C++中map和set的使用
(图片来源于网络)
个人主页: :✨✨✨初阶牛✨✨✨
强烈推荐优质专栏: C++的世界(持续更新中)
推荐专栏1: C语言初阶
推荐专栏2: C语言进阶
个人信条: 知行合一
本篇简介:>:讲解C++中的新容器,set与map对于常用的接口介绍。
金句分享:
✨人攀明月不可得,月行却与人想随。✨
目录
- 一、set
- 1.1 set特点介绍
- 1.2 set使用
-
- 1.21 构造函数
- 1.22 升/降序
- 1.23 其他接口
-
- (1) **容量(`capacity`)相关:**
- (2)**Modifiers(修改)**
- (3)**查找**
- 二、map
- 2.1 map的特点介绍
-
- 2.2 map的使用
-
- ✨构造函数
- [ ]的作用
- 三、实例
-
- 两个数组的交集
- 单词识别
一、set
1.1 set特点介绍
set的介绍
C++中的set是一个STL容器,它是一个自动排序的集合(即将数据存入set,我们通过迭代器顺序访问出来时,数据是有序的),内部使用红黑树(后面会讲解)来实现。它的特点是不允许重复元素,而且插入元素时自动进行排序。
set容器的特点
- 存入set后数据有序:
set是按照一定次序存储元素的容器,迭代器迭代出来的数据是有序的。 - 数据唯一(可以用于去重):每个
value必须是唯一的。set中的元素不能在容器中修改(元素总是const),但是可以从容器中插入或删除它们。 set在底层是用二叉搜索树(红黑树)实现的。
注意:set中查找某个元素,时间复杂度为: l o g 2 n log_2 n log2n,因为底层是红黑树。
1.2 set使用
1.21 构造函数
测试构造:
//测试构造
void test_Construct() {
set s1;//普通构造
//迭代器构造
//数组
int arr[] = { 2,2,1,1,5,5,5,1,7,9,8,10 };
set s2(arr,arr+sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int)); //默认就是升序
cout << "s2: ";
for (auto it : s2) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//vector
vector v = { 2,2,1,1,5,5,5,1,7,9,8,10 };
set s3(v.begin(), v.end()); //默认就是升序
cout << "s3: ";
for (auto it : s3) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//拷贝构造
set s4(s3);
cout << "s4: ";
for (auto it : s3) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
s2: 1 2 5 7 8 9 10
s3: 1 2 5 7 8 9 10
s4: 1 2 5 7 8 9 10
1.22 升/降序
void test_cmp() {
//set 降序
set<int, less<int>> s1;
s1.insert(3);
s1.insert(5);
s1.insert(2);
s1.insert(6);
s1.insert(7);
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(9);
s1.insert(1);
s1.insert(4);
s1.insert(8);
cout << "升序:s1: ";
for (auto it : s1) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//set升序
set<int, greater<int>> s2;
s2.insert({3,5,2,6,7,10,9,1,4,8});
cout << "降序:s2: ";
for (auto it : s2) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
升序:s1: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
降序:s2: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
1.23 其他接口
(1) 容量(capacity)相关:
| 接口名 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| empty( ) | 检测set是否为空,空返回true,否则返回false |
| size() | 获取set中有效数据的个数 |
(2)Modifiers(修改)
| 接口名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| insert | 向set中插入数据,可以是迭代器区间们也可以是单个的值 |
| erase | 删除指定位置的数据(可以提供迭代器,也可以是元素值) |
| void swap (set& x); | 交换两个set |
| void clear(); | 清除set中的数据 |
(3)查找
| 接口名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| iterator find (const value_type& val) const; | 查找元素 ,返回该元素的迭代器 |
| size_type count (const value_type& val) const; | 返回目标元素在set中出现的次数(由于set是不予讯重复元素的,所以这个接口意义不大) |
void test() {
set<int, greater<int>> s1;
s1.insert({ 3,5,2,6,7,10,9,1,4,8 });
cout << "有效数据的个数: " << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "是否为空容器: " << s1.empty() << endl;
//在set中意义不大的函数
cout << "容器中元素3出现了: " << s1.count(3) << endl;
set<int>:: iterator it = s1.find(2); //找到则返回这个元素的迭代器,没找到,则返回end()
cout <<"find(2): "<< * it << endl;
set<int, greater<int>> s2;
s2.insert({ 1,5,8 });
cout << "交换前:"<<endl;
cout << "s1: ";
for (auto it : s1) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s2: ";
for (auto it : s2) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
swap(s1, s2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
cout << "s1: ";
for (auto it : s1) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "s2: ";
for (auto it : s2) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << "清除:s1: ";
for (auto it : s1) {
cout << it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
有效数据的个数: 10
是否为空容器: 0
容器中元素3出现了: 1
find(2): 2
交换前:
s1: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
s2: 8 5 1
交换后:
s1: 8 5 1
s2: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
清除:s1:
二、map
2.1 map的特点介绍
map是一个关联容器,它提供了一种存储键值对的方法。它是按照键(key)进行排序和存储的,键必须是唯一的,而值(value)可以重复。map通常使用红黑树实现,所以它的查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度都是O(log n)。
那么何为键值对?
键值对是一种常用的数据存储结构,由“键”和“值”两部分组成。其中,“键”是唯一的,用于标识数据,而“值”则是与键相关联的数据。
其实很简单,例如: {“apple”, “苹果”}
下面是pair大概实现:
template <typename T1, typename T2>
struct pair {
T1 first; //键
T2 second; //值
pair() : first(), second() {}
pair(const T1& x, const T2& y): first(x), second(y) {}
template <typename U1, typename U2>
pair(const pair<U1, U2>& p) : first(p.first), second(p.second) {}
pair& operator=(const pair& rhs) {
if (this != &rhs) {
first = rhs.first;
second = rhs.second;
}
return *this;
}
};
2.2 map的使用

map和set的用法基本相同,只不过一个是键值对,一个是单个的值。
这里对于map就不过多介绍了。
✨构造函数
void test_map() {
// 构造空的map
map<string, int> map1;
cout << "map1:" << endl;
for (auto it : map1) {
cout << it.first << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 使用初始化列表构造
map<string, string> map2{
{"apple", "苹果"},
{"banana", "香蕉"},
{"orange", "橘子"}
};
cout << "map2:" << endl;
for (auto it : map2) {
cout << it.first << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 构造map并插入元素
map<string, int> map3;
map3.insert(pair<string, int>("panda", 1));
map3.insert(make_pair("", 2));
map3.insert(map<string, int>::value_type("monkey", 3));
cout << "map3:" << endl;
for (auto it : map3) {
cout << it.first << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "空格对应的值:" << map3[""];
}
运行结果:
map1:
map2:
apple苹果
banana香蕉
orange橘子
map3:
2
monkey3
panda1
空格对应的值:2
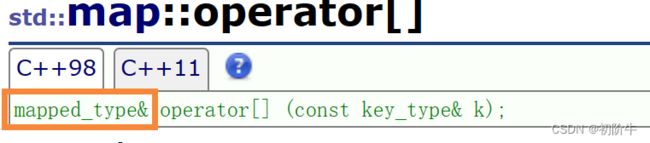
[ ]的作用
在 C++ 中,map 中的 [] 运算符可以用于访问和修改 map 中的元素,其作用如下:
- 若键值存在,返回对应的值;
- 若键值不存在,会与这个不存在的key和默认值构成一个键值对,自动插入默,并返回该默认值的引用。
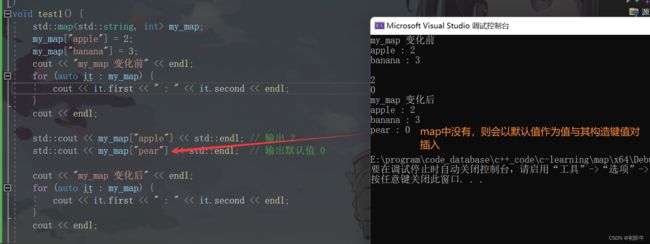
void test() {
std::map<std::string, int> my_map;
my_map["apple"] = 2;
my_map["banana"] = 3;
cout << "my_map 变化前" << endl;
for (auto it : my_map) {
cout << it.first << " : " << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
std::cout << my_map["apple"] << std::endl; // 输出 2
std::cout << my_map["pear"] << std::endl; // 输出默认值 0
cout << "my_map 变化后" << endl;
for (auto it : my_map) {
cout << it.first << " : " << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
运行结果:
my_map 变化前
apple : 2
banana : 3
2
0
my_map 变化后
apple : 2
banana : 3
pear : 0
注意map可以通过[key]访问对应的value。
关于map,本篇就主要介绍这[ ]接口了。
三、实例
两个数组的交集
(1)关于set的示例使用:
set在oj题中的应用
题目名称:两个数组的交集
题目链接: 传送门
(声明:题目来源于“力扣”)
题目描述
给定两个数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,返回 它们的交集 。输出结果中的每个元素一定是 唯一 的。我们可以 不考虑输出结果的顺序 。

解题思路:
将两个数组分别进set中去重得到s1和s2,然后将其中一个与另一个比较,判断是否存在则是交集。
示例代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int> ret; //用于返回结构的数组
//先通过set去重
set<int> s1;
for(int& it:nums1){
s1.insert(it);
}
set<int> s2;
for(int& it:nums2){
s2.insert(it);
}
for(auto& it:s1){
if(s2.count(it)){ //表示s1中的值在s2中可以找到
ret.push_back(it);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
单词识别
(2)关于map的使用
题目描述:
输入一个英文句子,把句子中的单词(不区分大小写)按出现次数按从多到少把单词和次数在屏幕上输出来,次数一样的按照单词小写的字典序排序输出,要求能识别英文单词和句号。
- 由于不区分大小写,可以先将字符串中所有的字母转化为小写。
- 将字符串按照空格划分,划分为一个个单词word。
- 将单词存入map,没出现一次单词,该单词的次数就+1;
- 最后按迭代器跑一遍即可。
示例代码:
#include