混淆矩阵、准确率、查准率、查全率、DSC、IoU、敏感度的计算
1.背景介绍
在训练的模型的时候,需要评价模型的好坏,就涉及到混淆矩阵、准确率、查准率、查全率、DSC、IoU、敏感度的计算。
2、混淆矩阵的概念
所谓的混淆矩阵如下表所示:
TP:真正类,真的正例被预测为正例
FN:假负类,样本为正例,被预测为负类
FP:假正类 ,原本实际为负,但是被预测为正例
TN:真负类,真的负样本被预测为负类。
从混淆矩阵当中,可以得到更高级的分类指标:Accuracy(准确率),Precision(查准率),Recall(查全率),Specificity(特异性),Sensitivity(灵敏度)。
3. 常用的分类指标
3.1 Accuracy(准确率)
不管是哪个类别,只要预测正确,其数量都放在分子上,而分母是全部数据量。常用于表示模型的精度,当数据类别不平衡时,不能用于模型的评价。
![]()
3.2 Precision(查准率)
即所有预测为正的样本中,预测正确的样本的所占的比重。
![]()
3.3 Recall(查全率)
真实的为正的样本,被正确检测出来的比重。
![]()
3.4 Specificity(特异性)
特异性指标,也称 负正类率(False Positive Rate, FPR),计算的是模型错识别为正类的负类样本占所有负类样本的比例,一般越低越好。
![]()
3.5 DSC(Dice coefficient)
Dice系数,是一种相似性度量,度量二进制图像分割的准确性。
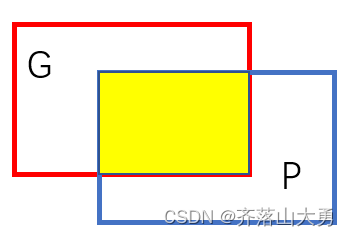
如图所示红色的框的区域时Groudtruth,而蓝色的框为预测值Prediction。
![]()
3.6 IoU(交并比)
![]()
3.7 Sensitivity(灵敏度)
反应的时预测正确的区域在Groundtruth中所占的比重。
![]()
4. 计算程序
ConfusionMatrix 这个类可以直接计算出混淆矩阵
from collections import defaultdict, deque
import datetime
import time
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.distributed as dist
import errno
import os
class SmoothedValue(object):
"""Track a series of values and provide access to smoothed values over a
window or the global series average.
"""
def __init__(self, window_size=20, fmt=None):
if fmt is None:
fmt = "{value:.4f} ({global_avg:.4f})"
self.deque = deque(maxlen=window_size)
self.total = 0.0
self.count = 0
self.fmt = fmt
def update(self, value, n=1):
self.deque.append(value)
self.count += n
self.total += value * n
def synchronize_between_processes(self):
"""
Warning: does not synchronize the deque!
"""
if not is_dist_avail_and_initialized():
return
t = torch.tensor([self.count, self.total], dtype=torch.float64, device='cuda')
dist.barrier()
dist.all_reduce(t)
t = t.tolist()
self.count = int(t[0])
self.total = t[1]
@property
def median(self):
d = torch.tensor(list(self.deque))
return d.median().item()
@property
def avg(self):
d = torch.tensor(list(self.deque), dtype=torch.float32)
return d.mean().item()
@property
def global_avg(self):
return self.total / self.count
@property
def max(self):
return max(self.deque)
@property
def value(self):
return self.deque[-1]
def __str__(self):
return self.fmt.format(
median=self.median,
avg=self.avg,
global_avg=self.global_avg,
max=self.max,
value=self.value)
class ConfusionMatrix(object):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.mat = None
def update(self, a, b):
n = self.num_classes
if self.mat is None:
# 创建混淆矩阵
self.mat = torch.zeros((n, n), dtype=torch.int64, device=a.device)
with torch.no_grad():
# 寻找GT中为目标的像素索引
k = (a >= 0) & (a < n)
# 统计像素真实类别a[k]被预测成类别b[k]的个数(这里的做法很巧妙)
inds = n * a[k].to(torch.int64) + b[k]
self.mat += torch.bincount(inds, minlength=n**2).reshape(n, n)
def reset(self):
if self.mat is not None:
self.mat.zero_()
def compute(self):
h = self.mat.float()
# 计算全局预测准确率(混淆矩阵的对角线为预测正确的个数)
acc_global = torch.diag(h).sum() / h.sum()
# 计算每个类别的准确率
acc = torch.diag(h) / h.sum(1)
# 计算每个类别预测与真实目标的iou
iu = torch.diag(h) / (h.sum(1) + h.sum(0) - torch.diag(h))
return acc_global, acc, iu
def reduce_from_all_processes(self):
if not torch.distributed.is_available():
return
if not torch.distributed.is_initialized():
return
torch.distributed.barrier()
torch.distributed.all_reduce(self.mat)
def __str__(self):
acc_global, acc, iu = self.compute()
return (
'global correct: {:.1f}\n'
'average row correct: {}\n'
'IoU: {}\n'
'mean IoU: {:.1f}').format(
acc_global.item() * 100,
['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (acc * 100).tolist()],
['{:.1f}'.format(i) for i in (iu * 100).tolist()],
iu.mean().item() * 100)
class DiceCoefficient(object):
def __init__(self, num_classes: int = 2, ignore_index: int = -100):
self.cumulative_dice = None
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.ignore_index = ignore_index
self.count = None
def update(self, pred, target):
if self.cumulative_dice is None:
self.cumulative_dice = torch.zeros(1, dtype=pred.dtype, device=pred.device)
if self.count is None:
self.count = torch.zeros(1, dtype=pred.dtype, device=pred.device)
# compute the Dice score, ignoring background
pred = F.one_hot(pred.argmax(dim=1), self.num_classes).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).float()
dice_target = build_target(target, self.num_classes, self.ignore_index)
self.cumulative_dice += multiclass_dice_coeff(pred[:, 1:], dice_target[:, 1:], ignore_index=self.ignore_index)
self.count += 1
@property
def value(self):
if self.count == 0:
return 0
else:
return self.cumulative_dice / self.count
def reset(self):
if self.cumulative_dice is not None:
self.cumulative_dice.zero_()
if self.count is not None:
self.count.zeros_()
def reduce_from_all_processes(self):
if not torch.distributed.is_available():
return
if not torch.distributed.is_initialized():
return
torch.distributed.barrier()
torch.distributed.all_reduce(self.cumulative_dice)
torch.distributed.all_reduce(self.count)
分类指标的计算
import torch
# SR : Segmentation Result
# GT : Ground Truth
def get_accuracy(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
corr = torch.sum(SR==GT)
tensor_size = SR.size(0)*SR.size(1)*SR.size(2)*SR.size(3)
acc = float(corr)/float(tensor_size)
return acc
def get_sensitivity(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
# Sensitivity == Recall
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
# TP : True Positive
# FN : False Negative
TP = ((SR==1)+(GT==1))==2
FN = ((SR==0)+(GT==1))==2
SE = float(torch.sum(TP))/(float(torch.sum(TP+FN)) + 1e-6)
return SE
def get_specificity(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
# TN : True Negative
# FP : False Positive
TN = ((SR==0)+(GT==0))==2
FP = ((SR==1)+(GT==0))==2
SP = float(torch.sum(TN))/(float(torch.sum(TN+FP)) + 1e-6)
return SP
def get_precision(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
# TP : True Positive
# FP : False Positive
TP = ((SR==1)+(GT==1))==2
FP = ((SR==1)+(GT==0))==2
PC = float(torch.sum(TP))/(float(torch.sum(TP+FP)) + 1e-6)
return PC
def get_F1(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
# Sensitivity == Recall
SE = get_sensitivity(SR,GT,threshold=threshold)
PC = get_precision(SR,GT,threshold=threshold)
F1 = 2*SE*PC/(SE+PC + 1e-6)
return F1
def get_JS(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
# JS : Jaccard similarity
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
Inter = torch.sum((SR+GT)==2)
Union = torch.sum((SR+GT)>=1)
JS = float(Inter)/(float(Union) + 1e-6)
return JS
def get_DC(SR,GT,threshold=0.5):
# DC : Dice Coefficient
SR = SR > threshold
GT = GT == torch.max(GT)
Inter = torch.sum((SR+GT)==2)
DC = float(2*Inter)/(float(torch.sum(SR)+torch.sum(GT)) + 1e-6)
return DC
参考文献:
混淆矩阵的概念-CSDN博客