静态分析C语言生成函数调用关系的利器——cflow(二)
大纲
- 环境准备
- 选择项目
- 分析代码
-
- 简单分析
- 高级分析
-
- 坑:不能显示main函数所有调用函数的调用栈
- 坑2:重定义错误
- 坑3:缺失编译时产生的文件
- 坑4:缺失工程的头文件包含路径指定
- 坑5:操作系统的坑
-
- 只存在于windows操作系统上的文件
- 坑6:大小顶问题
- 最终展示
- 参考资料
从最开始写《IT项目研发过程中的利器》这系列博文已经过去6年。最近几年,相关软件有所迭代,也出现很多其他有意思的“利器”。最近准备把这系列做个修补,同时新增其他语言(比如Golang和Python)品类的“利器”供大家把玩。
在《静态分析C语言生成函数调用关系的利器——cflow》一文中,我们介绍了如何使用cflow查看C语言代码中函数的调用关系。其中指出cflow(老版本)不能直接导出dot文件,需要使用其他工具来做辅助。但是最新版的cflow(v1.7)已经支持导出dot了。
目前市面上介绍cflow的例子都比较简单(包括我写的那篇《静态分析C语言生成函数调用关系的利器——cflow》),比如函数都在一个文件里的,且调用关系也不复杂。但是现实工作中,我们的代码工程结构可能很复杂,导致看了类似博文的同学也不知道在实际生产中怎么应用。
于是本文就开始上难度,不仅要分析多层调用,还要结构复杂。这篇可能是全网目前能找到的最复杂使用cflow去做大型项目源码分析的例子了。
环境准备
我的测试环境是Ubuntu 12。
uname -a
Linux fangliang 5.15.0-91-generic #101-Ubuntu SMP Tue Nov 14 13:30:08 UTC 2023 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
我们可以直接使用apt安装cflow。graphviz则是用于在最后一步将dot文件转换成图片,我们先提前将其安装好。
sudo apt-get install cflow
sudo apt-get install graphviz
选择项目
我挑选的分析项目是libevent,它是很多著名项目的底层库,比如Google Chrome、Memcached、Transmission。
我们可以从https://github.com/libevent/libevent.git获取其代码。它的代码结构还是蛮正规的。

它有很多代码都是在根目录,而我们这次要分析的是test目录下test-time.c文件中的main函数调用栈。
/*
* Copyright (c) 2002-2007 Niels Provos
* Copyright (c) 2007-2012 Niels Provos and Nick Mathewson
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* 3. The name of the author may not be used to endorse or promote products
* derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
* OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED.
* IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT
* NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
* DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF
* THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*/
#include "event2/event-config.h"
#include "util-internal.h"
#include 分析代码
简单分析
进入libevent目录,执行下面指令
cflow ./test/test-time.c --format=dot > test_time.dot
dot -T gif test_time.dot -o test_time.gif

可以看到我们只能看到定义在test-time.c中的函数的调用栈,而像右下角的event_add则没有显示更深的调用栈。这个在现实工作中肯定是不能满足需求的。
高级分析
高级分析可以将main函数所有调用的函数的底层调用栈也会显示出来。但是整个过程还是蛮曲折的。本文主要讲解如何挖坑和填坑。
坑:不能显示main函数所有调用函数的调用栈
我们可以给cflow指定一个文件,分析出其调用栈。于是这个问题的根本原因是我们没有给它提供足够多的文件,比如上例中event_add的实现在哪个文件里是需要提供给cflow的。
最简单办法就是我们把所有的基础c文件(跟目录下的c文件)都给cflow来分析。
cflow ./test/test-time.c ./*.c --format=dot > test_time.dot
比较多的是XXX redefined,this is the place of previous definition,即重定义。
坑2:重定义错误
这类错误主要是符号类型错误,我们只要加入相关指令即可,修改如下
cflow ./test/test-time.c ./*.c \
-i^s --brief \
--define '__attribute__\(c\)'\
--define '__typeof\(c\)=int' \
--symbol __inline:=inline\
--symbol __inline__:=inline\
--symbol __const__:=const\
--symbol __const:=const\
--symbol __restrict:=restrict\
--symbol __extension__:qualifier\
--symbol __asm__:wrapper\
--symbol __nonnull:wrapper\
--symbol __wur:wrapper \
--format=dot > test_time.dot
执行完会报这个错:找不到event2这个文件夹下的event-config.h。
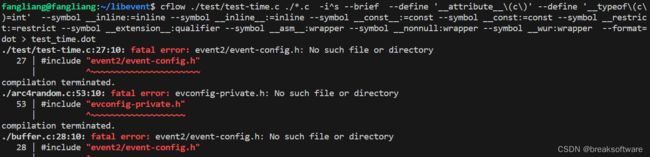
经过寻找,这个文件并不存在。这说明该文件是在编译时生成的。
坑3:缺失编译时产生的文件
解决办法也就是编译libevent了。
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. # Default to Unix Makefiles.
make
这个时候event-config.h生成了,它的位置是libevent/build/include/event2/event-config.h。
find -name "event-config.h"
./build/include/event2/event-config.h
然后我们要把这个目录加入到cflow的检索路径下,即加入
–include-dir=./build/include/
cflow ./test/test-time.c ./*.c \
-i^s --brief \
--define '__attribute__\(c\)'\
--define '__typeof\(c\)=int' \
--symbol __inline:=inline\
--symbol __inline__:=inline\
--symbol __const__:=const\
--symbol __const:=const\
--symbol __restrict:=restrict\
--symbol __extension__:qualifier\
--symbol __asm__:wrapper\
--symbol __nonnull:wrapper\
--symbol __wur:wrapper \
--include-dir=./build/include/ \
--format=dot > test_time.dot
坑4:缺失工程的头文件包含路径指定
解决办法就是找到这些文件所在的目录,然后在指令中指定即可。
–include-dir=./include
–include-dir=./ \
cflow ./test/test-time.c ./*.c \
-i^s --brief \
--define '__attribute__\(c\)'\
--define '__typeof\(c\)=int' \
--symbol __inline:=inline\
--symbol __inline__:=inline\
--symbol __const__:=const\
--symbol __const:=const\
--symbol __restrict:=restrict\
--symbol __extension__:qualifier\
--symbol __asm__:wrapper\
--symbol __nonnull:wrapper\
--symbol __wur:wrapper \
--include-dir=./build/include/ \
--include-dir=./include \
--include-dir=./ \
--format=dot > test_time.dot
坑5:操作系统的坑
libevent是支持在多种操作系统上编译的,其中就包括windows。而我们这次是在linux上编译,而cflow是不区分系统的,于是我们需要手工解决这个问题。
只存在于windows操作系统上的文件
wepoll.c是只服务于windows操作系统。针对这个文件,我直接将其后缀修改成cw,这样就可以避开cflow的检索(因为我们在指令中指定了*.c)。

类似的文件还有event_iocp.c和buffer_iocp.c,我们都对它们进行后缀名修改处理。
这个时候只剩下下面这个错了。#error “Endianness not defined!”。

坑6:大小顶问题
这个问题一般不会遇到,因为操作系统基本确定了大小顶。但是cflow是代码分析工具,它不关心操作系统是什么。于是这个问题我们也要手工处理。先看下代码
/* blk0() and blk() perform the initial expand. */
/* I got the idea of expanding during the round function from SSLeay */
#if defined(LITTLE_ENDIAN)
#define blk0(i) \
(block->l[i] = (rol(block->l[i], 24) & 0xFF00FF00) | \
(rol(block->l[i], 8) & 0x00FF00FF))
#elif defined(BIG_ENDIAN)
#define blk0(i) block->l[i]
#else
#error "Endianness not defined!"
#endif
解决方案也很简单,我们在cflow的指令中指定一个宏——LITTLE_ENDIAN。
-D LITTLE_ENDIAN
题外话,可能通过下面指令确定是大小顶。小顶是1,大顶是0。
echo -n I | od -to2 | head -n1 | cut -f2 -d" " | cut -c6
修改后的指令是
cflow ./test/test-time.c ./*.c \
-i^s --brief \
--define '__attribute__\(c\)'\
--define '__typeof\(c\)=int' \
--symbol __inline:=inline\
--symbol __inline__:=inline\
--symbol __const__:=const\
--symbol __const:=const\
--symbol __restrict:=restrict\
--symbol __extension__:qualifier\
--symbol __asm__:wrapper\
--symbol __nonnull:wrapper\
--symbol __wur:wrapper \
--include-dir=./build/include/ \
--include-dir=./include \
--include-dir=./ \
-D LITTLE_ENDIAN \
--format=dot > test_time.dot
最终展示
经过上面处理,就没有错误出现了。我们可以使用下面指令生成图片。
dot -T gif test_time.dot -o test_time.gif
如果图片看不行,可以通过下面指令生成svg文件。
dot -T svg test_time.dot -o test_time.svg
可以从https://github.com/f304646673/tools/blob/main/cflow/images/test_time.svg下载查看。
参考资料
- https://www.gnu.org/software/cflow/manual/cflow.html
- https://libevent.org/
- https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Libevent




