countOne:1,
changeFlag:''
};
clickOne(){
let {countOne} = this.state
this.setState({countOne:countOne+1})
};
static getDerivedStateFromProps (nextProps){
console.log('变化执行')
return{
changeFlag:'state 值变化执行'
}
}
render() {
const {countOne,changeFlag} = this.state
return (
countOne 值为{countOne}
{changeFlag}
);
}
}
7.组件定义方法
方式 1:ES5 的Function 定义
function FunCom(props){
return 这是Function 定义的组件
}
ReactDOM.render(方式 2: ES5的 createClass 定义
const CreateClassCom = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return 这是React.createClass定义的组件
}
});
方式 3:ES6 的 extends
class Com extends React.Component {
render(){
return(这是React.Component定义的组件)
}
}
调用
export default class Seven extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
区别: ES5的 createClass是利用function模拟class的写法做出来的es6; 通过es6新增class的属性创建的组件此组件创建简单.
8.通过 ref 属性获取 component
方式 1:也是最早的用法,通过 this.refs[属性名获取] 也可以作用到组件上,从而拿到组件实例
class RefOne extends React.Component{
componentDidMount() {
this.refs['box'].innerHTML='这是 div 盒子,通过 ref 获取'
}
render(){
return(
)
}
}
方式 2:回调函数,在dom节点或组件上挂载函数,函数的入参是dom节点或组件实例,达到的效果与字符串形式是一样的,都是获取其引用
class RefTwo extends React.Component{
componentDidMount() {
this.input.value='这是输入框默认值';
this.input.focus();
}
render(){
return(
{ this.input = comp; }}/>
)
}
}
方式 3:React.createRef() React 16.3版本后,使用此方法来创建ref。将其赋值给一个变量,通过ref挂载在dom节点或组件上,该ref的current属性,将能拿到dom节点或组件的实例
class RefThree extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.myRef=React.createRef();
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log(this.myRef.current);
}
render(){
return
}
}
方式 4:React.forwardRef
React 16.3版本后提供的,可以用来创建子组件,以传递ref
class RefFour extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.myFourRef=React.forwardRef();
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log(this.myFourRef.current);
}
render(){
return
}
}
子组件通过React.forwardRef来创建,可以将ref传递到内部的节点或组件,进而实现跨层级的引用。forwardRef在高阶组件中可以获取到原始组件的实例.这个功能在技巧 18 会着重讲
9.static 使用
场景:声明静态方法的关键字,静态方法是指即使没有组件实例也可以直接调用
export default class Nine extends React.Component {
static update(data) {
console.log('静态方法调用执行啦')
}
render() {
return (
这是 static 关键字技能
);
}
}
Nine.update('2')
注意: 1.ES6的class,我们定义一个组件的时候通常是定义了一个类,而static则是创建了一个属于这个类的属性或者方法
2.组件则是这个类的一个实例,component的props和state是属于这个实例的,所以实例还未创建
3.所以static并不是react定义的,而加上static关键字,就表示该方法不会被实例继承,而是直接通过类来调用,所以也是无法访问到 this
4.getDerivedStateFromProps也是通过静态方法监听值,详情请见技巧 6
10.constructor和super
回顾:
1.谈这两个属性之前,先回顾一下ES6 函数定义方法
2.每一个使用class方式定义的类默认都有一个constructor函数, 这个函数是构造函数的主函数, 该函数体内部的this指向生成的实例
3.super关键字用于访问和调用一个对象的父对象上的函数
export default class Ten extends React.Component {
constructor() { // class 的主函数
super() // React.Component.prototype.constructor.call(this),其实就是拿到父类的属性和方法
this.state = {
arr:[]
}
}
render() {
return (
这是技巧 10
);
}
}
11.PropTypes
场景:检测传入子组件的数据类型
类型检查PropTypes自React v15.5起已弃用,请使用prop-types
方式 1:旧的写法
class PropTypeOne extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
{this.props.email}
{this.props.name}
);
}
}
PropTypeOne.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string, //值可为array,bool,func,number,object,symbol
email: function(props, propName, componentName) { //自定义校验
if (
!/^([a-zA-Z0-9_-])+@([a-zA-Z0-9_-])+(.[a-zA-Z0-9_-])+/.test(
props[propName]
)
) {
return new Error(
"组件" + componentName + "里的属性" + propName + "不符合邮箱的格式"
);
}
},
};
方法 2:利用 ES7 的静态属性关键字 static
class PropTypeTwo extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
name:PropTypes.string
};
render() {
return (
{this.props.name}
);
}
}
12.使用类字段声明语法
场景:可以在不使用构造函数的情况下初始化本地状态,并通过使用箭头函数声明类方法,而无需额外对它们进行绑定
class Counter extends Component {
state = { value: 0 };
handleIncrement = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({
value: prevState.value + 1
}));
};
handleDecrement = () => {
this.setState(prevState => ({
value: prevState.value - 1
}));
};
render() {
return (
{this.state.value}
)
}
}
13.异步组件
1.场景:路由切换,如果同步加载多个页面路由会导致缓慢
2.核心 API:
loader:需要加载的组件
loading:未加载出来的页面展示组件
delay:延迟加载时间
timeout:超时时间
3.使用方法:
安装 react-loadable ,babel插件安装 syntax-dynamic-import. react-loadable是通过webpack的异步import实现的
const Loading = () => {
return loading;
};
const LoadableComponent = Loadable({
loader: () => import("../../components/TwoTen/thirteen"),
loading: Loading
});
export default class Thirteen extends React.Component {
render() {
return 4.Loadable.Map()
并行加载多个资源的高阶组件
14.动态组件
场景:做一个 tab 切换时就会涉及到组件动态加载
实质上是利用三元表达式判断组件是否显示
class FourteenChildOne extends React.Component {
render() {
return 这是动态组件 1;
}
}
class FourteenChildTwo extends React.Component {
render() {
return 这是动态组件 2;
}
}
export default class Fourteen extends React.Component {
state={
oneShowFlag:true
}
tab=()=>{
this.setState({oneShowFlag:!this.state.oneShowFlag})
}
render() {
const {oneShowFlag} = this.state
return (
{this.state.oneShowFlag?如果是单个组件是否显示可以用短路运算
oneShowFlag&&15.递归组件
场景:tree组件
利用React.Fragment或者 div 包裹循环
class Item extends React.Component {
render() {
const list = this.props.children || [];
return (
{list.map((item, index) => {
return (
{item.name}
{// 当该节点还有children时,则递归调用本身
item.children && item.children.length ? (
- {item.children}
) : null}
);
})}
);
}
}
16.受控组件和不受控组件
受控组件:组件的状态通过React 的状态值 state 或者 props 控制
class Controll extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = { value: "这是受控组件默认值" };
}
render() {
return {this.state.value};
}
}
不受控组件:组件不被 React的状态值控制,通过 dom 的特性或者React 的ref 来控制
class NoControll extends React.Component {
render() {
return {this.props.value};
}
}
导入代码:
export default class Sixteen extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log("ref 获取的不受控组件值为", this.refs["noControll"]);
}
render() {
return (
17.高阶组件(HOC)
17.1 定义
1.就是类似高阶函数的定义,将组件作为参数或者返回一个组件的组件;
2.作用:
抽取重复代码,实现组件复用,常见场景,页面复用;
条件渲染,控制组件的渲染逻辑(渲染劫持),常见场景,权限控制;
捕获/劫持被处理组件的生命周期,常见场景,组件渲染性能追踪、日志打点
17.2 实现方法
1.属性代理
import React,{Component} from 'react';
const Seventeen = WrappedComponent =>
class extends React.Component {
render() {
const props = {
...this.props,
name: "这是高阶组件"
};
return 2.反向继承
原理就是利用 super 改变改组件的 this 方向,继而就可以在该组件处理容器组件的一些值
const Seventeen = (WrappedComponent)=>{
return class extends WrappedComponent {
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({baseName:'这是通过反向继承修改后的基础组件名称'})
}
render(){
return super.render();
}
}
}
class WrappedComponent extends React.Component {
state={
baseName:'这是基础组件'
}
render() {
const {baseName} = this.state
return
基础组件值为{baseName}
}
}
export default Seventeen(WrappedComponent);
18.元素是否显示
一般用三元表达式
flag?显示内容:''
flag&&显示内容
19.Dialog 组件创建
Dialog 应该是用的比较多的组件,下面有三种不同的创建方法 方式 1:通过 state 控制组件是否显示
class NineteenChildOne extends React.Component {
render() {
const Dialog = () => 这是弹层1;
return this.props.dialogOneFlag && ;
}
}
方式 2:通过ReactDom.render创建弹层-挂载根节点外层
通过原生的createElement,appendChild, removeChild和react 的ReactDOM.render,ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode来控制元素的显示和隐藏
NineteenChild.jsx
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
class Dialog {
constructor(name) {
this.div = document.createElement("div");
this.div.style.width = "200px";
this.div.style.height = "200px";
this.div.style.backgroundColor = "green";
this.div.style.position = "absolute";
this.div.style.top = "200px";
this.div.style.left = "400px";
this.div.id = "dialog-box";
}
show(children) {
// 销毁
const dom = document.querySelector("#dialog-box");
if(!dom){ //兼容多次点击
// 显示
document.body.appendChild(this.div);
ReactDOM.render(children, this.div);
}
}
destroy() {
// 销毁
const dom = document.querySelector("#dialog-box");
if(dom){//兼容多次点击
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(this.div);
dom.parentNode.removeChild(dom);
}
}
}
export default {
show: function(children) {
new Dialog().show(children);
},
hide: function() {
new Dialog().destroy();
}
};
nineteen.jsx
twoSubmit=()=>{
Dialog.show('这是弹层2')
}
twoCancel=()=>{
Dialog.hide()
}
20.React.memo
作用:当类组件的输入属性相同时,可以使用 pureComponent 或 shouldComponentUpdate 来避免组件的渲染。现在,你可以通过把函数组件包装在 React.memo 中来实现相同的功能
import React from "react";
function areEqual(prevProps, nextProps) {
/*
如果把 nextProps 传入 render 方法的返回结果与
将 prevProps 传入 render 方法的返回结果一致则返回 true,
否则返回 false
*/
if (prevProps.val === nextProps.val) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// React.memo()两个参数,第一个是纯函数,第二个是比较函数
export default React.memo(function twentyChild(props) {
console.log("MemoSon rendered : " + Date.now());
return {props.val};
}, areEqual);
21.React.PureComponent
作用:
1.React.PureComponent 和 React.Component类似,都是定义一个组件类。
2.不同是React.Component没有实现shouldComponentUpdate(),而 React.PureComponent通过props和state的浅比较实现了。
3.React.PureComponent是作用在类中,而React.memo是作用在函数中。
4.如果组件的props和state相同时,render的内容也一致,那么就可以使用React.PureComponent了,这样可以提高组件的性能
class TwentyOneChild extends React.PureComponent{ //组件直接继承React.PureComponent
render() {
return {this.props.name}
}
}
export default class TwentyOne extends React.Component{
render(){
return (
22.React.Component
作用:是基于ES6 class的React组件,React允许定义一个class或者function作为组件,那么定义一个组件类,就需要继承React.Component
export default class TwentyTwo extends React.Component{ //组件定义方法
render(){
return (
这是技巧22
)
}
}
23.在 JSX 打印 falsy 值
定义:
1.falsy 值 (虚值) 是在 Boolean 上下文中认定为 false 的值;
2.值有 0,“”,‘’,``,null,undefined,NaN
export default class TwentyThree extends React.Component{
state={myVariable:null}
render(){
return (
{String(this.state.myVariable)}
)
}
}
虚值如果直接展示,会发生隐式转换,为 false,所以页面不显示
24.ReactDOM.createPortal
作用:组件的render函数返回的元素会被挂载在它的父级组件上,createPortal 提供了一种将子节点渲染到存在于父组件以外的 DOM 节点的优秀的方案
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import {Button} from "antd"
const modalRoot = document.body;
class Modal extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.el = document.createElement("div");
this.el.style.width = "200px";
this.el.style.height = "200px";
this.el.style.backgroundColor = "green";
this.el.style.position = "absolute";
this.el.style.top = "200px";
this.el.style.left = "400px";
}
componentDidMount() {
modalRoot.appendChild(this.el);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
modalRoot.removeChild(this.el);
}
render() {
return ReactDOM.createPortal(this.props.children, this.el);
}
}
function Child() {
return (
这个是通过ReactDOM.createPortal创建的内容
);
}
export default class TwentyFour extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { clicks: 0 };
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState(prevState => ({
clicks: prevState.clicks + 1
}));
}
render() {
return (
点击次数: {this.state.clicks}
);
}
}
这样元素就追加到指定的元素下面啦
25.在 React 使用innerHTML
场景:有些后台返回是 html 格式字段,就需要用到 innerHTML 属性
export default class TwentyFive extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
这是渲染的 HTML 内容" }}>
);
}
}
26.React.createElement
语法:
React.createElement( type, [props], […children] )
源码:
export default class TwentySix extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
{React.createElement(
"div",
{ id: "one", className: "two" },
React.createElement("span", { id: "spanOne" }, "这是第一个 span 标签"),
React.createElement("br"),
React.createElement("span", { id: "spanTwo" }, "这是第二个 span 标签")
)}
);
}
}
原理:实质上 JSX 的 dom 最后转化为 js 都是React.createElement
// jsx 语法
this is spanOne
this is spanTwo
// 转化为 js
React.createElement(
"div",
{ id: "one", class: "two" },
React.createElement( "span", { id: "spanOne" }, "this is spanOne"),
React.createElement("span", { id: "spanTwo" }, "this is spanTwo")
);
27.React.cloneElement
语法:
React.cloneElement(
element,
[props],
[...children]
)
作用:这个方法的作用是复制组件,给组件传值或者添加属性
核心代码
React.Children.map(children, child => {
return React.cloneElement(child, {
count: _this.state.count
});
});
28.React.Fragment
作用:React.Fragment可以让你聚合一个子元素列表,并且不在DOM中增加额外节点
核心代码
render() {
const { info } = this.state;
return (
{info.map((item, index) => {
return (
{item.name}
{item.age}
);
})}
);
}
29.循环元素
内部没有封装像 vue 里面 v-for 的指令,而是通过 map 遍历
{arr.map((item,index)=>{
return(
{item.name}
{item.age}
)
})}
30.给 DOM 设置和获取自定义属性
作用:有些要通过自定义属性传值
export default class Thirty extends React.Component {
click = e => {
console.log(e.target.getAttribute("data-row"));
};
render() {
return (
点击获取属性
);
}
}
31.绑定事件
场景:交互就会涉及到事件点击,然后点击选中值传参也是一个很常见场景
import React from "react";
import { Button } from 'antd'
export default class Three extends React.Component {
state = {
flag: true,
flagOne: 1
};
click(data1,data2){
console.log('data1 值为',data1)
console.log('data2 值为',data2)
}
render() {
return (
);
}
}
使用方法在源码 routes.js 有详细使用
32.React-Router
32.1 V3和 V4的区别
1.V3或者说V早期版本是把router 和 layout components 分开;
2.V4是集中式 router,通过 Route 嵌套,实现 Layout 和 page 嵌套,Layout 和 page 组件 是作为 router 的一部分;
3.在V3 中的 routing 规则是 exclusive,意思就是最终只获取一个 route;
4.V4 中的 routes 默认是 inclusive 的,这就意味着多个; 可以同时匹配和呈现.如果只想匹配一个路由,可以使用Switch,在 中只有一个 会被渲染,同时可以再在每个路由添加exact,做到精准匹配 Redirect,浏览器重定向,当多有都不匹配的时候,进行匹配
32.2 使用
import { HashRouter as Router, Switch } from "react-router-dom";
class App extends React.Component{
render(){
const authPath = '/login' // 默认未登录的时候返回的页面,可以自行设置
let authed = this.props.state.authed || localStorage.getItem('authed') // 如果登陆之后可以利用redux修改该值
return (
{renderRoutes(routes, authed, authPath)}
)
}
}
V4是通过 Route 嵌套,实现 Layout 和 page 嵌套,Switch切换路由的作用
33.样式引入方法
方式 1:import 导入
import './App.css';
方式 2:内联方式
import React from 'react';
const Header = () => {
const heading = '头部组件'
return(
{heading}
)
}
或者
import React from 'react';
const footerStyle = {
width: '100%',
backgroundColor: 'green',
padding: '50px',
font: '30px',
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold'
}
export const Footer = () => {
return(
底部组件
)
}
34.动态绑定 className
原理:通过三元表达式控制 className 值
render(){
const flag=true
return (
这是技巧 34
)
}
组件类
组件类,详细分的话有三种类,第一类说白了就是我平时用于继承的基类组件Component,PureComponent,还有就是react提供的内置的组件,比如Fragment,StrictMode,另一部分就是高阶组件forwardRef,memo等。
Component
Component是class组件的根基。类组件一切始于Component。对于React.Component使用,我们没有什么好讲的。我们这里重点研究一下react对Component做了些什么。
react/src/ReactBaseClasses.js
function Component(props, context, updater) {
this.props = props;
this.context = context;
this.refs = emptyObject;
this.updater = updater || ReactNoopUpdateQueue;
}
这就是Component函数,其中updater对象上保存着更新组件的方法。
我们声明的类组件是什么时候以何种形式被实例化的呢?
react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberClassComponent.js
constructClassInstance
function constructClassInstance(
workInProgress,
ctor,
props
){
const instance = new ctor(props, context);
instance.updater = {
isMounted,
enqueueSetState(){
/* setState 触发这里面的逻辑 */
},
enqueueReplaceState(){},
enqueueForceUpdate(){
/* forceUpdate 触发这里的逻辑 */
}
}
}
对于Component, react 处理逻辑还是很简单的,实例化我们类组件,然后赋值updater对象,负责组件的更新。然后在组件各个阶段,执行类组件的render函数,和对应的生命周期函数就可以了。
⭐️PureComponent
PureComponent和 Component用法,差不多一样,唯一不同的是,纯组件PureComponent会浅比较,props和state是否相同,来决定是否重新渲染组件。所以一般用于性能调优,减少render次数。
什么叫做浅比较,我这里举个列子:
class Index extends React.PureComponent{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state={
data:{
name:'alien',
age:28
}
}
}
handerClick= () =>{
const { data } = this.state
data.age++
this.setState({ data })
}
render(){
const { data } = this.state
return
你的姓名是: { data.name }
年龄: { data.age }
}
}
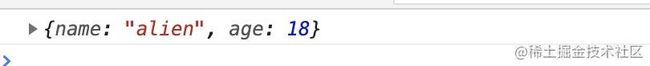
点击按钮,没有任何反应,因为PureComponent会比较两次data对象,都指向同一个data,没有发生改变,所以不更新视图。
解决这个问题很简单,只需要在handerClick事件中这么写:
this.setState({ data:{...data} })
浅拷贝就能根本解决问题。
memo
React.memo和PureComponent作用类似,可以用作性能优化,React.memo 是高阶组件,函数组件和类组件都可以使用, 和区别PureComponent是 React.memo只能对props的情况确定是否渲染,而PureComponent是针对props和state。
React.memo 接受两个参数,第一个参数原始组件本身,第二个参数,可以根据一次更新中props是否相同决定原始组件是否重新渲染。是一个返回布尔值,true 证明组件无须重新渲染,false证明组件需要重新渲染,这个和类组件中的shouldComponentUpdate()正好相反 。
React.memo: 第二个参数 返回 true 组件不渲染 , 返回 false 组件重新渲染。 shouldComponentUpdate: 返回 true 组件渲染 , 返回 false 组件不渲染。
接下来我们做一个场景,控制组件在仅此一个props数字变量,一定范围渲染。
例子:
控制 props 中的 number :
- 1 只有
number更改,组件渲染。 - 2 只有
number小于 5 ,组件渲染。
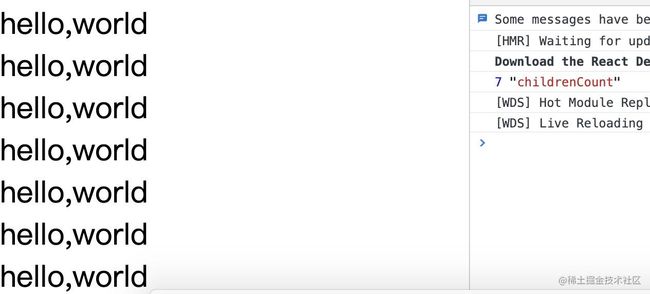
function TextMemo(props){
console.log('子组件渲染')
if(props)
return hello,world
}
const controlIsRender = (pre,next)=>{
if(pre.number === next.number ){ // number 不改变 ,不渲染组件
return true
}else if(pre.number !== next.number && next.number > 5 ) { // number 改变 ,但值大于5 , 不渲染组件
return true
}else { // 否则渲染组件
return false
}
}
const NewTexMemo = memo(TextMemo,controlIsRender)
class Index extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state={
number:1,
num:1
}
}
render(){
const { num , number } = this.state
return
改变num:当前值 { num }
改变number: 当前值 { number }
完美达到了效果,React.memo一定程度上,可以等价于组件外部使用shouldComponentUpdate ,用于拦截新老props,确定组件是否更新。
forwardRef
官网对forwardRef的概念和用法很笼统,也没有给定一个具体的案例。很多同学不知道 forwardRef具体怎么用,下面我结合具体例子给大家讲解forwardRef应用场景。
1 转发引入Ref
这个场景实际很简单,比如父组件想获取孙组件,某一个dom元素。这种隔代ref获取引用,就需要forwardRef来助力。
function Son (props){
const { grandRef } = props
return
i am alien
这个是想要获取元素
}
class Father extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
}
render(){
return
this.node = node } />
}
}
效果
react不允许ref通过props传递,因为组件上已经有 ref 这个属性,在组件调和过程中,已经被特殊处理,forwardRef出现就是解决这个问题,把ref转发到自定义的forwardRef定义的属性上,让ref,可以通过props传递。
2 高阶组件转发Ref
一文吃透hoc文章中讲到,由于属性代理的hoc,被包裹一层,所以如果是类组件,是通过ref拿不到原始组件的实例的,不过我们可以通过forWardRef转发ref。
function HOC(Component){
class Wrap extends React.Component{
render(){
const { forwardedRef ,...otherprops } = this.props
return 如上,解决了高阶组件引入Ref的问题。
lazy
React.lazy 和 Suspense 技术还不支持服务端渲染。如果你想要在使用服务端渲染的应用中使用,我们推荐 Loadable Components 这个库
React.lazy和Suspense配合一起用,能够有动态加载组件的效果。React.lazy 接受一个函数,这个函数需要动态调用 import()。它必须返回一个 Promise ,该 Promise 需要 resolve 一个 default export 的 React 组件。
我们模拟一个动态加载的场景。
父组件
import Test from './comTest'
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(()=> new Promise((resolve)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve({
default: ()=> 我们用setTimeout来模拟import异步引入效果。
Test
class Test extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log('--componentDidMount--')
}
render(){
return
 }
}
}
}
效果
Suspense
何为Suspense, Suspense 让组件“等待”某个异步操作,直到该异步操作结束即可渲染。
用于数据获取的 Suspense 是一个新特性,你可以使用 `` 以声明的方式来“等待”任何内容,包括数据。本文重点介绍它在数据获取的用例,它也可以用于等待图像、脚本或其他异步的操作。
上面讲到高阶组件lazy时候,已经用 lazy + Suspense模式,构建了异步渲染组件。我们看一下官网文档中的案例:
const ProfilePage = React.lazy(() => import('./ProfilePage')); // 懒加载
Fragment
react不允许一个组件返回多个节点元素,比如说如下情况
render(){
return
}
如果我们想解决这个情况,很简单,只需要在外层套一个容器元素。
render(){
return
}
但是我们不期望,增加额外的dom节点,所以react提供Fragment碎片概念,能够让一个组件返回多个元素。 所以我们可以这么写
还可以简写成:
<>
和Fragment区别是,Fragment可以支持key属性。<>不支持key属性。
温馨提示。我们通过map遍历后的元素,react底层会处理,默认在外部嵌套一个``。
比如:
{
[1,2,3].map(item=>{ item.name })
}
react底层处理之后,等价于:
<Fragment>
<span>span>
<span>span>
<span>span>
Fragment>
Profiler
Profiler这个api一般用于开发阶段,性能检测,检测一次react组件渲染用时,性能开销。
Profiler 需要两个参数:
第一个参数:是 id,用于表识唯一性的Profiler。
第二个参数:onRender回调函数,用于渲染完成,接受渲染参数。
实践:
const index = () => {
const callback = (...arg) => console.log(arg)
return
{ renderRoutes(menusList) }
}
结果
onRender
-
0 -id:
root->Profiler树的id。 -
1 -phase:
mount->mount挂载 ,update渲染了。 -
2 -actualDuration:
6.685000262223184-> 更新committed花费的渲染时间。 -
3 -baseDuration:
4.430000321008265-> 渲染整颗子树需要的时间 -
4 -startTime :
689.7299999836832-> 本次更新开始渲染的时间 -
5 -commitTime :
698.5799999674782-> 本次更新committed 的时间 -
6 -interactions:
set{}-> 本次更新的interactions的集合
尽管 Profiler 是一个轻量级组件,我们依然应该在需要时才去使用它。对一个应用来说,每添加一些都会给 CPU 和内存带来一些负担。
StrictMode
StrictMode见名知意,严格模式,用于检测react项目中的潜在的问题,。与 Fragment 一样, StrictMode 不会渲染任何可见的 UI 。它为其后代元素触发额外的检查和警告。
严格模式检查仅在开发模式下运行;它们不会影响生产构建。
StrictMode目前有助于:
- ①识别不安全的生命周期。
- ②关于使用过时字符串
ref API的警告 - ③关于使用废弃的
findDOMNode方法的警告 - ④检测意外的副作用
- ⑤检测过时的
context API
实践:识别不安全的生命周期
对于不安全的生命周期,指的是UNSAFE_componentWillMount,UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps , UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate
外层开启严格模式:
{ renderRoutes(menusList) }
我们在内层组件中,使用不安全的生命周期:
class Index extends React.Component{
UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps(){
}
render(){
return
}
}
结果
工具类
接下来我们一起来探究一下react工具类函数的用法。
createElement
一提到createElement,就不由得和JSX联系一起。我们写的jsx,最终会被 babel,用createElement编译成react元素形式。我写一个组件,我们看一下会被编译成什么样子,
如果我们在render里面这么写:
render(){
return
生命周期
Flagment
{ /* */ }
text文本
}
会被编译成这样:
render() {
return React.createElement("div", { className: "box" },
React.createElement("div", { className: "item" }, "\u751F\u547D\u5468\u671F"),
React.createElement(Text, { mes: "hello,world" }),
React.createElement(React.Fragment, null, " Flagment "),
"text\u6587\u672C");
}
当然我们可以不用jsx模式,而是直接通过createElement进行开发。
createElement模型:
React.createElement(
type,
[props],
[...children]
)
createElement参数:
第一个参数: 如果是组件类型,会传入组件,如果是dom元素类型,传入div或者span之类的字符串。
第二个参数: 第二个参数为一个对象,在dom类型中为属性,在组件类型中为props。
**其他参数: **依次为children,根据顺序排列。
createElement做了些什么?
经过createElement处理,最终会形成 $$typeof = Symbol(react.element)对象。对象上保存了该react.element的信息。
cloneElement
可能有的同学还傻傻的分不清楚cloneElement和createElement区别和作用。
createElement把我们写的jsx,变成element对象; 而cloneElement的作用是以 element 元素为样板克隆并返回新的 React 元素。返回元素的 props 是将新的 props 与原始元素的 props 浅层合并后的结果。
那么cloneElement感觉在我们实际业务组件中,可能没什么用,但是在一些开源项目,或者是公共插槽组件中用处还是蛮大的,比如说,我们可以在组件中,劫持children element,然后通过cloneElement克隆element,混入props。经典的案例就是 react-router中的Swtich组件,通过这种方式,来匹配唯一的 Route并加以渲染。
我们设置一个场景,在组件中,去劫持children,然后给children赋能一些额外的props:
function FatherComponent({ children }){
const newChildren = React.cloneElement(children, { age: 18})
return { newChildren }
}
function SonComponent(props){
console.log(props)
return hello,world
}
class Index extends React.Component{
render(){
return
}
}
打印:
完美达到了效果!
createContext
createContext用于创建一个Context对象,createContext对象中,包括用于传递 Context 对象值 value的Provider,和接受value变化订阅的Consumer。
const MyContext = React.createContext(defaultValue)
createContext接受一个参数defaultValue,如果Consumer上一级一直没有Provider,则会应用defaultValue作为value。只有当组件所处的树中没有匹配到 Provider 时,其 defaultValue 参数才会生效。
我们来模拟一个 Context.Provider和Context.Consumer的例子:
function ComponentB(){
/* 用 Consumer 订阅, 来自 Provider 中 value 的改变 */
return
{ (value) =>
}
function ComponentA(props){
const { name , mes } = props
return
姓名: { name }
想对大家说: { mes }
}
function index(){
const [ value , ] = React.useState({
name:'alien',
mes:'let us learn React '
})
return
}
打印结果:
Provider和Consumer的良好的特性,可以做数据的存和取,Consumer一方面传递value,另一方面可以订阅value的改变。
Provider还有一个特性可以层层传递value,这种特性在react-redux中表现的淋漓尽致。
createFactory
React.createFactory(type)
返回用于生成指定类型 React 元素的函数。类型参数既可以是标签名字符串(像是 ‘div’ 或 ‘span’),也可以是 React 组件 类型 ( class 组件或函数组件),或是 React fragment 类型。
使用:
const Text = React.createFactory(()=>hello,world)
function Index(){
return
效果
报出警告,这个api将要被废弃,我们这里就不多讲了,如果想要达到同样的效果,请用React.createElement
createRef
createRef可以创建一个 ref 元素,附加在react元素上。
用法:
class Index extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.node = React.createRef()
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log(this.node)
}
render(){
return my name is alien
}
}
个人觉得createRef这个方法,很鸡肋,我们完全可以class类组件中这么写,来捕获ref。
class Index extends React.Component{
node = null
componentDidMount(){
console.log(this.node)
}
render(){
return this.node } > my name is alien
}
}
或者在function组件中这么写:
function Index(){
const node = React.useRef(null)
useEffect(()=>{
console.log(node.current)
},[])
return my name is alien
}
isValidElement
这个方法可以用来检测是否为react element元素,接受待验证对象,返回true或者false。这个api可能对于业务组件的开发,作用不大,因为对于组件内部状态,都是已知的,我们根本就不需要去验证,是否是react element 元素。 但是,对于一起公共组件或是开源库,isValidElement就很有作用了。
实践
我们做一个场景,验证容器组件的所有子组件,过滤到非react element类型。
没有用isValidElement验证之前:
const Text = () => hello,world
class WrapComponent extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
}
render(){
return this.props.children
}
}
function Index(){
return
}
过滤之前的效果
我们用isValidElement进行react element验证:
class WrapComponent extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.newChidren = this.props.children.filter(item => React.isValidElement(item) )
}
render(){
return this.newChidren
}
}
过滤之后效果
过滤掉了非react element 的 Let's learn react together!。
Children.map
接下来的五个api都是和react.Chidren相关的,我们来分别介绍一下,我们先来看看官网的描述,React.Children 提供了用于处理 this.props.children 不透明数据结构的实用方法。
有的同学会问遍历 children用数组方法,map ,forEach 不就可以了吗? 请我们注意一下不透明数据结构,什么叫做不透明结构?
我们先看一下透明的结构:
class Text extends React.Component{
render(){
return hello,world
}
}
function WrapComponent(props){
console.log(props.children)
return props.children
}
function Index(){
return
}
打印
但是我们把Index结构改变一下:
function Index(){
return
{ new Array(3).fill(0).map(()=>
}
打印
这个数据结构,我们不能正常的遍历了,即使遍历也不能遍历,每一个子元素。此时就需要 react.Chidren 来帮忙了。
但是我们把WrapComponent组件用react.Chidren处理children:
function WrapComponent(props){
const newChildren = React.Children.map(props.children,(item)=>item)
console.log(newChildren)
return newChildren
}
此时就能正常遍历了,达到了预期效果。
注意 如果 children 是一个 Fragment 对象,它将被视为单一子节点的情况处理,而不会被遍历。
Children.forEach
Children.forEach和Children.map 用法类似,Children.map可以返回新的数组,Children.forEach仅停留在遍历阶段。
我们将上面的WrapComponent方法,用Children.forEach改一下。
function WrapComponent(props){
React.Children.forEach(props.children,(item)=>console.log(item))
return props.children
}
Children.count
children 中的组件总数量,等同于通过 map 或 forEach 调用回调函数的次数。对于更复杂的结果,Children.count可以返回同一级别子组件的数量。
我们还是把上述例子进行改造:
function WrapComponent(props){
const childrenCount = React.Children.count(props.children)
console.log(childrenCount,'childrenCount')
return props.children
}
function Index(){
return
{ new Array(3).fill(0).map((item,index) => new Array(2).fill(1).map((item,index1)=>
}
效果:
Children.toArray
Children.toArray返回,props.children扁平化后结果。
function WrapComponent(props){
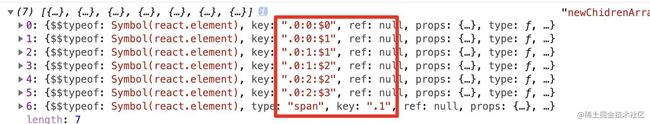
const newChidrenArray = React.Children.toArray(props.children)
console.log(newChidrenArray,'newChidrenArray')
return newChidrenArray
}
function Index(){
return
{ new Array(3).fill(0).map((item,index)=>new Array(2).fill(1).map((item,index1)=>
}
效果:
newChidrenArray ,就是扁平化的数组结构。React.Children.toArray() 在拉平展开子节点列表时,更改 key 值以保留嵌套数组的语义。也就是说, toArray 会为返回数组中的每个 key 添加前缀,以使得每个元素 key 的范围都限定在此函数入参数组的对象内。
Children.only
验证 children 是否只有一个子节点(一个 React 元素),如果有则返回它,否则此方法会抛出错误。
不唯一
function WrapComponent(props){
console.log(React.Children.only(props.children))
return props.children
}
function Index(){
return
{ new Array(3).fill(0).map((item,index)=>
}
效果
唯一
function WrapComponent(props){
console.log(React.Children.only(props.children))
return props.children
}
function Index(){
return
}
效果
React.Children.only() 不接受 React.Children.map() 的返回值,因为它是一个数组而并不是 React 元素。
react-hooks
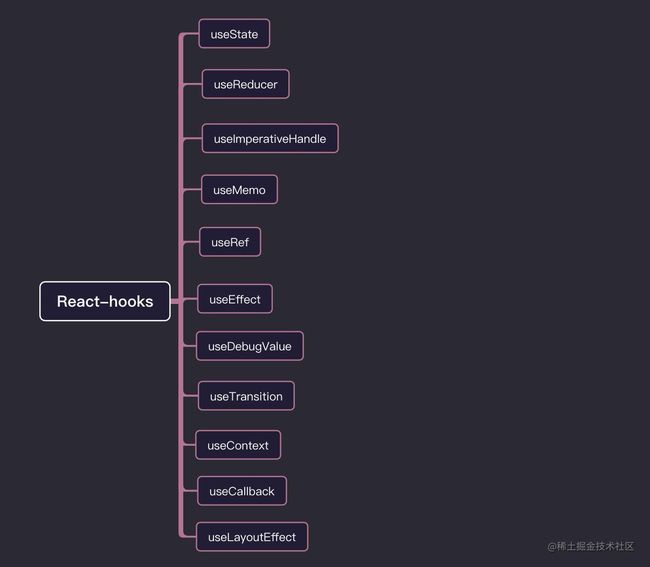
对于react-hooks,我已经写了三部曲,介绍了react-hooks使用,自定义hooks,以及react-hooks原理,感兴趣的同学可以去看看,文章末尾有链接,对于常用的api,我这里参考了react-hooks如何使用那篇文章。并做了相应精简化和一些内容的补充。
useState
useState可以弥补函数组件没有state的缺陷。useState可以接受一个初识值,也可以是一个函数action,action返回值作为新的state。返回一个数组,第一个值为state读取值,第二个值为改变state的dispatchAction函数。
我们看一个例子:
const DemoState = (props) => {
/* number为此时state读取值 ,setNumber为派发更新的函数 */
let [number, setNumber] = useState(0) /* 0为初始值 */
return (
{ number }
)
}
useEffect
useEffect可以弥补函数组件没有生命周期的缺点。我们可以在useEffect第一个参数回调函数中,做一些请求数据,事件监听等操作,第二个参数作为dep依赖项,当依赖项发生变化,重新执行第一个函数。
useEffect可以用作数据交互。
/* 模拟数据交互 */
function getUserInfo(a){
return new Promise((resolve)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve({
name:a,
age:16,
})
},500)
})
}
const DemoEffect = ({ a }) => {
const [ userMessage , setUserMessage ] :any= useState({})
const div= useRef()
const [number, setNumber] = useState(0)
/* 模拟事件监听处理函数 */
const handleResize =()=>{}
/* useEffect使用 ,这里如果不加限制 ,会是函数重复执行,陷入死循环*/
useEffect(()=>{
/* 请求数据 */
getUserInfo(a).then(res=>{
setUserMessage(res)
})
/* 操作dom */
console.log(div.current) /* div */
/* 事件监听等 */
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize)
/* 只有当props->a和state->number改变的时候 ,useEffect副作用函数重新执行 ,如果此时数组为空[],证明函数只有在初始化的时候执行一次相当于componentDidMount */
},[ a ,number ])
return (
{ userMessage.name }
{ userMessage.age }
setNumber(1) } >{ number }
)
}
useEffect可以用作事件监听,还有一些基于dom的操作。,别忘了在useEffect第一个参数回调函数,返一个函数用于清除事件监听等操作。
const DemoEffect = ({ a }) => {
/* 模拟事件监听处理函数 */
const handleResize =()=>{}
useEffect(()=>{
/* 定时器 延时器等 */
const timer = setInterval(()=>console.log(666),1000)
/* 事件监听 */
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize)
/* 此函数用于清除副作用 */
return function(){
clearInterval(timer)
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize)
}
},[ a ])
return (
)
}
useMemo
useMemo接受两个参数,第一个参数是一个函数,返回值用于产生保存值。 第二个参数是一个数组,作为dep依赖项,数组里面的依赖项发生变化,重新执行第一个函数,产生新的值。
应用场景: 1 缓存一些值,避免重新执行上下文
const number = useMemo(()=>{
/** ....大量的逻辑运算 **/
return number
},[ props.number ]) // 只有 props.number 改变的时候,重新计算number的值。
2 减少不必要的dom循环
/* 用 useMemo包裹的list可以限定当且仅当list改变的时候才更新此list,这样就可以避免selectList重新循环 */
{useMemo(() => (
{
selectList.map((i, v) => (
{i.patentName}
))}
), [selectList])}
3 减少子组件渲染
/* 只有当props中,list列表改变的时候,子组件才渲染 */
const goodListChild = useMemo(()=> useCallback
useMemo 和 useCallback 接收的参数都是一样,都是在其依赖项发生变化后才执行,都是返回缓存的值,区别在于 useMemo 返回的是函数运行的结果, useCallback 返回的是函数。 返回的callback可以作为props回调函数传递给子组件。
/* 用react.memo */
const DemoChildren = React.memo((props)=>{
/* 只有初始化的时候打印了 子组件更新 */
console.log('子组件更新')
useEffect(()=>{
props.getInfo('子组件')
},[])
return 子组件
})
const DemoUseCallback=({ id })=>{
const [number, setNumber] = useState(1)
/* 此时usecallback的第一参数 (sonName)=>{ console.log(sonName) }
经过处理赋值给 getInfo */
const getInfo = useCallback((sonName)=>{
console.log(sonName)
},[id])
return
{/* 点击按钮触发父组件更新 ,但是子组件没有更新 */}
useRef
useRef的作用:
- 一 是可以用来获取
dom元素,或者class组件实例 。 - 二
react-hooks原理文章中讲过,创建useRef时候,会创建一个原始对象,只要函数组件不被销毁,原始对象就会一直存在,那么我们可以利用这个特性,来通过useRef保存一些数据。
const DemoUseRef = ()=>{
const dom= useRef(null)
const handerSubmit = ()=>{
/* 表单组件 dom 节点 */
console.log(dom.current)
}
return
{/* ref 标记当前dom节点 */}
表单组件
}
useLayoutEffect
useEffect执行顺序: 组件更新挂载完成 -> 浏览器 dom 绘制完成 -> 执行 useEffect 回调。 useLayoutEffect 执行顺序: 组件更新挂载完成 -> 执行 useLayoutEffect 回调-> 浏览器dom绘制完成。
所以说 useLayoutEffect 代码可能会阻塞浏览器的绘制 。我们写的 effect和 useLayoutEffect,react在底层会被分别打上PassiveEffect,HookLayout,在commit阶段区分出,在什么时机执行。
const DemoUseLayoutEffect = () => {
const target = useRef()
useLayoutEffect(() => {
/*我们需要在dom绘制之前,移动dom到制定位置*/
const { x ,y } = getPositon() /* 获取要移动的 x,y坐标 */
animate(target.current,{ x,y })
}, []);
return (
)
}
useReducer
在react-hooks原理那篇文章中讲解到,useState底层就是一个简单版的useReducer
useReducer 接受的第一个参数是一个函数,我们可以认为它就是一个 reducer , reducer 的参数就是常规 reducer 里面的 state 和 action ,返回改变后的 state , useReducer 第二个参数为 state 的初始值 返回一个数组,数组的第一项就是更新之后 state 的值 ,第二个参数是派发更新的 dispatch 函数。
我们来看一下useReducer如何使用:
const DemoUseReducer = ()=>{
/* number为更新后的state值, dispatchNumbner 为当前的派发函数 */
const [ number , dispatchNumbner ] = useReducer((state,action)=>{
const { payload , name } = action
/* return的值为新的state */
switch(name){
case 'add':
return state + 1
case 'sub':
return state - 1
case 'reset':
return payload
}
return state
},0)
return
当前值:{ number }
{ /* 派发更新 */ }
{ /* 把dispatch 和 state 传递给子组件 */ }
useContext
我们可以使用 useContext ,来获取父级组件传递过来的 context 值,这个当前值就是最近的父级组件 Provider 设置的 value 值,useContext 参数一般是由 createContext 方式引入 ,也可以父级上下文 context 传递 ( 参数为 context )。useContext 可以代替 context.Consumer 来获取 Provider 中保存的 value 值
/* 用useContext方式 */
const DemoContext = ()=> {
const value:any = useContext(Context)
/* my name is alien */
return my name is { value.name }
}
/* 用Context.Consumer 方式 */
const DemoContext1 = ()=>{
return
{/* my name is alien */}
{ (value)=> my name is { value.name } }
}
export default ()=>{
return
}
useImperativeHandle
useImperativeHandle 可以配合 forwardRef 自定义暴露给父组件的实例值。这个很有用,我们知道,对于子组件,如果是class类组件,我们可以通过ref获取类组件的实例,但是在子组件是函数组件的情况,如果我们不能直接通过ref的,那么此时useImperativeHandle和 forwardRef配合就能达到效果。
useImperativeHandle接受三个参数:
- 第一个参数ref: 接受
forWardRef传递过来的ref。 - 第二个参数
createHandle:处理函数,返回值作为暴露给父组件的ref对象。 - 第三个参数
deps:依赖项deps,依赖项更改形成新的ref对象。
我们来模拟给场景,用useImperativeHandle,使得父组件能让子组件中的input自动赋值并聚焦。
function Son (props,ref) {
console.log(props)
const inputRef = useRef(null)
const [ inputValue , setInputValue ] = useState('')
useImperativeHandle(ref,()=>{
const handleRefs = {
/* 声明方法用于聚焦input框 */
onFocus(){
inputRef.current.focus()
},
/* 声明方法用于改变input的值 */
onChangeValue(value){
setInputValue(value)
}
}
return handleRefs
},[])
return
}
const ForwarSon = forwardRef(Son)
class Index extends React.Component{
inputRef = null
handerClick(){
const { onFocus , onChangeValue } =this.cur
onFocus()
onChangeValue('let us learn React!')
}
render(){
return
(this.inputRef = node)} />
}
}
useDebugValue
useDebugValue 可用于在 React 开发者工具中显示自定义 hook 的标签。这个hooks目的就是检查自定义hooks
function useFriendStatus(friendID) {
const [isOnline, setIsOnline] = useState(null);
// ...
// 在开发者工具中的这个 Hook 旁边显示标签
// e.g. "FriendStatus: Online"
useDebugValue(isOnline ? 'Online' : 'Offline');
return isOnline;
}
我们不推荐你向每个自定义 Hook 添加 debug 值。当它作为共享库的一部分时才最有价值。在某些情况下,格式化值的显示可能是一项开销很大的操作。除非需要检查 Hook,否则没有必要这么做。因此,useDebugValue 接受一个格式化函数作为可选的第二个参数。该函数只有在 Hook 被检查时才会被调用。它接受 debug 值作为参数,并且会返回一个格式化的显示值。
useTransition
useTransition允许延时由state改变而带来的视图渲染。避免不必要的渲染。它还允许组件将速度较慢的数据获取更新推迟到随后渲染,以便能够立即渲染更重要的更新。
const TIMEOUT_MS = { timeoutMs: 2000 }
const [startTransition, isPending] = useTransition(TIMEOUT_MS)
useTransition接受一个对象,timeoutMs代码需要延时的时间。- 返回一个数组。第一个参数: 是一个接受回调的函数。我们用它来告诉
React需要推迟的state。 第二个参数: 一个布尔值。表示是否正在等待,过度状态的完成(延时state的更新)。
下面我们引入官网的列子,来了解useTransition的使用。
const SUSPENSE_CONFIG = { timeoutMs: 2000 };
function App() {
const [resource, setResource] = useState(initialResource);
const [startTransition, isPending] = useTransition(SUSPENSE_CONFIG);
return (
<>
{isPending ? " 加载中..." : null}
在这段代码中,我们使用 startTransition 包装了我们的数据获取。这使我们可以立即开始获取用户资料的数据,同时推迟下一个用户资料页面以及其关联的 Spinner 的渲染 2 秒钟( timeoutMs 中显示的时间)。
Taro使用笔记
CLI 工具安装
# 使用 npm 安装 CLI
$ npm install -g @tarojs/cli
# OR 使用 yarn 安装 CLI
$ yarn global add @tarojs/cli
# OR 安装了 cnpm,使用 cnpm 安装 CLI
$ cnpm install -g @tarojs/cli
如果安装过程出现sass相关的安装错误
npm install -g mirror-config-china
项目初始化
使用命令创建模板项目:
taro init myApp
npm 5.2+ 也可在不全局安装的情况下使用 npx 创建模板项目:
npx @tarojs/cli init myApp
编译
使用 Taro 的 build 命令可以把 Taro 代码编译成不同端的代码,然后在对应的开发工具中查看效果。
Taro 编译分为 dev 和 build 模式:
- dev 模式(增加 --watch 参数) 将会监听文件修改。
- build 模式(去掉 --watch 参数) 将不会监听文件修改,并会对代码进行压缩打包。
- dev 模式生成的文件较大,设置环境变量
NODE_ENV为production可以开启压缩,方便预览,但编译速度会下降。
微信小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:weapp
$ yarn build:weapp
# npm script
$ npm run dev:weapp
$ npm run build:weapp
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type weapp --watch
$ taro build --type weapp
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type weapp --watch
$ npx taro build --type weapp
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type weapp --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type weapp --watch # Mac
下载并打开微信开发者工具,然后选择项目根目录进行预览。
百度小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:swan
$ yarn build:swan
# npm script
$ npm run dev:swan
$ npm run build:swan
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type swan --watch
$ taro build --type swan
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type swan --watch
$ npx taro build --type swan
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type swan --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type swan --watch # Mac
支付宝小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:alipay
$ yarn build:alipay
# npm script
$ npm run dev:alipay
$ npm run build:alipay
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type alipay --watch
$ taro build --type alipay
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type alipay --watch
$ npx taro build --type alipay
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type alipay --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type alipay --watch # Mac
字节跳动小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:tt
$ yarn build:tt
# npm script
$ npm run dev:tt
$ npm run build:tt
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type tt --watch
$ taro build --type tt
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type tt --watch
$ npx taro build --type tt
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type tt --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type tt --watch # Mac
QQ 小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:qq
$ yarn build:qq
# npm script
$ npm run dev:qq
$ npm run build:qq
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type qq --watch
$ taro build --type qq
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type qq --watch
$ npx taro build --type qq
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type qq --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type qq --watch # Mac
京东小程序
# yarn
$ yarn dev:jd
$ yarn build:jd
# npm script
$ npm run dev:jd
$ npm run build:jd
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type jd --watch
$ taro build --type jd
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type jd --watch
$ npx taro build --type jd
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type jd --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type jd --watch # Mac
企业微信小程序
yarn add @tarojs/plugin-platform-weapp-qy
Taro 项目配置
config = {
// ...
plugins: [
'@tarojs/plugin-platform-weapp-qy'
]
}
# yarn
$ yarn dev:qywx
$ yarn build:qywx
# npm script
$ npm run dev:qywx
$ npm run build:qywx
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type qywx --watch
$ taro build --type qywx
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type qywx --watch
$ npx taro build --type qywx
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type qywx --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type qywx --watch # Mac
钉钉小程序
Taro v3.1+ 开始支持
Taro v3.3.8+: 请使用 @tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-dd 插件的 ~0.1.0 版本
Taro v3.1 & v3.2: 请使用 @tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-dd 插件的 ~0.0.5 版本
yarn add @tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-dd
Taro 项目配置
config = {
// ...
plugins: [
'@tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-dd'
]
}
# yarn
$ yarn dev:dd
$ yarn build:dd
# npm script
$ npm run dev:dd
$ npm run build:dd
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type dd --watch
$ taro build --type dd
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type dd --watch
$ npx taro build --type dd
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type dd --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type dd --watch # Mac
支付宝 IOT 小程序
安装插件
yarn add @tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-iot
Taro 项目配置
config = {
// ...
plugins: [
'@tarojs/plugin-platform-alipay-iot'
]
}
# yarn
$ yarn dev:iot
$ yarn build:iot
# npm script
$ npm run dev:iot
$ npm run build:iot
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type iot --watch
$ taro build --type iot
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type iot --watch
$ npx taro build --type iot
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type iot --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type iot --watch # Mac
飞书小程序
yarn add @tarojs/plugin-platform-lark
Taro 项目配置
config = {
// ...
plugins: [
'@tarojs/plugin-platform-lark'
]
}
编译
# yarn
$ yarn dev:lark
$ yarn build:lark
# npm script
$ npm run dev:lark
$ npm run build:lark
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type lark --watch
$ taro build --type lark
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type lark --watch
$ npx taro build --type lark
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type lark --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type lark --watch # Mac
快手小程序
Taro v3.1+ 开始支持
Taro v3.3+: 请使用 taro-plugin-platform-kwai 插件的 1.0 或以上版本
Taro v3.2: 请使用 taro-plugin-platform-ks 插件的 1.2.x 版本
Taro v3.1: 请使用 taro-plugin-platform-ks 插件的 1.0.x 版本
插件安装
yarn add @tarojs/plugin-platform-kwai
Taro 项目配置
config = {
// ...
plugins: [
'@tarojs/plugin-platform-kwai'
]
}
编译
# yarn
$ yarn dev:kwai
$ yarn build:kwai
# npm script
$ npm run dev:kwai
$ npm run build:kwai
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type kwai --watch
$ taro build --type kwai
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type kwai --watch
$ npx taro build --type kwai
# watch 同时开启压缩
$ set NODE_ENV=production && taro build --type kwai --watch # Windows
$ NODE_ENV=production taro build --type kwai --watch # Mac
h5
# yarn
$ yarn dev:h5
$ yarn build:h5
# npm script
$ npm run dev:h5
$ npm run build:h5
# 仅限全局安装
$ taro build --type h5 --watch
$ taro build --type h5
# npx 用户也可以使用
$ npx taro build --type h5 --watch
$ npx taro build --type h5
React native
React Native 端开发流程
由浅入深的实战《教程》。
如果发现不一致的情况可以使用 Taro 升级命令 taro update self [版本号] 和 taro update project [版本号]来分别将 CLI 和项目依赖升级到指定版本; 或者也可以手动安装相应版本 CLI,修改 package.json 依赖版本号,然后重装依赖来解决。
# 使用Taro 升级命令更新CLI版本到最新版本
$ taro update self [版本号]
# 使用Taro 升级命令更新CLI版本到指定版本
$ taro update self
# 使用Taro 升级命令将项目依赖升级到与@tarojs/cli一致的版本
$ taro update project
# 使用Taro 升级命令将项目依赖升级到指定版本
$ taro update project [版本号]
更多资源 https://github.com/NervJS/awesome-taro
https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/composition
项目目录结构
├── dist 编译结果目录
|
├── config 项目编译配置目录
| ├── index.js 默认配置
| ├── dev.js 开发环境配置
| └── prod.js 生产环境配置
|
├── src 源码目录
| ├── pages 页面文件目录
| | └── index index 页面目录
| | ├── index.js index 页面逻辑
| | ├── index.css index 页面样式
| | └── index.config.js index 页面配置
| |
| ├── app.js 项目入口文件
| ├── app.css 项目总通用样式
| └── app.config.js 项目入口配置
|
├── project.config.json 微信小程序项目配置 project.config.json
├── project.tt.json 字节跳动小程序项目配置 project.config.json
├── project.swan.json 百度小程序项目配置 project.swan.json
├── project.qq.json QQ 小程序项目配置 project.config.json
|
├── babel.config.js Babel 配置
├── tsconfig.json TypeScript 配置
├── .eslintrc ESLint 配置
|
└── package.json
编译配置
└── config 项目编译配置目录
├── index.js 默认配置
├── dev.js 开发环境配置
└── prod.js 生产环境配置
用于配置 Taro 项目的编译行为、修改 Webpack 配置等,详情请参考编译配置和编译配置详情。
page
└── src 源码目录
└── pages 页面文件目录
└── index index 页面目录
├── index.js index 页面逻辑
├── index.css index 页面样式
└── index.config.js index 页面配置
- 页面配置
page.config.js 对应小程序规范的页面配置文件 page.json,优势在于它是 JS 文件可以编写逻辑。配置以微信小程序的页面配置为规范。详情请参考页面配置。
- 页面样式
页面的样式文件可以通过 ES6 规范的 import 进行引入。
pages/index/index.js
import ‘./index.css’;
Copy
- 页面路由
页面路由与小程序规范一致,需要在小程序全局配置 app.config.js 中进行配置。
项目配置
└──project.config.json 微信小程序项目配置 project.config.json
各类小程序平台均有自己的项目配置文件,Taro 支持对它们进行适配,详情请参考项目配置。
babel配置
└── babel.config.js Babel 配置
请参考 Babel 配置
Eslint 配置
└── .eslintrc ESLint 配置
ESLint 配置请参考 Github
编译配置
编译配置存放于项目根目录下的 config 目录中,包含三个文件:
index.js是通用配置dev.js是项目预览时的配置prod.js是项目打包时的配置
详细的编译配置文档请查阅:编译配置详情
默认配置
const config = {
// 项目名称
projectName: 'Awesome Next',
// 项目创建日期
date: '2020-6-2',
// 设计稿尺寸
designWidth: 750,
// 设计稿尺寸换算规则
deviceRatio: {
640: 2.34 / 2,
750: 1,
828: 1.81 / 2
},
// 项目源码目录
sourceRoot: 'src',
// 项目产出目录
outputRoot: 'dist',
// Taro 插件配置
plugins: [],
// 全局变量设置
defineConstants: {},
// 文件 copy 配置
copy: {
patterns: [
],
options: {
}
},
// 框架,react,nerv,vue, vue3 等
framework: 'react',
// 小程序端专用配置
mini: {
postcss: {
autoprefixer: {
enable: true
},
// 小程序端样式引用本地资源内联配置
url: {
enable: true,
config: {
limit: 10240
}
},
cssModules: {
enable: false, // 默认为 false,如需使用 css modules 功能,则设为 true
config: {
namingPattern: 'module', // 转换模式,取值为 global/module
generateScopedName: '[name]__[local]___[hash:base64:5]'
}
}
},
// 自定义 Webpack 配置
webpackChain (chain, webpack) {}
},
// H5 端专用配置
h5: {
publicPath: '/',
staticDirectory: 'static',
postcss: {
autoprefixer: {
enable: true
},
cssModules: {
enable: false, // 默认为 false,如需使用 css modules 功能,则设为 true
config: {
namingPattern: 'module', // 转换模式,取值为 global/module
generateScopedName: '[name]__[local]___[hash:base64:5]'
}
}
},
// 自定义 Webpack 配置
webpackChain (chain, webpack) {},
devServer: {}
}
};
module.exports = function(merge) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
return merge({}, config, require('./dev'));
}
return merge({}, config, require('./prod'));
};
设计稿及尺寸单位
在 Taro 中尺寸单位建议使用 px、 百分比 %,Taro 默认会对所有单位进行转换。在 Taro 中书写尺寸按照 1:1 的关系来进行书写,即从设计稿上量的长度 100px,那么尺寸书写就是 100px,当转成微信小程序的时候,尺寸将默认转换为 100rpx,当转成 H5 时将默认转换为以 rem 为单位的值。
如果你希望部分 px 单位不被转换成 rpx 或者 rem ,最简单的做法就是在 px 单位中增加一个大写字母,例如 Px 或者 PX 这样,则会被转换插件忽略。
结合过往的开发经验,Taro 默认以 750px 作为换算尺寸标准,如果设计稿不是以 750px 为标准,则需要在项目配置 config/index.js 中进行设置,例如设计稿尺寸是 640px,则需要修改项目配置 config/index.js 中的 designWidth 配置为 640:
/config/index.js
const config = {
projectName: 'myProject',
date: '2018-4-18',
designWidth: 640,
....
}
目前 Taro 支持 750、 640 、 828 三种尺寸设计稿,他们的换算规则如下:
const DEVICE_RATIO = {
'640': 2.34 / 2,
'750': 1,
'828': 1.81 / 2
}
建议使用 Taro 时,设计稿以 iPhone 6 750px 作为设计尺寸标准。
如果你的设计稿是 375 ,不在以上三种之中,那么你需要把 designWidth 配置为 375,同时在 DEVICE_RATIO 中添加换算规则如下:
const DEVICE_RATIO = {
'640': 2.34 / 2,
'750': 1,
'828': 1.81 / 2,
'375': 2 / 1
}
api
在编译时,Taro 会帮你对样式做尺寸转换操作,但是如果是在 JS 中书写了行内样式,那么编译时就无法做替换了,针对这种情况,Taro 提供了 API Taro.pxTransform 来做运行时的尺寸转换。
Taro.pxTransform(10) // 小程序:rpx,H5:rem
配置
默认配置会对所有的 px 单位进行转换,有大写字母的 Px 或 PX 则会被忽略。
参数默认值如下:
{
onePxTransform: true, // 设置 1px 是否需要被转换(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#onepxtransform-boolean)
unitPrecision: 5, // REM 单位允许的小数位。(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#unitprecision-number)
propList: ['*'], // 允许转换的属性。(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#proplist-array)
selectorBlackList: [], // 黑名单里的选择器将会被忽略。(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#selectorblacklist)
replace: true, // 直接替换而不是追加一条进行覆盖。(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#replace-boolean)
mediaQuery: false, // 允许媒体查询里的 px 单位转换 (https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#mediaquery-boolean)
minPixelValue: 0 // 设置一个可被转换的最小 px 值(https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/size#minpixelvalue-number)
}
/config/index.js
{
h5: {
publicPath: '/',
staticDirectory: 'static',
postcss: {
autoprefixer: {
enable: true
},
pxtransform: {
enable: true,
config: {
selectorBlackList: ['body']
}
}
}
},
mini: {
// ...
postcss: {
pxtransform: {
enable: true,
config: {
selectorBlackList: ['body']
}
}
}
}
}
CSS 编译时忽略(过滤)
当前忽略单个属性的最简单的方法,就是 px 单位使用大写字母。
/* `px` is converted to `rem` */
.convert {
font-size: 16px; // converted to 1rem
}
/* `Px` or `PX` is ignored by `postcss-pxtorem` but still accepted by browsers */
.ignore {
border: 1Px solid; // ignored
border-width: 2PX; // ignored
}
全局配置
根目录下的 app.config.js 文件用来对小程序进行全局配置,配置项遵循微信小程序规范,并且对所有平台进行统一。
注意:
app.config.js里 require 或 import 引用的 js 文件目前没有经过 Babel 编译语法。- 多端差异化逻辑可以使用
process.env.TARO_ENV变量作条件判断来实现。 app.config.js不支持多端文件的形式,如app.weapp.js这样是不起作用的。
通用配置项
在 H5、React Native、所有小程序均支持的配置。
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pages | String Array | 是 | 页面路径列表 |
| window | Object | 否 | 全局的默认窗口表现 |
| tabBar | Object | 否 | 底部 tab 栏的表现 |
| subPackages | Object Array | 否 | 分包结构配置 |
pages
如开发目录为:
├── app.js
├── app.json
├── app.wxss
├── pages
│ │── index
│ │ ├── index.wxml
│ │ ├── index.js
│ │ ├── index.json
│ │ └── index.wxss
│ └── logs
│ ├── logs.wxml
│ └── logs.js
└── utils
app.config.js
export default {
pages: [
'pages/index/index',
'pages/logs/logs'
]
}
window
用于设置小程序的状态栏、导航条、标题、窗口背景色,其配置项如下。
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| navigationBarBackgroundColor | HexColor(十六进制颜色值) | #000000 | 导航栏背景颜色,如 #000000 |
| navigationBarTextStyle | String | white | 导航栏标题颜色,仅支持 black / white |
| navigationBarTitleText | String | 导航栏标题文字内容 | |
| navigationStyle | String | default | 导航栏样式,仅支持以下值:default 默认样式;custom 自定义导航栏,只保留右上角胶囊按钮 |
| backgroundColor | String | 窗口的背景色 | |
| backgroundTextStyle | String | dark | 下拉 loading 的样式,仅支持 dark / light |
| backgroundColorTop | String | #ffffff | 顶部窗口的背景色,仅 iOS 支持 |
| backgroundColorBottom | String | #ffffff | 底部窗口的背景色,仅 iOS 支持 |
| enablePullDownRefresh | boolean | false | 是否开启当前页面的下拉刷新。 |
| onReachBottomDistance | Number | 50 | 页面上拉触底事件触发时距页面底部距离,单位为 px |
| pageOrientation | String | portrait | 屏幕旋转设置,支持 auto / portrait / landscape 详见 响应显示区域变化 |
各端支持程度如下#
| 属性 | 微信 | 百度 | 字节跳动 | 支付宝 | H5 | RN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| navigationBarBackgroundColor | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| navigationBarTextStyle | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| navigationBarTitleText | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| navigationStyle | ✔️(微信客户端 6.6.0) | ✔️(百度 App 版本 11.1.0) | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| backgroundColor | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| backgroundTextStyle | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| backgroundColorTop | ✔️(微信客户端 6.5.16) | ✘ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| backgroundColorBottom | ✔️(微信客户端 6.5.16) | ✘ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| enablePullDownRefresh | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ |
| onReachBottomDistance | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| pageOrientation | ✔️ 2.4.0 (auto) / 2.5.0 (landscape) | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
app.config.js
export default {
pages: [
'pages/index/index',
'pages/logs/logs'
],
window: {
navigationBarBackgroundColor: '#ffffff',
navigationBarTextStyle: 'black',
navigationBarTitleText: '微信接口功能演示',
backgroundColor: '#eeeeee',
backgroundTextStyle: 'light'
}
}
tabBar
如果小程序是一个多 tab 应用(客户端窗口的底部或顶部有 tab 栏可以切换页面),可以通过 tabBar 配置项指定 tab 栏的表现,以及 tab 切换时显示的对应页面。
其配置项如下其配置项如下
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | HexColor(十六进制颜色值) | 是 | tab 上的文字默认颜色,仅支持十六进制颜色 | |
| selectedColor | HexColor(十六进制颜色值) | 是 | tab 上的文字选中时的颜色,仅支持十六进制颜色 | |
| backgroundColor | HexColor(十六进制颜色值) | 是 | tab 的背景色,仅支持十六进制颜色 | |
| borderStyle | String | 是 | black | tabbar 上边框的颜色, 仅支持 black / white |
| list | Array | 是 | tab 的列表,详见 list 属性说明,最少 2 个、最多 5 个 tab | |
| position | String | 否 | bottom | tabBar的位置,仅支持 bottom / top |
| custom | Boolean | 否 | false | 自定义 tabBar |
其中 list 接受一个数组,只能配置最少 2 个、最多 5 个 tab。tab 按数组的顺序排序,每个项都是一个对象,其属性值如下:
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pagePath | String | 是 | 页面路径,必须在 pages 中先定义 |
| text | String | 是 | tab 上按钮文字 |
| iconPath | String | 否 | 图片路径,icon 大小限制为40kb,建议尺寸为 81px * 81px,不支持网络图片。 当 position 为 top 时,不显示 icon。 |
| selectedIconPath | String | 否 | 选中时的图片路径,icon 大小限制为40kb,建议尺寸为 81px * 81px,不支持网络图片。 当 position 为 top 时,不显示 icon。 |
各端支持程度如下#
| 属性 | 微信 | 百度 | 字节跳动 | 支付宝 | H5 | RN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| color | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| selectedColor | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| backgroundColor | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| borderStyle | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| list | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| position | ✔️ | ✘ | ✔️ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| custom | ✔️(基础库 2.5.0 以上) | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
subPackages#
H5 和 RN 会把
subPackages合入pages
启用分包加载时,声明项目分包结构
小程序端特有属性#
只在部分小程序中支持的属性,H5、RN 均不支持。
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| networkTimeout | Object | 网络超时时间 |
| debug | Boolean | 是否开启 debug 模式,默认关闭 |
| permission | Object | 小程序接口权限相关设置 |
| requiredBackgroundModes | String Array | 需要在后台使用的能力,如「音乐播放」 |
| preloadRule | Object | 分包预下载规则 |
| entryPagePath | String | 小程序默认启动首页 |
| workers | String | Worker 代码放置的目录 |
| navigateToMiniProgramAppIdList | String Array | 需要跳转的小程序列表,详见 wx.navigateToMiniProgram |
networkTimeout#
各类网络请求的超时时间,单位均为毫秒。
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| request | Number | 否 | 60000 | Taro.request 的超时时间,单位:毫秒 |
| connectSocket | Number | 否 | 60000 | Taro.connectSocket 的超时时间,单位:毫秒 |
| uploadFile | Number | 否 | 60000 | Taro.uploadFile 的超时时间,单位:毫秒 |
| downloadFile | Number | 否 | 60000 | Taro.downloadFile 的超时时间,单位:毫秒 |
permission
小程序接口权限相关设置。字段类型为 Object,结构为:
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| scope.userLocation | PermissionObject | 否 | 位置相关权限声明 |
PermissionObject 结构:
| 属性 | 类型 | 必填 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| desc | string | 是 | 小程序获取权限时展示的接口用途说明。最长 30 个字符 |
app.config.js
export default {
pages: [
'pages/index/index',
'pages/logs/logs'
],
permission: {
'scope.userLocation': {
desc: '你的位置信息将用于小程序位置接口的效果展示'
}
}
}
requiredBackgroundModes
申明需要后台运行的能力,类型为数组。目前支持以下项目:
audio: 后台音乐播放location: 后台定位
app.config.js
export default {
"pages": ["pages/index/index"],
"requiredBackgroundModes": ["audio", "location"]
}
微信小程序特有属性
只在微信小程序中支持的属性。
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| functionalPages | Boolean | 是否启用插件功能页,默认关闭 |
| plugins | Object | 使用到的插件 |
| resizable | Boolean | iPad 小程序是否支持屏幕旋转,默认关闭 |
| usingComponents | Object | 全局自定义组件配置 |
| sitemapLocation | String | 指明 sitemap.json 的位置 |
| style | String | 指定使用升级后的weui样式 |
| useExtendedLib | Object | 指定需要引用的扩展库 |
| entranceDeclare | Object | 微信消息用小程序打开 |
| darkmode | boolean | 小程序支持 DarkMode |
| themeLocation | String | 指明 theme.json 的位置 |
| lazyCodeLoading | String | 配置自定义组件代码按需注入 |
| singlePage | Object | 单页模式相关配置 |
百度小程序特有属性
只在百度小程序中支持的属性。
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| routes | Array Object | 小程序自定义路由相关设置 |
| dynamicLib | Object | 引入动态库 |
export default {
"pages": [
"pages/home/home",
"pages/list/list",
"pages/detail/detail"
],
"subPackage": [
{
"root": "packageA",
"pages": [
"pages/home/home",
"pages/list/list",
"pages/detail/detail"
]
}
],
"routes": [
{
// 投放入口,scheme中的path
"path": "home",
// 真实的物理存储路径
"page": "pages/home/home"
},
{
"path": "list",
"page": "pages/list/list"
},
{
"path": "foo/bar",
"page": "pages/list/list"
}
]
}
QQ小程序特有属性
只在 QQ 小程序中支持的属性。
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| groupIdList | String Object | 需要打开群资料卡的群号列表 |
路由功能
Taro 遵循微信小程序的路由规范。只需要修改全局配置的 pages 属性,配置为 Taro 应用中每个页面的路径即可。
路由跳转
可以通过 Taro 提供的 API 来跳转到目的页面。路由 API 的详细用法请查看 API 文档的 导航 章节。
// 跳转到目的页面,打开新页面
Taro.navigateTo({
url: '/pages/page/path/name'
})
// 跳转到目的页面,在当前页面打开
Taro.redirectTo({
url: '/pages/page/path/name'
})
路由传参
可以通过在所有跳转的 url 后面添加查询字符串参数进行跳转传参,例如:
// 传入参数 id=2&type=test
Taro.navigateTo({
url: '/pages/page/path/name?id=2&type=test'
})
获取
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { View } from '@tarojs/components'
class Index extends Component {
// 建议在页面初始化时把 getCurrentInstance() 的结果保存下来供后面使用,
// 而不是频繁地调用此 API
$instance = getCurrentInstance()
componentDidMount () {
// 获取路由参数
console.log($instance.router.params) // 输出 { id: 2, type: 'test' }
}
render () {
return (
<View className='index' />
)
}
}
export default Index
Taro 案例分析
搭建redux环境
安装
npm install redux react-redux redux-thunk redux-logger
创建文件src/store/index.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from 'redux'
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk'
import rootReducer from '../reducers'
const composeEnhancers =
typeof window === 'object' &&
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ?
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({
// Specify extension’s options like name, actionsBlacklist, actionsCreators, serialize...
}) : compose
const middlewares = [
thunkMiddleware
]
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
middlewares.push(require('redux-logger').createLogger())
}
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(
applyMiddleware(...middlewares),
// other store enhancers if any
)
export default function configStore () {
const store = createStore(rootReducer, enhancer)
return store
}
创建src/reducers/index.js
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import home from './home'
export default combineReducers({
home,
})
创建src/reducers/home.js
import {
HOME_INFO, HOME_SEARCH_COUNT, HOME_RECOMMEND, HOME_PIN
} from '@constants/home'
const INITIAL_STATE = {
homeInfo: {},
searchCount: 0,
pin: [],
recommend: []
}
export default function home(state = INITIAL_STATE, action) {
switch(action.type) {
case HOME_INFO: {
return {
...state,
homeInfo: action.payload
}
}
case HOME_SEARCH_COUNT: {
return {
...state,
searchCount: action.payload.count
}
}
case HOME_PIN: {
// 每3个分成一组
const pin = []
action.payload.forEach((item, index) => {
const groupIndex = parseInt(index / 3)
if (!pin[groupIndex]) {
pin[groupIndex] = []
}
pin[groupIndex].push(item)
})
return { ...state, pin }
}
case HOME_RECOMMEND: {
return {
...state,
recommend: state.recommend.concat(action.payload.rcmdItemList)
}
}
default:
return state
}
}
创建src/constants/home.js
export const HOME_INFO = 'HOME_INFO'
export const HOME_SEARCH_COUNT = 'HOME_SEARCH_COUNT'
export const HOME_PIN = 'HOME_PIN'
export const HOME_RECOMMEND = 'HOME_RECOMMEND'
修改src/app.js
import { Component } from 'react'
import './app.scss'
import {Provider} from "react-redux";
import configStore from './store'
const store = configStore()
class App extends Component {
componentDidMount () {}
componentDidShow () {}
componentDidHide () {}
componentDidCatchError () {}
// this.props.children 是将要会渲染的页面
render () {
return (
{this.props.children}
)
// return this.props.children
}
}
export default App
举个简单的例子
首先创建src/constants/test.js
test.js
export const type = {
INCREMENT: 'INCREMENT',
DECREMENT: 'DECREMENT'
}
创建action
import {type} from "../constants/test";
export function add(){
return {
type: type.INCREMENT
}
}
export function remove(){
return {
type: type.DECREMENT
}
}
创建reducer
import {type} from '../constants/test'
const test = (state={count: 0}, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case type.INCREMENT:
return {...state,count: state.count + 1}
case type.DECREMENT:
return {...state,count: state.count - 1}
default:
return state;
}
}
export default test;
import { combineReducers } from 'redux'
import test from './test'
export default combineReducers({
test
})
页面中进行测试
import React,{Component} from 'react';
import {Button, View} from "@tarojs/components";
import {connect} from "react-redux";
import * as actions from "../../../../actions/test";
@connect(state => state.test, {...actions})
class Test extends Component{
state = {
count: 0
}
handleAdd = () => {
this.props.add()
}
handleRemove = () => {
this.props.remove()
}
render(){
const { count } = this.props
return (
<View>
{count}
<Button onClick={this.handleAdd}>+</Button>
<Button onClick={this.handleRemove}>-</Button>
</View>
)
}
}
export default Test;
搭建基于redux环境的接口请求
创建src/actions/home.js
import {
HOME_INFO, HOME_SEARCH_COUNT, HOME_RECOMMEND, HOME_PIN
} from '@constants/home'
import {
API_HOME, API_HOME_SEARCH_COUNT, API_HOME_RECOMMEND, API_HOME_PIN
} from '@constants/api'
import { createAction } from '@utils/redux'
/**
* 首页数据
* @param {*} payload
*/
export const dispatchHome = payload => createAction({
url: API_HOME,
type: HOME_INFO,
payload
})
/**
* 商品总数
* @param {*} payload
*/
export const dispatchSearchCount = payload => createAction({
url: API_HOME_SEARCH_COUNT,
type: HOME_SEARCH_COUNT,
payload
})
/**
* 拼团
* @param {*} payload
*/
export const dispatchPin = payload => createAction({
url: API_HOME_PIN,
type: HOME_PIN,
payload
})
/**
* 推荐商品
* @param {*} payload
*/
export const dispatchRecommend = payload => createAction({
url: API_HOME_RECOMMEND,
type: HOME_RECOMMEND,
payload
})
创建src/constants/api.js
/**
* NOTE HOST、HOST_M 是在 config 中通过 defineConstants 配置的
* 只所以不在代码中直接引用,是因为 eslint 会报 no-undef 的错误,因此用如下方式处理
*/
/* eslint-disable */
export const host = HOST
export const hostM = HOST_M
/* eslint-enable */
// pic
export const CDN = 'https://yanxuan.nosdn.127.net'
// home
export const API_HOME = `${host}/xhr/index/index.json`
export const API_HOME_SEARCH_COUNT = `${host}/xhr/search/displayBar.json`
export const API_HOME_PIN = `${hostM}/pin/min/item/recommend.json`
export const API_HOME_RECOMMEND = `${host}/xhr/rcmd/index.json`
创建src/utils/redux.js
/**
* 适当封装 Redux,简化调用
*/
/* eslint-disable import/prefer-default-export */
import fetch from './request'
export function createAction(options) {
const { url, payload, method, fetchOptions, cb, type } = options
return (dispatch) => {
return fetch({ url, payload, method, ...fetchOptions }).then((res) => {
dispatch({ type, payload: cb ? cb(res) : res })
return res
})
}
}
创建src/utils/request.js
import Taro from '@tarojs/taro'
import { API_USER, API_USER_LOGIN } from '@constants/api'
const CODE_SUCCESS = '200'
const CODE_AUTH_EXPIRED = '600'
function getStorage(key) {
return Taro.getStorage({ key }).then(res => res.data).catch(() => '')
}
function updateStorage(data = {}) {
return Promise.all([
Taro.setStorage({ key: 'token', data: data['3rdSession'] || '' }),
Taro.setStorage({ key: 'uid', data: data['uid'] || ''})
])
}
/**
* 简易封装网络请求
* // NOTE 需要注意 RN 不支持 *StorageSync,此处用 async/await 解决
* @param {*} options
*/
export default async function fetch(options) {
const { url, payload, method = 'GET', showToast = true, autoLogin = true } = options
const token = await getStorage('token')
const header = token ? { 'WX-PIN-SESSION': token, 'X-WX-3RD-Session': token } : {}
if (method === 'POST') {
header['content-type'] = 'application/json'
}
return Taro.request({
url,
method,
data: payload,
header
}).then(async (res) => {
const { code, data } = res.data
if (code !== CODE_SUCCESS) {
if (code === CODE_AUTH_EXPIRED) {
await updateStorage({})
}
return Promise.reject(res.data)
}
if (url === API_USER_LOGIN) {
await updateStorage(data)
}
// XXX 用户信息需展示 uid,但是 uid 是登录接口就返回的,比较蛋疼,暂时糅合在 fetch 中解决
if (url === API_USER) {
const uid = await getStorage('uid')
return { ...data, uid }
}
return data
}).catch((err) => {
const defaultMsg = err.code === CODE_AUTH_EXPIRED ? '登录失效' : '请求异常'
if (showToast) {
Taro.showToast({
title: err && err.errorMsg || defaultMsg,
icon: 'none'
})
}
if (err.code === CODE_AUTH_EXPIRED && autoLogin) {
Taro.navigateTo({
url: '/pages/user-login/user-login'
})
}
return Promise.reject({ message: defaultMsg, ...err })
})
}
首先在页面中引入action
import * as actions from '@actions/home'
同时引入connect
import {connect} from "react-redux"
使用注解方式进行使用
@connect(state => state.home, { ...actions })
调用方法
this.props.dispatchHome().then(() => {
this.setState({ loaded: true })
})
Redux基础知识
1 Redux 是什么
- redux是的诞生是为了给 React 应用提供「可预测化的状态管理」机制。
- Redux会将整个应用状态(其实也就是数据)存储到到一个地方,称为store
- 这个store里面保存一棵状态树(state tree)
- 组件改变state的唯一方法是通过调用store的dispatch(派遣)方法,触发一个action,这个action被对应的reducer处理,于是state完成更新
- 组件可以派发(dispatch)行为(action)给store,而不是直接通知其它组件
- 其它组件可以通过订阅store中的状态(state)来刷新自己的视图
- Redux 专注于状态管理,和react解耦
- 单一状态,单项数据流
- 核心概念:store, state, action, reducer
原理图
创建reducer
- 可以使用单独的一个reducer,也可以将多个reducer合并为一个reducer,即:
combineReducers() - action发出命令后将state放入reucer加工函数中,返回新的state,对state进行加工处理
创建action
- 用户是接触不到state的,只能有view触发,所以,这个action可以理解为指令,需要发出多少动作就有多少指令
- action是一个对象,必须有一个叫type的参数,定义action类型
创建的store,使用createStore方法
- store 可以理解为有多个加工机器的总工厂
- 提供subscribe,dispatch,getState这些方法。
举例:
赵政委的主要功能
- 老赵有一个保险箱(store),所有人的状态,在那里都有记录(state)
- 需要改变的时候,需要告诉专员(dispatch)要干什么(action)
- 处理变化的人(reducer)拿到state和action,生成新的state
走马上任
- 首先通过reducer新建store,随时通过store.getState获取状态
- 需要状态变更,store.dispatch(action)来修改状态
- Reducer函数接受state和action,返回新的state,可以用store.subscribe监听每次的修改
官方案例:
import { createStore } from 'redux';
/**
* 这是一个 reducer,形式为 (state, action) => state 的纯函数。
* 描述了 action 如何把 state 转变成下一个 state。
*
* state 的形式取决于你,可以是基本类型、数组、对象、
* 甚至是 Immutable.js 生成的数据结构。惟一的要点是
* 当 state 变化时需要返回全新的对象,而不是修改传入的参数。
*
* 下面例子使用 `switch` 语句和字符串来做判断,但你可以写帮助类(helper)
* 根据不同的约定(如方法映射)来判断,只要适用你的项目即可。
*/
function counter(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + 1;
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - 1;
default:
return state;
}
}
// 创建 Redux store 来存放应用的状态。
// API 是 { subscribe, dispatch, getState }。
let store = createStore(counter);
// 可以手动订阅更新,也可以事件绑定到视图层。
store.subscribe(() =>
console.log(store.getState())
);
// 改变内部 state 惟一方法是 dispatch 一个 action。
// action 可以被序列化,用日记记录和储存下来,后期还可以以回放的方式执行
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
// 1
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
// 2
store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' });
// 1
2 Redux如何和React一起使用
手动连接,老赵怎么管理独立团呢
- 把store.dispatch 方法传递给组件,内部可以调用修改状态
- Subscribe订阅render函数,每次修改都重新渲染
- Redux相关内容,移到单独的文件index.redux.js单独管理
在src目录下分别redux/action/ redux/reducer/ redux/store/
在 action 目录下新建 index.js
/**
* Action类型:用户事件操作
* @type {{INCREMENT: string, DECREMENT: string}}
*/
export const type = {
INCREMENT: 'INCREMENT',
DECREMENT: 'DECREMENT'
}
export function add(){
return {
type: type.INCREMENT
}
}
export function remove(){
return {
type: type.DECREMENT
}
}
在 reducer 目录下新建 index.js
/*
* Reducer: 数据处理
*/
import { type } from "./../action";
const counter = (state=0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case type.INCREMENT:
return state + 1
case type.DECREMENT:
return state - 1
default:
return state;
}
}
export default counter;
在 store 目录下新建 index.js
/*
* 引入createStore 保存数据源
*/
import { createStore } from "redux";
// 引入所有的reducer
import reducer from "./../reducer";
export default ()=>createStore(reducer)
修改src根目录下的index.js
import configureStore from './redux/store/index';
const store = configureStore();
function render(){
ReactDOM.render(<App store={store}/>, document.getElementById('root'));
}
render()
store.subscribe(render)
修改App.js 文件
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import {Button, Flex, WingBlank} from 'antd-mobile';
import {add, remove} from './redux/action'
class App extends React.Component{
state = {
count: 0
}
static defaultProps = {
num: 1
}
add = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count+1
})
}
remove = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count-1
})
}
render(){
const store = this.props.store
const num = store.getState()
return (
{this.state.count}
{num}
);
}
}
export default App;
3 处理异步、调试工具、更优雅的和React结合
- Redux处理异步,需要redux-thunk插件
- Npm install redux-devtools-extension并且开启
- 使用react-redux优雅的链接react和redux
处理异步
Redux 默认只处理同步,异步任务需要react-thunk中间件
- 安装及使用redux-thunk插件
- yarn add redux-thunk --save
- 使用applyMiddleware开启thunk中间件
- Action可以返回函数,使用dispatch提交action
示例:
修改 src/redux/store/index.js
/*
* 引入createStore 保存数据源
*/
import {createStore, applyMiddleware} from "redux";
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
// 引入所有的reducer
import counter from "./../reducer";
export default () => createStore(counter, applyMiddleware(thunk))
同时在 src/redux/action/index.js 代码中新增
export function addAsync() {
return dispatch => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(add())
}, 2000)
}
}
在 App.js 代码中新增
import {add, remove, addAsync} from './redux/action'
4 调试工具
Chrome 搜索 redux 安装
- 新建store的时候判断window.devToolsExtension
- 使用compose结合thunk和window.devToolsExtension
- 调试窗口的redux选项卡,实时看到state
5 使用react-redux
- npm install react-redux --save
- 忘记subscribe,记住reducer, action 和 dispatch即可
- React-redux提供Provider和connect俩个接口来链接
React-redux 具体使用
- Provider 组件在应用最外层,传入store即可,只用一次
- Connect 负责从外部获取组件需要的参数
- Connect 可以用装饰器的方式来写
示例:
修改 src/index.js 添加项目根组件
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import configureStore from './redux/store/index';
import { Provider } from "react-redux"; // 添加, document.getElementById('root'));
}
render()
store.subscribe(render)*/
ReactDOM.render(
(
),
document.getElementById('root')
);
// If you want your app to work offline and load faster, you can change
// unregister() to register() below. Note this comes with some pitfalls.
// Learn more about service workers: https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA
serviceWorker.unregister();
修改 src/App.js 文件 引入 react-redux connect
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {Button, Flex, WingBlank} from 'antd-mobile';
import {add, remove, addAsync} from './redux/action'
class App extends React.Component{
state = {
count: 0
}
static defaultProps = {
num: 1
}
add = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count+1
})
}
remove = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count-1
})
}
render(){
/*const store = this.props.store
const num = store.getState()*/
const num = this.props.num;
const addAsync = this.props.addAsync;
const remove = this.props.remove;
return (
{this.state.count}
{/*
{num}
*/}
{num}
);
}
}
//将state.num 绑定到 props 的num
const mapStateToProps = state => {
console.log(state);
return {
num: state
};
};
const actionCreators = {add, remove, addAsync}
export default connect(mapStateToProps,actionCreators)(App);
其中的代码修改处
/*const store = this.props.store
const num = store.getState()*/
const num = this.props.num;
const addAsync = this.props.addAsync;
const remove = this.props.remove;
{/*
{num}
*/}
{num}
最后将state.num 绑定到 props 的num
//将state.num 绑定到 props 的num
const mapStateToProps = state => {
console.log(state);
return {
num: state
};
};
const actionCreators = {add, remove, addAsync}
export default connect(mapStateToProps,actionCreators)(App);
6 使用装饰器优化connect代码
- Npm run eject 弹出个性化配置
- Npm install babel-plugin-transform-decorators-legacy插件
- package.json 里 babel加上plugins配置
yarn add babel-plugin-transform-decorators-legacy --save-dev
babel-plugin-transform-decorators-legacy
进而可以使用注解的方式
示例:
安装plugins
{
"plugins": [
["@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators", { "legacy": true }],
[
"import",
{
"libraryName": "antd-mobile",
"style": "css"
}
]
]
}
修改 src/App.js 代码
import React from 'react';
import './App.css';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
import {Button, Flex, WingBlank} from 'antd-mobile';
import {add, remove, addAsync} from './redux/action'
//将state.num 绑定到 props 的num
/*const mapStateToProps = state => {
console.log(state);
return {
num: state
};
};
const actionCreators = {add, remove, addAsync}
@connect(
mapStateToProps,actionCreators
)*/
@connect(
state=>({num: state}),
{add, remove, addAsync}
)
class App extends React.Component{
state = {
count: 0
}
static defaultProps = {
num: 1
}
add = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count+1
})
}
remove = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count-1
})
}
render(){
/*const store = this.props.store
const num = store.getState()*/
const num = this.props.num;
const addAsync = this.props.addAsync;
const remove = this.props.remove;
return (
{this.state.count}
{/*
{num}
*/}
{num}
);
}
}
// export default connect(mapStateToProps,actionCreators)(App);
export default App;
taro + taro-ui + dva
我们引入dva
npm i dva-core dva-loading --save
新建dva.js
import { create } from 'dva-core';
import { createLogger } from 'redux-logger';
import createLoading from 'dva-loading';
let app;
let store;
let dispatch;
function createApp(opt) {
// redux日志
// opt.onAction = [createLogger()];
app = create(opt);
app.use(createLoading({}));
if (!global.registered) opt.models.forEach(model => app.model(model));
global.registered = true;
app.start();
store = app._store;
app.getStore = () => store;
dispatch = store.dispatch;
app.dispatch = dispatch;
return app;
}
export default {
createApp,
getDispatch() {
return app.dispatch;
}
}
并在入口文件导入
import dva from './utils/dva'
const dvaApp = dva.createApp({
initialState: {},
models: models,
});
const store = dvaApp.getStore();
封装下request网络请求
import Taro from '@tarojs/taro';
import { baseUrl, noConsole } from '../config';
export default (options = { method: 'GET', data: {} }) => {
if (!noConsole) {
console.log(`${new Date().toLocaleString()}【 M=${options.url} 】P=${JSON.stringify(options.data)}`);
}
return Taro.request({
url: baseUrl + options.url,
data: options.data,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
method: options.method.toUpperCase(),
}).then((res) => {
const { statusCode, data } = res;
if (statusCode >= 200 && statusCode < 300) {
if (!noConsole) {
console.log(`${new Date().toLocaleString()}【 M=${options.url} 】【接口响应:】`,res.data);
}
if (data.status !== 'ok') {
Taro.showToast({
title: `${res.data.error.message}~` || res.data.error.code,
icon: 'none',
mask: true,
});
}
return data;
} else {
throw new Error(`网络请求错误,状态码${statusCode}`);
}
})
}