python合并多个dict---合并多个字典值---字典值相加
文章目录
- 序
- 多个dict同key值相加
-
- collection.Counter
- 传参
- 重载+号
- 多个dict合并
- 练习
序
主要是借助Counter、函数传参和+运算符重载!各有优劣!
多个dict同key值相加
collection.Counter
借助collections.Counter,但是它只适用于值为整数或者小数类型**,否则报错!**
from collections import Counter
a = {"1":2}
b = {"1":30}
print(dict(Counter(a)+Counter(b)))
a = {"1":2.0}
b = {"1":30.5}
print(dict(Counter(a)+Counter(b)))
传参
借助函数传参,但是不能同key相加。如下:
a = {"1":2}
b = {"2":3}
def merge_dicts(**kwargs):
return kwargs
merge_dicts(**a, **b)
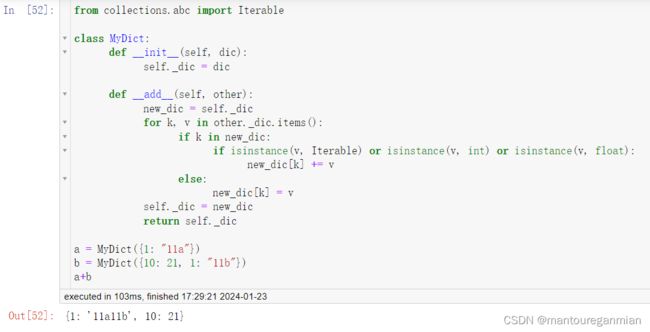
重载+号
写代码多。
from collections.abc import Iterable
class MyDict:
def __init__(self, dic):
self._dic = dic
def __add__(self, other):
new_dic = self._dic
for k, v in other._dic.items():
if k in new_dic:
if isinstance(v, Iterable) or isinstance(v, int) or isinstance(v, float):
new_dic[k] += v
else:
new_dic[k] = v
self._dic = new_dic
return self._dic
a = MyDict({1: "11a"})
b = MyDict({10: 21, 1: "11b"})
a+b
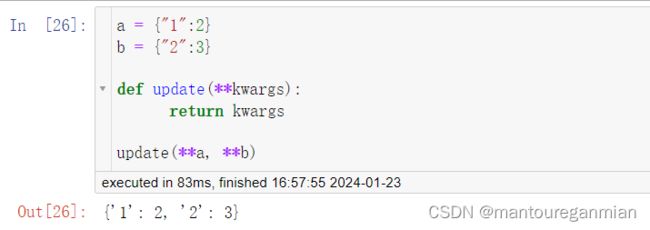
多个dict合并
两种方法
# 方法一, 借助函数传参
a = {"1":2}
b = {"2":3}
def update(**kwargs):
return kwargs
update(**a, **b)
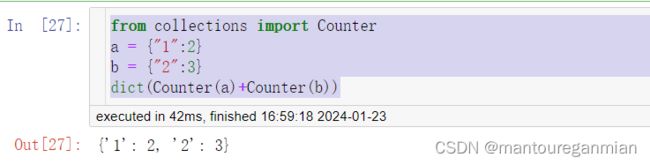
# 方法二
from collections import Counter
a = {"1":2}
b = {"2":3}
dict(Counter(a)+Counter(b))
练习
请您对以上三种方法的弊端进行复现。