4.1 -Springboot 编写http接口
Springboot 编写http接口
回到第一章:目录
文章目录
- Springboot 编写http接口
- 前言
- 新建一个springboot工程
- 一、前后台不分离模式,get和post请求接口的编写方法。
- 二、无前台,仅后台系统间交互的get和post请求接口编写方法
- 三、前后台分离,restful风格的http接口编写方法
- 四 、使用postman测试以上接口
-
- **1、前后台不分离**
- 2、仅有后台的http接口
- 3、restful风格接口
前言
基于 springboot 框架,快速的编写http接口。
1、前后台不分离模式,get和post请求接口的编写方法。
2、无前台,仅后台系统间交互的get和post请求接口编写方法。
3、前后台分离,restful风格的http接口编写方法
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
新建一个springboot工程
1、在resources目录下创建配置文件:
application.yml
server:
port: 9001
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.119.1:3306/devops_play?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
username: root
password: MySql@0004
thymeleaf:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
check-template-location: true
suffix: .html
encoding: UTF-8
content-type: text/html
mode: HTML5
cache: false
devtools:
restart:
enabled: true
2、pom文件增加
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.10.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
MainApp.java
package com;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan("com.controller")
@EntityScan("com.entity")
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApp.class, args);
}
}
User.java
package com.entity;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;
public class User {
/**id 自增主键*/
private Long id;
private String userName;
/**用户姓名*/
private String realName;
/**用户登录密码*/
private String password;
/**用户性别:1-男;2=女*/
private int sex;
/**用户邮箱*/
private String email;
/**手机号*/
private String mobile;
/**创建时间*/
private Date createDate;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", userName='" + userName + '\'' +
", realName='" + realName + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", mobile='" + mobile + '\'' +
", createDate=" + createDate +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return sex == user.sex && Objects.equals(userName, user.userName) && Objects.equals(realName, user.realName) && Objects.equals(password, user.password) && Objects.equals(email, user.email) && Objects.equals(mobile, user.mobile);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(userName, realName, password, sex, email, mobile);
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getRealName() {
return realName;
}
public void setRealName(String realName) {
this.realName = realName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(int sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
}
一、前后台不分离模式,get和post请求接口的编写方法。
1、 编写 html页面和样式文件css
新建index.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>用户管理演示title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/css/my.css">
head>
<body>
<div id="main-container" >
<div id="div-header" >
<h3 style="margin-bottom:0;">用户管理h3>
hr>
div>
<div id="div-content" >
br>
<hr>
<button class="buttonUser" id="addUserButton" onclick="addUser()">添加用户button><br/><br/>
<button class="buttonUser" id="searchUserButton" onclick="searchUser()">查询用户button> <br/><br/>
<button class="buttonUser" id="delUserButton" onclick="delUser()">删除用户button>
<br><br><br><br>
<p>当前版本V1.0p>
div>
div>
<script type="text/javascript">
//点击按钮跳转到登录页面
function addUser()
{
alert("你点击了添加用户按钮。");
}
function searchUser()
{
alert("你点击了查询用户按钮。");
}
function delUser()
{
alert("你点击了删除用户按钮。");
}
script>
body>
html>
新建样式文件my.css
/*所有的 p 标签的样式*/
p {
color:black;
}
/**最外层区域的样式*/
#main-container
{
position:absolute;/**采用绝对布局*/
width:100%;/**宽度填满浏览器*/
height:100%;/**高度填满浏览器*/
background-color:#D0D0D0/**设置背景色为灰色*/
}
/** 头部 区域的样式*/
#div-header
{
text-align:center;/** 区域元素居中显示*/
color:red;/** 设置字体颜色为红色 */
position:relative;/**采用相对布局*/
height:80px;/** 高度 80像素*/
width:800px; /** 宽度 800像素*/
margin-left:50px; /** 距离左边的边距 50像素*/
}
/** 内容 区域的样式*/
#div-content
{
text-align:center;/** 该div区域的所有文本居中显示*/
position:absolute;/**采用相对布局*/
background-color:#D0D0D9; /**设置背景色为灰色*/
height:600px;/** 高度 600像素*/
width:800px;/** 宽度 800像素*/
border:2px dashed; /** 边框的像素 2, dashed 含义为 虚线框*/
border-color:gray; /** 边框颜色为灰色*/
box-shadow: 2px 2px 5px #D0D0D9; /** 边框阴影效果*/
margin-top:20px; /** 上边距20 像素*/
margin-bottom:10px; /** 下边距10 像素*/
margin-right:50px; /** 右边距50 像素*/
margin-left:50px; /** 左边距50 像素*/
border-radius:25px; /** 边框的圆角像素 25像素*/
}
2、新建UserController对象,编写http接口
package com.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Controller 表明这个是controller,提供http访问能力。
* @RequestMapping("/") 表示要访问这个controller类里的方法的根路径,
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/")
public class UserController {
/**
* GET POST 请求均可以接收到;
* 返回的是一个 index.html页面
* 传入的参数name,可以在 url地址后面,也可以在body里
* @RequestMapping("/index") 和 类名上的 @RequestMapping("/") 拼接起来,访问路劲为 /index
* RequestMapping 支持http所有的请求方式,如get,post,put,delete等
* @param name
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(String name) {
System.out.println("/index 接受到的参数为:" + name);
return "index.html";
}
/**
* 仅支持 GET 请求方式
* 返回的是一个 index.html页面
* 传入的参数name,可以在 url地址后面,也可以在body里
* GetMapping 只支持get类请求
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/getIndex")
public String index2(String name) {
System.out.println("/getIndex 接受到的参数为:" + name);
return "index.html";
}
/**
* 仅支持 POST 请求方式
* 返回的是一个 index.html页面
* 传入的参数name,可以在 url地址后面,也可以在body里 form-data x-www-form-urlencoded 格式均可
PostMapping 只支持 post 类请求
* @param name
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/postIndex")
public String index3(String name) {
System.out.println("/postIndex 接受到的参数为:" + name);
return "index.html";
}
/**
* 仅支持 POST 请求方式
* 返回的是一个 index.html页面
* 传入的参数name,必须在请求的body里,x-www-form-urlencoded 格式或json格式
* @param name
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/postIndex2")
public String index4(@RequestBody String name) {
System.out.println("/postIndex 接受到的参数为:" + name);
return "index.html";
}
}
二、无前台,仅后台系统间交互的get和post请求接口编写方法
1、编写UserController2对象,内容为:
package com.controller;
import com.entity.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* RestController 注解,表示这是一个restful风格的http接口对象。
* 返回的内容为字符串,而不是一个html页面的名字。
* 返回的字符串,可以是数字,任意格式字符。比如json格式,xml格式,及其他自定义格式等。
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController2 {
/** 新增用户 接口
* 请求路径:/user/addJson
* 请求方法:post
* 参数:User对象的json格式,如:
* {"userName":"zhc2","realName":"xxt","password":"123456","sex":"1","email":"[email protected]","mobile":"19524585455","createDate":"Sat Jan 23 16:26:01 CST 2021"}
RequestBody 表示这个post请求,必须有请求体。
* */
@PostMapping("/addJson")
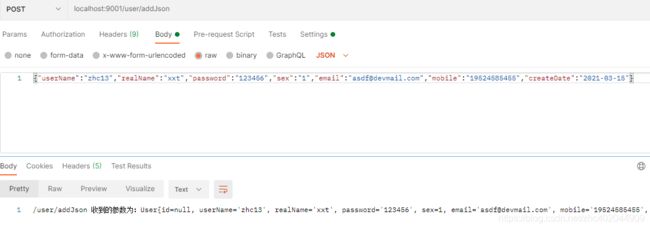
public String addUser(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("/user/addJson 收到的参数为:"+user.toString());
return "/user/addJson 收到的参数为:"+user.toString();
}
/** 新增用户 接口
* 请求路径:/user/addForm
* 请求方法:post
* 参数:User对象参数所需要的key-value的格式,如:
* userName=zhc2
* realName=xxt
* password=123456
* sex=1
* [email protected]
* mobile=19524585455
* createDate=Sat Jan 23 16:26:01 CST 2021
* */
@PostMapping("/addForm")
public String addUser2(User user){
System.out.println("/user/addForm 收到的参数为:"+user.toString());
return "/user/addForm 收到的参数为:"+user.toString();
}
/** 新增用户 接口
* 请求路径:/user/addGet?userName=zhc2&realName=xxt&password=123456&sex=1&email=asdf@devmail.com&mobile=19524585455&createDate=Sat Jan 23 16:26:01 CST 2021
* 请求方法:get
* */
@GetMapping("/addGet")
public String addUser3(User user){
System.out.println("/user/addForm 收到的参数为:"+user.toString());
return "/user/addForm 收到的参数为:"+user.toString();
}
/**根据id查询用户*/
@GetMapping("/get")
public String getUser(Long id){
System.out.println("/user/get 收到的参数为:"+id);
return "/user/get 收到的参数为:"+id;
}
}
三、前后台分离,restful风格的http接口编写方法
restful风格 一般要求请求和返回必须用json格式字符进行交互,但不是必须的。
1、新增RestFulController对象,内容为:
package com.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* Restful风格 规范了http请求的方式,这是一种约定的写法,最明显就是:
* 新增用put请求方式
* 删除用delete请求方式
* 修改用post请求方式
* 查询用get请求方式
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class RestFulController {
/**
* 增
* @param name
* @return
*/
@PutMapping("/add")
public String add(String name){
System.out.println("add 请求参数为:"+name);
return "add 请求参数为:"+name;
}
/**
* 删
* @param name
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping("/del")
public String del(String name){
System.out.println("del 请求参数为:"+name);
return "del 请求参数为:"+name;
}
/**
* 改
* @param name
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/update")
public String update(String name){
System.out.println("del 请求参数为:"+name);
return "del 请求参数为:"+name;
}
/**
* 查
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
public String list(String name){
System.out.println("list 请求参数为:"+name);
return "list 请求参数为:"+name;
}
/**
* 查 1 个
* {id} 配合 @PathVariable 是路径参数的写法,大多用来根据id查询某个数据
* 访问路径如 :/list/1 ,/list/2 等,
* @param id
* @return
*/
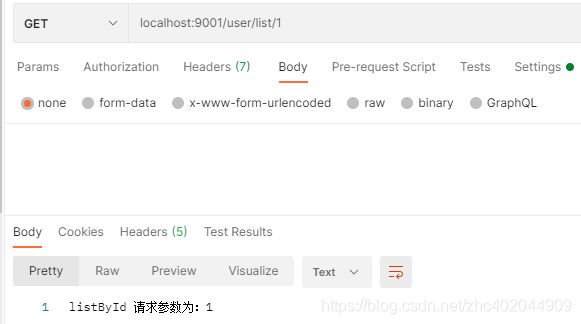
@GetMapping("/list/{id}")
public String listById(@PathVariable Long id){
System.out.println("listById 请求参数为:"+id);
return "listById 请求参数为:"+id;
}
}
四 、使用postman测试以上接口
1、前后台不分离
请求方式get
参数可以填在url后面
也可以填在form-data里