数据结构----ArrayList的简介、使用、扩容机制、使用ArrayList实现杨辉三角
文章目录
- 1.ArrayList简介
- 2. ArrayList使用
-
- 2.1 ArrayList的构造
-
- 2.1.1 无参构造(ArrayList() )
- 2.1.2 含参构造:指定顺序表初始容量(ArrayList(int initialCapacity))
- 2.1.3 含参构造:利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList(ArrayList(Collection c))
- 2.2 ArrayList常见操作
- 2.3 ArrayList的遍历
- 2.4 ArrayList的扩容机制
-
- 2.4.1 详解Add()方法扩容
- 2.4.2 扩容机制代码
- 3. ArrayList的具体使用
-
- 3.1 使用ArrayList实现杨辉三角
- 3.1 使用ArrayList实现打扑克牌
- 4. 优缺点
1.ArrayList简介
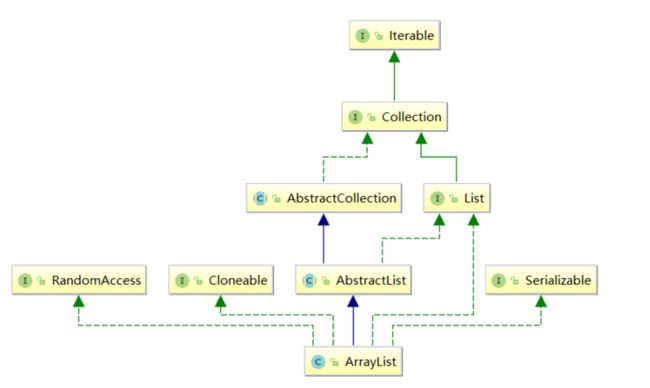
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下:
【说明】
- ArrayList是以泛型方式实现的,使用时必须要先实例化
- ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
- ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
- ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
- 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
- ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
2. ArrayList使用
需要注意的是,ArrayList是可变长度的,即它的底层是一段连续的空间,并且它可以根据需要自动扩容和缩减容量,是一个动态类型的顺序表,因此在使用ArrayList时无需担心容量的问题。
2.1 ArrayList的构造
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 无参构造 |
| ArrayList(Collection c) | 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定顺序表初始容量 |
2.1.1 无参构造(ArrayList() )
// 构造一个空的列表
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();

我们看到这个代码时,可以认为当调用无参构造方法时,其实并没有分配内存.
2.1.2 含参构造:指定顺序表初始容量(ArrayList(int initialCapacity))
// 构造一个具有15个容量的列表
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(15);
list1.add(1);
// list1.add("hello"); // 编译失败,List已经限定了,list2中只能存储整形元素
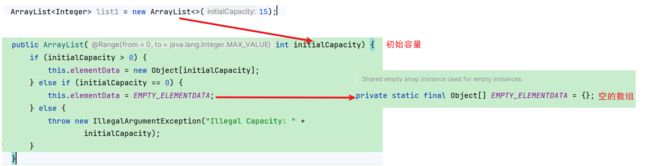
当有参构造方法中传入的数组指定容量的大小大于0时,作为数组的容量大小,当等于0时,返回已经定义过的空数组,当小于0时,抛出IllegalArgumentException异常
2.1.3 含参构造:利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList(ArrayList(Collection c))
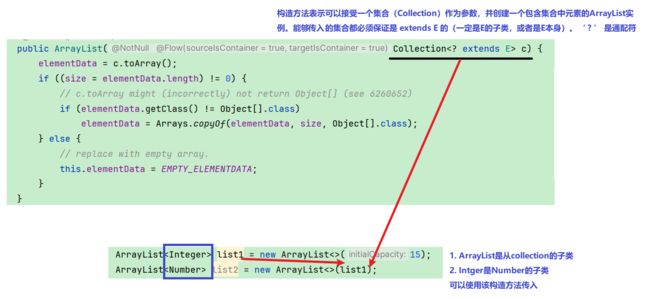
ArrayList(Collection c):这个构造方法接受一个集合(Collection)作为参数,并创建一个包含集合中元素的ArrayList实例。注意,这里的能够引用的集合都必须保证是 extends E 的(一定是E的子类,或者是E本身)。‘ ? ’ 是通配符。
// list3构造好之后,与list中的元素一致
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(15);
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(list1);
【注意】:
避免省略类型,否则:任意类型的元素都可以存放,使用时将是一场灾难
List list3 = new ArrayList();
list4.add("111");
list4.add(100);
2.2 ArrayList常见操作
ArrayList虽然提供的方法比较多,但是常用方法如下所示,需要用到其他方法时,可以查看ArrayList的帮助文档。
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List< E > subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
【代码示例】:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("JavaSE");
list.add("JavaWeb");
list.add("JavaEE");
list.add("JVM");
list.add("测试课程");
System.out.println(list);
// 获取list中有效元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());
// 获取和设置index位置上的元素,注意index必须介于[0, size)间
System.out.println(list.get(1));
list.set(1, "JavaWEB");
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// 在list的index位置插入指定元素,index及后续的元素统一往后搬移一个位置
list.add(1, "Java数据结构");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除指定元素,找到了就删除,该元素之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置
list.remove("JVM");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除list中index位置上的元素,注意index不要超过list中有效元素个数,否则会抛出下标越界异常
list.remove(list.size()-1);
System.out.println(list);
// 检测list中是否包含指定元素,包含返回true,否则返回false
if(list.contains("测试课程")){
list.add("测试课程");
}
// 查找指定元素第一次出现的位置:indexOf从前往后找,lastIndexOf从后往前找
list.add("JavaSE");
System.out.println(list.indexOf("JavaSE"));
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("JavaSE"));
// 使用list中[0, 4)之间的元素构成一个新的SubList返回,但是和ArrayList共用一个elementData数组
List<String> ret = list.subList(0, 4);
System.out.println(ret);
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size());
}
- remove(object o)方法
源码:
//删除 index 位置元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
//删除遇到的第一个 o
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
使用实例:
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.add(4);
arrayList.add(5);
System.out.println(arrayList);
arrayList.remove(2);
arrayList.remove(new Integer(5));
由源码知:
- 当使用arrayList.remove(2);会默认删除的是 12下标的数据。
- 当使用arrayList.remove(new Integer(5));传进去的是一个 Object 的引用类型时,才会删除里面的对象
- 使用subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)截取方法构建List时并不产生新的对象
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.add(4);
arrayList.add(5);
System.out.println(arrayList);
List<Integer> arrayList1= arrayList.subList(1, 3);//截取并不产生的新对象
System.out.println(arrayList1);
arrayList1.set(0, 99);
System.out.println(arrayList);//[1, 99, 3, 4, 5]
System.out.println(arrayList1);//[99, 3]
运行结果:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[2, 3]
[1, 99, 3, 4, 5]
[99, 3]
从代码结果也可以看出,当修改list3时,原arrayList的值也会改变,可见截取方法构建List时并不产生新的对象,所以这里是把下标地址直接给了arrayList1,而不是拷贝了字符串。
- ArrayList中重写了toString方法实现打印
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(1);
arrayList.add(2);
arrayList.add(3);
arrayList.add(4);
arrayList.add(5);
System.out.println(arrayList);
运行结果:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
我们在ArrayList中搜索toString()方法(使用ctrl+F搜索)
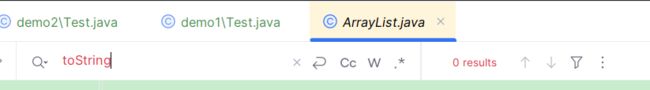
发现在ArrayList并没有toString()方法,向上一层搜索

发现在AbstractList仍然也没有toString()方法,继续向上一层搜索
发现存在toString()方法
public String toString() {
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = it.next();
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
这里面的第一行的: Iterator< E > it = iterator();就是迭代器,它的作用是遍历我们当前的集合。
2.3 ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList 可以使用三方方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
// 使用下标+for遍历
//该方法使用索引访问 ArrayList 的每个元素,并通过 list.get(i) 方法获取元素的值。
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 借助foreach遍历
//直接将集合中的每个元素赋值给循环变量 integer ,然后对其进行处理
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.print(integer + " ");
}
System.out.println();
//使用迭代器进行遍历
//迭代器提供了一种在遍历方式
//通过 it.hasNext() 判断是否还有下一个元素,然后使用 it.next() 获取当前元素的值
Iterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
在使用迭代器遍历时,会不断移动it迭代器,然后通过 it.hasNext() 判断是否还有下一个元素,然后使用 it.next() 获取当前元素的值,实现集合的遍历过程
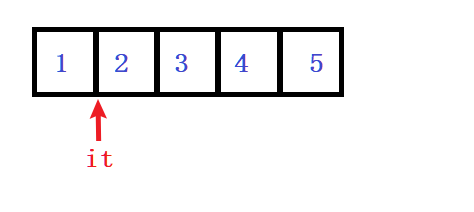
【注意】:
- ArrayList最常使用的遍历方式是:for循环+下标 以及 foreach
- 迭代器是设计模式的一种,后序容器接触多了再给大家铺垫
2.4 ArrayList的扩容机制
2.4.1 详解Add()方法扩容
由 2.1.1 上面的构造方法知,在使用无参构造方法实例化ArrayList时,其实并没有分配内存,那么为什么可以使用add对ArrayList添加元素没有报错呢?
【结论】:
当调用无参构造方法时,其实并没有分配内存,但是当第一次使用add给ArrayList中添加元素时,会分配大小为10的数组
2.4.2 扩容机制代码
ArrayList是一个动态类型的顺序表,即:在插入元素的过程中会自动扩容。以下是ArrayList源码中扩容方式:
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空间
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空间
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认容量大小
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 获取旧空间大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 调用copyOf扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
【总结】:
- 检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
- 预估需要库容的大小
- 初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
- 如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
- 真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败- 使用copyOf进行扩容
3. ArrayList的具体使用
使用ArrayList模拟实现二维数组结构:
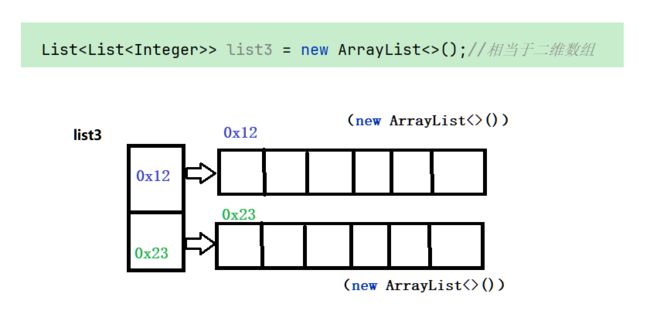
list3的每一个元素都是一个list
3.1 使用ArrayList实现杨辉三角
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。如下图所示:
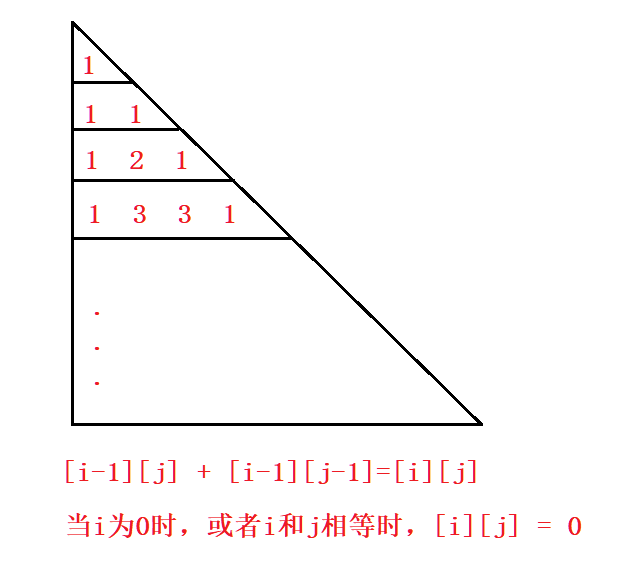
题目链接:杨辉三角
public List<List<Integer>> generate1(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
//第一行数据
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
ret.add(list);
//第二行之后的数据
for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
//准备当前行
List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();
//准备当前行的第一个数据
curRow.add(1);//每一行的第一个元素为1
//准备当前行的中间数据
List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i - 1);
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
int value = preRow.get(j) + preRow.get(j - 1);
curRow.add(value);
}
//准备当前行的最后一个数据
curRow.add(1);
//把这个数据添加到结果集合中
ret.add(curRow);
}
return ret;
}
public List<List<Integer>> generate2(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 0 || i == j) {
curRow.add(1);//每一行的第一个元素 和 对角线的位置的数字 为1
} else {
List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i - 1);//获取上一行的Arraylist
int value = preRow.get(j) + preRow.get(j - 1);
curRow.add(value);
}
}
ret.add(curRow);
}
return ret;
}
3.1 使用ArrayList实现打扑克牌
Card类
class Card {
private String color;
private int num;
public Card(String color, int num) {
this.color = color;
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + this.color + " " + this.num + "]";
}
}
CardDemo类:
实现关于扑克牌的方法
class CardDemo {
private static final String[] colors = {"♠", "♣", "♥", "♦"};
List<Card> cards = new ArrayList<>(52);
//初始化一副牌
public List<Card> initCard() {
//遍历所有牌的花色
for (int i = 0; i < colors.length; i++) {
//遍历所有牌的牌面数字
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
//构建一张牌
Card card = new Card(colors[i], j);
//将牌添加到集合中
cards.add(card);
}
}
//返回这副牌
return cards;
}
//洗牌方法
public void shuffle() {
Random random = new Random();
//从后往前遍历牌
for (int i = cards.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
//获取与当前牌要进行交换的牌的下标值
int randomNum = random.nextInt(i);
//将两张牌进行交换
swap(cards, randomNum, i);
}
}
private static void swap(List<Card> cards, int randomNum, int index) {
Card card = cards.get(randomNum);
cards.set(randomNum, cards.get(index));
cards.set(index, card);
}
//给三个人分发牌,传入的参数代表给每个人分发的牌的张数
public List<List<Card>> dealCards(List<Card> cards, int nums) {
//创建三个集合代表三个人
List<Card> person1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> hands = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < (nums * 3); i++) {
Card card = cards.remove(0);
if (i % 3 == 0) {
person1.add(card);
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
person2.add(card);
} else if (i % 3 == 2) {
person3.add(card);
}
}
hands.add(person1);
hands.add(person2);
hands.add(person3);
return hands;
}
其中dealCards方法有更简便地实现:
public List<List<Card>> dealCards(List<Card> cards, int nums) {
//创建三个集合代表三个人
List<Card> person1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Card> person3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> hands = new ArrayList<>();
hands.add(person1);
hands.add(person2);
hands.add(person3);
for (int i = 0; i < nums ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
Card card = cards.remove(0);
hands.get(j).add(card);
}
}
return hands;
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建牌
CardDemo cardDemo = new CardDemo();
List<Card> cards = cardDemo.initCard();
System.out.println("创建牌如下:");
System.out.println(cards);
//洗牌
cardDemo.shuffle();
System.out.println("洗牌后的牌如下:");
System.out.println(cards);
//分发牌
System.out.println("分发牌之后每人的牌如下:");
List<List<Card>> hands = cardDemo.dealCards2(cards, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"个人的牌如下:");
System.out.println(hands.get(i));
}
System.out.println("剩下的牌如下:");
System.out.println(cards);
//揭牌
System.out.println("揭牌:");
List<List<Card>> hands2 = cardDemo.dealCards2(cards, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"个人的牌如下:");
System.out.println(hands2.get(i));
}
System.out.println("剩下的牌如下:");
System.out.println(cards);
}
}
运行结果:
创建牌如下:
[[♠ 1], [♠ 2], [♠ 3], [♠ 4], [♠ 5], [♠ 6], [♠ 7], [♠ 8], [♠ 9], [♠ 10], [♠ 11], [♠ 12], [♠ 13], [♣ 1], [♣ 2], [♣ 3], [♣ 4], [♣ 5], [♣ 6], [♣ 7], [♣ 8], [♣ 9], [♣ 10], [♣ 11], [♣ 12], [♣ 13], [♥ 1], [♥ 2], [♥ 3], [♥ 4], [♥ 5], [♥ 6], [♥ 7], [♥ 8], [♥ 9], [♥ 10], [♥ 11], [♥ 12], [♥ 13], [♦ 1], [♦ 2], [♦ 3], [♦ 4], [♦ 5], [♦ 6], [♦ 7], [♦ 8], [♦ 9], [♦ 10], [♦ 11], [♦ 12], [♦ 13]]
洗牌后的牌如下:
[[♠ 13], [♦ 10], [♠ 11], [♦ 3], [♠ 12], [♥ 8], [♥ 2], [♣ 5], [♥ 10], [♥ 12], [♠ 7], [♦ 8], [♦ 4], [♣ 7], [♣ 13], [♣ 9], [♣ 1], [♦ 12], [♦ 6], [♦ 9], [♦ 13], [♥ 4], [♦ 11], [♦ 1], [♦ 7], [♠ 1], [♥ 3], [♥ 7], [♥ 6], [♠ 8], [♥ 9], [♣ 6], [♥ 11], [♠ 9], [♠ 10], [♣ 8], [♥ 1], [♦ 5], [♣ 10], [♣ 12], [♠ 5], [♣ 11], [♠ 6], [♠ 2], [♥ 5], [♥ 13], [♠ 3], [♠ 4], [♣ 3], [♦ 2], [♣ 2], [♣ 4]]
分发牌之后每人的牌如下:
第1个人的牌如下:
[[♠ 13], [♦ 3], [♥ 2], [♥ 12], [♦ 4]]
第2个人的牌如下:
[[♦ 10], [♠ 12], [♣ 5], [♠ 7], [♣ 7]]
第3个人的牌如下:
[[♠ 11], [♥ 8], [♥ 10], [♦ 8], [♣ 13]]
剩下的牌如下:
[[♣ 9], [♣ 1], [♦ 12], [♦ 6], [♦ 9], [♦ 13], [♥ 4], [♦ 11], [♦ 1], [♦ 7], [♠ 1], [♥ 3], [♥ 7], [♥ 6], [♠ 8], [♥ 9], [♣ 6], [♥ 11], [♠ 9], [♠ 10], [♣ 8], [♥ 1], [♦ 5], [♣ 10], [♣ 12], [♠ 5], [♣ 11], [♠ 6], [♠ 2], [♥ 5], [♥ 13], [♠ 3], [♠ 4], [♣ 3], [♦ 2], [♣ 2], [♣ 4]]
揭牌:
第1个人的牌如下:
[[♣ 9]]
第2个人的牌如下:
[[♣ 1]]
第3个人的牌如下:
[[♦ 12]]
剩下的牌如下:
[[♦ 6], [♦ 9], [♦ 13], [♥ 4], [♦ 11], [♦ 1], [♦ 7], [♠ 1], [♥ 3], [♥ 7], [♥ 6], [♠ 8], [♥ 9], [♣ 6], [♥ 11], [♠ 9], [♠ 10], [♣ 8], [♥ 1], [♦ 5], [♣ 10], [♣ 12], [♠ 5], [♣ 11], [♠ 6], [♠ 2], [♥ 5], [♥ 13], [♠ 3], [♠ 4], [♣ 3], [♦ 2], [♣ 2], [♣ 4]]
4. 优缺点
优点:
- 动态大小:ArrayList的大小是可以动态调整的,可以根据需要灵活地添加或删除元素。
- 快速随机访问:ArrayList内部使用数组实现,通过索引可以非常快速地访问到元素,时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 支持泛型:ArrayList支持泛型,可以存储任意类型的对象,提高了代码的安全性和可读性。
- 迭代器遍历:ArrayList提供了迭代器(Iterator)接口用于遍历集合中的元素,可以方便地对集合中的元素进行操作。
- 自动扩容:当ArrayList中的元素达到其容量上限时,会自动扩容,不需要人工干预。
缺点:
-
添加和删除元素的效率低:当需要在 ArrayList 中间插入或删除元素时,需要移动后续元素来填补空缺或收缩数组,这导致插入和删除操作的时间复杂度为 O(n) 。 如果需要频繁进行这些操作,使用 ArrayList 的性能可能不佳。
-
扩容代价较高:扩容操作的时间复杂度为O(n),会引起一定的性能损耗。
-
不适合频繁的插入和删除操作:由于扩容和移动元素的操作,ArrayList不适合频繁进行插入和删除操作的场景。
-
不支持基本数据类型:ArrayList只能存储对象类型,对于基本数据类型(如int、boolean等),需要使用对应的包装类进行封装后才能存储。