Java 代码编写红黑树
在程序中什么是树?
程序中的树,它是一种抽象的数据类型(ADT), 用来模仿具有树形接口性质的数据集合,它是由n(n>0)个有限节点连接他们的边组成一个具有层次关系的集合。为什么把他叫做树呢?因为它跟现实生活中的树有所相同有所不同,程序中的树是根朝上,叶朝下,而现实生活中的树是 根朝下,叶朝上
节点
1.,路径:顺着节点的边从一个节点走到另一个节点,所经过的节点的顺序排列就称之为‘路径2, 根:树顶端的节点称之为根,一棵树只有一个根,如果要把一个节点和边的集合称之为树。那么从根到其他任何一个节点都必须偶且只有一条路口
3,父节点:如果该节点有子节点,这个就是这个子节点的父节点
4,子节点:一个节点含有的子树的节点称之为该节点的子节点
5,兄弟接地:处于同一个节点下并且级别相同的2个节点称之为父节点
6,叶节点:没有子节点的节点称之为叶节点
7,子树:每个节点都可以作为子树的根,它和它所有的子节点,子节点的子节点等都包含在子树中
8,节点的层次:从根开始定义,根为第一层,根的子节点为第二层,一次类推
9,深度:对于任意节点n,n的深度为从根到n的唯一路径长,根的深度为0;(从上往下看)
10,高度:对于任意节点n,n的高度为从n到一片树叶的最长的路径,所有树叶的高度为0;(从下往上看)
什么是二叉树
二叉树就是:一个节点下最多只有 2个 子节点的数据结构就叫做二叉树
二叉搜索树
要求:若它的的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有的字节都小于根节点的值
若它的的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有的字节大小于根节点的值
它的左,右子树也分别为二叉排序树
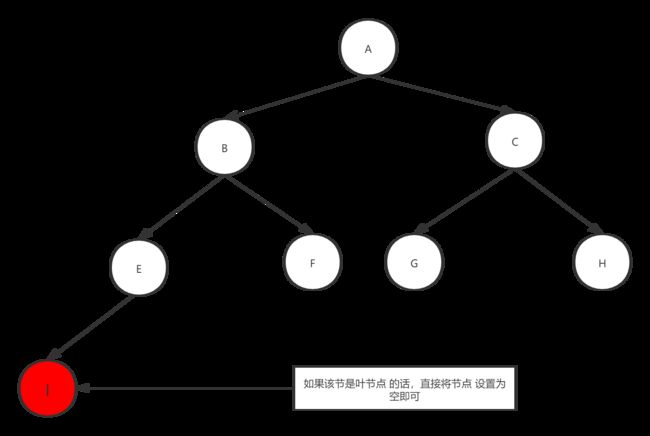
二叉搜索树删除一个叶节点
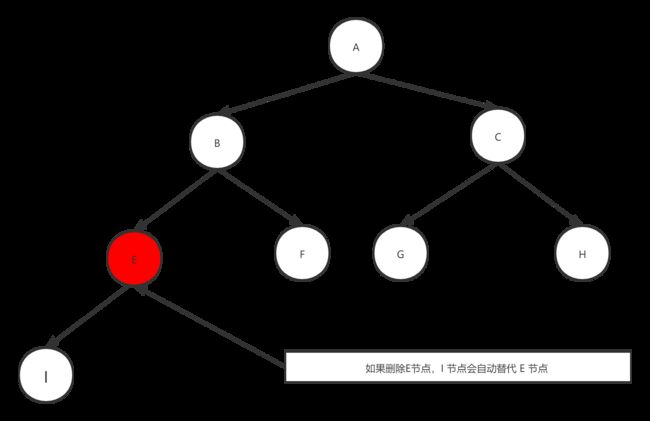
删除一个有子节点的节点
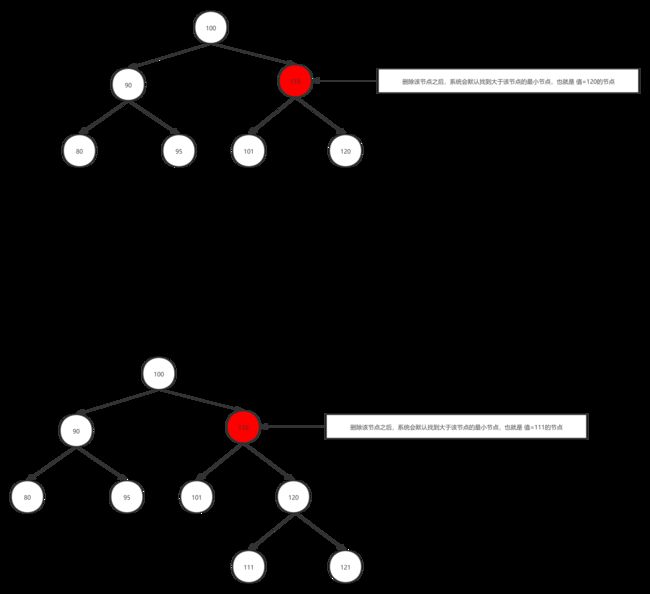
删除有2个子节点的节点
删除节点有必要吗?
通过上面的删除分析,我们发现删除其实挺复杂的,那么我们可以采用逻辑删除的方法进行删除即可!
二分查找算法
假如有个数组为:[1,2,3,4,5…100]
暴力算法: 运气好时,性能不错,运气不好时,性能暴跌
二分查找算法:数据源必须是有序数组,性能非常不错,每次迭代查询都可以排除掉一半的结果
二分查找
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] num = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100};
int i = BinarySearchTest.binarySearch(num, 70);
System.out.println(i);
}
/*
*@description: 必须是有序数组
*@params: result
*@author: FengRui
*@return: arr,data
*@date: 2021/8/8 16:19
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr,int data){
Integer low = 0;
Integer height = arr.length-1;
while (low<= height){
int mid =low+(height-low)/2;
if (arr[mid]<data){
low=mid+1;
}else if (arr[mid]>data){
height=mid-1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return 0;
}
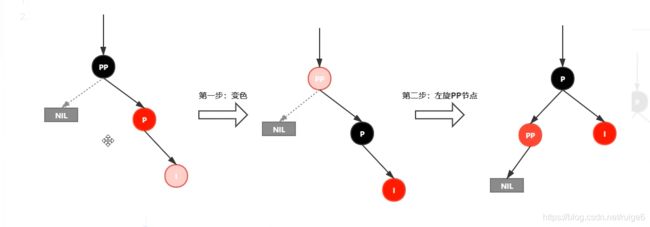
红黑树的性质

注:
红黑树并不是一个完美平衡二叉查找树,从上图可以看出,P的左子树比右子树的节点高。
但左子树和右子树的黑节点的层数是相等的,也即任意一个节点到叶节点的路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点
这种红黑树的平衡为黑色完美平衡
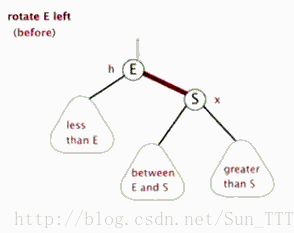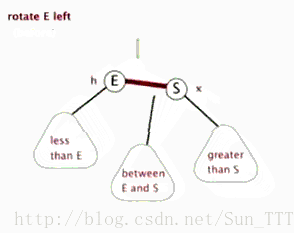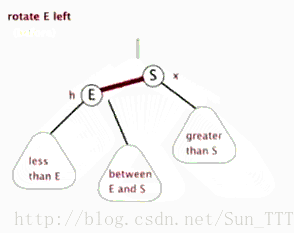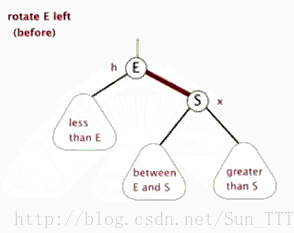
左旋
以某个节点作为支点(旋转节点),旋转节点的右子节点变为旋转节点的父节点(旋转节点变为有节点的坐姿节点),
旋转节点的右子节点的左子节点变为旋转节点的右子节点,旋转节点的右子节点的右子节点不变
右旋
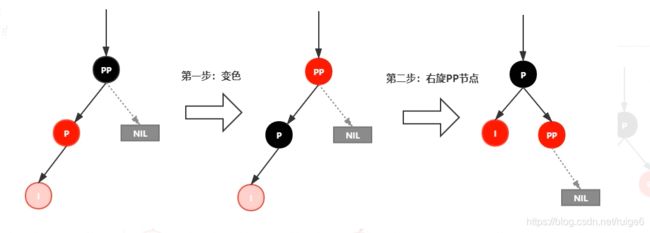
以某个节点作为支点(旋转节点),旋转节点的左子节点变为旋转节点的父节点(旋转节点变为左子节点的右子节点),旋转节点的左子节点的右子节点变为旋转节点的左子节点,旋转节点的左子节点的左子节点不变

注意:红黑树插入一定是红色的节点插入,因为红色节点插入有可能会破坏红黑树的特性,但是如果插入黑色的节点是一定会破坏红黑树的特性
红黑树插入的五种情况
情景一:红黑树为 空树
最简单的一种情景,直接把插入节点作为根节点就行
情景二:插入节点的Key 已经存在
直接将节点的值替换就行了
情景三:插入节点的父节点为黑节点
由于插入的节点是红色的,当插入的节点的父节点时的黑色时,并不会影响红黑树的平衡,直接插入即可,无需做自平衡。
情景四:插入节点的父节点为红色节点
如果插入节点的父节点为红色,那么该父节点不可能为根节点,所以插入节点是存在祖父节点的
这一点很关键,以为后续的旋转坑定需要祖父节点参与
代码
/**
* @Classname FengRui
* @Description 手写红黑树
* @Date 2021-08-10 19:08
* 1. 创建 RBTree,定义颜色
* 2. 创建 RBNode
* 3. 辅助方法定义: parentOf(node),isRed(node),setRed(node),setBlack(node),inOrderPrint()
* 4. 左旋方法定义:leftRotate(node)
* 5. 右旋方法定义:rightRotate(node)
* 6. 公开插入接口方法定义 insert(k,key,v value)
* 7. 内部插入接口方法定义,insert(RBnode node)
* 8. 修正插入导致红黑树失衡的方法定义: insertFixUp(RBNode node)
* 9. 测试红黑树正确性
*
*/
public class RBTree<K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLOCK=false;
/**
* 树根的引用
* */
private RBNode root;
public RBNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
/**
* 获取当前节点的父节点
*
* */
private RBNode parentOf(RBNode rbNode){
if (rbNode!=null){
return rbNode.getParent();
}
return null;
}
/**
*
* 节点是否为红色
* @param node
* */
private boolean isRed(RBNode node){
if (node!=null){
return node.getColor()==RED;
}
return false;
}
/**
*
* 节点是否为黑色
* @param node
* */
private boolean isBlock(RBNode node){
if (node!=null){
return node.getColor()== BLOCK;
}
return false;
}
/**
*
* 设置节点为红色
* @param node
* */
private void setRed(RBNode node){
if (node!=null){
node.setColor(RED);
}
}
/**
*
* 设置节点为黑色
* @param node
* */
private void setBlock(RBNode node){
if (node!=null){
node.setColor(BLOCK);
}
}
/**
* 中序打印二叉树
* */
private void inOrderPrint(){
this.inOrderPrint(root);
}
private void inOrderPrint(RBNode node){
if (node!=null){
inOrderPrint(node.left);
System.out.println("key:"+node.key+",value:"+node.value);
inOrderPrint(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 公开的插入方法
* @param key
* @param value
* */
public void insert(K key,V value){
RBNode node = new RBNode();
node.setKey(key);
node.setValue(value);
node.setColor(RED);
insert(node);
}
private void insert(RBNode node){
RBNode parent = null;
RBNode x = this.root;
while (x!=null){
parent = x;
//cmp >0 说明node。key 大于 key,需要到x的 右子树查找
//cmp == 0 说明 node。key 等于 x。key 说明需要进行替换操作
//cmp < 0 说明node。key 小于 x。key 说明需要到 x 的左子树进行查询
int cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp>0){
x = x.right;
}else if(cmp<0){
x = x.left;
}else{
x.setValue(node.getValue());
return;
}
}
node.parent = parent;
if (parent != null){
int cmp = node.key.compareTo(parent.key);
if (cmp>0){
//当前node 的key 比 parent 的 key 大, 需要把node 放入 parent 的右子节点
parent.right = node;
}else{
//当前node 的key 比 parent 的key 小,需要把node 放入 parent 的 左子节点
parent.left = node;
}
}else{
this.root = node;
}
//需要调用 修复红黑树平衡的方法
insertFixUp(node);
}
/**
* 插入后修复红黑树平衡的方法
* 情景1:红黑树为空树 将跟节点染色即可
* 情景2:插入节点的key 已经存在了 直接替换即可
* 情景3:插入节点的父节点为黑色 因为你所插入的路径,黑色节点没有变化,所以红黑树依然是平衡,所以不需要处理
* 情景4 需要我去处理
* 情景4: 插入节点的父节点为红色
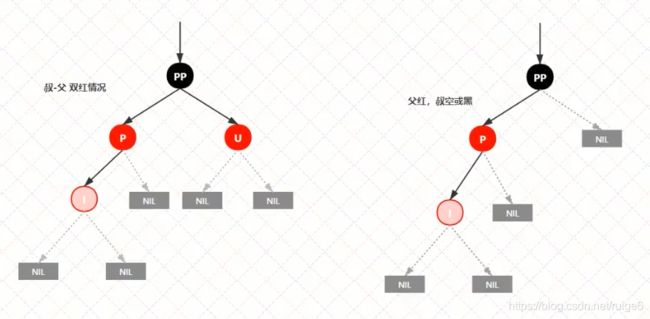
* 情景4.1: 叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红) 并且为红色(父-叔),将爸爸和叔叔染色为 黑色,并且再以爷爷节点为当前节点进行下一轮操作
* 情景4.2: 叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
* 情景4.2.1 加入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL 情况) 将父节点变黑,祖父节点变红,然后以祖父节点进行左旋
* 情景4.2.2 加入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR 情况) 以父节点进行左旋,然后将 将自己变黑,祖父节点变红,进行左旋
* 情景4.3: 叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点 为爷爷节点的右子树
* 情景4.3.1: 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况) 将父节点变黑,祖父节点变红,以祖父节点进行右旋
* 情景4.3.2: 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况) 父节点进行左旋,然后自己变黑,祖父节点变红,然后进行右旋
* */
private void insertFixUp(RBNode node){
this.root.color = BLOCK;
RBNode parent = parentOf(node);
RBNode gparent = parentOf(parent);
//情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
if (parent!=null && parent.color==RED){
//如果父节点时红色,那么一定存在爷爷节点。因为根节点不可能是红色
RBNode uncle = null;
if (parent == gparent.left){
uncle = gparent.right;
//情景4.1:插入节点的父节点为红色 将爸爸和叔叔染色为 黑色,并且再以爷爷节点为当前节点进行下一轮操作
if (uncle!=null&&isRed(uncle)){
setBlock(parent);
setBlock(uncle);
setRed(gparent);
insertFixUp(gparent);
return;
}
// 情景4.2: 叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
// 叔叔节点不存在,或为黑色 将父节点变黑,祖父节点变红,然后以祖父节点进行左旋
if (uncle ==null || isBlock(uncle)){
//情景4.2.1 加入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL 情况) 将父节点变黑,祖父节点变红,然后以祖父节点进行左旋
if (node == parent.left){
setBlock(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
return;
}
if (node == parent.right){
//情景 4.2.2 加入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR 情况) 以父节点进行左旋,然后将 将自己变黑,祖父节点变红,进行左旋
leftRotate(parent);
insertFixUp(parent);
return;
}
}
}else{ //父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
uncle = gparent.left;
//情景4.1:插入节点的父节点为红色 将爸爸和叔叔染色为 黑色,并且再以爷爷节点为当前节点进行下一轮操作
if (uncle!=null&&isRed(uncle)){
setBlock(parent);
setBlock(uncle);
setRed(gparent);
insertFixUp(gparent);
return;
}
if (uncle==null || isBlock(uncle)){
//情景4.3.2: 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况) 父节点进行左旋,然后自己变黑,祖父节点变红,然后进行右旋
if (node == parent.left){
rightRotate(parent);
insertFixUp(parent);
return;
}
//情景4.3.1: 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况) 将父节点变黑,祖父节点变红,以祖父节点进行右旋
if (node == parent.right){
setBlock(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
return;
}
}
//情景4.3: 叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点 为爷爷节点的右子树
}
}
}
/**
* 左旋方法
* 左旋示意图:左旋x节点
* P P
* | |
* x y
* / \ -----> / \
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
* 1.将 x 的右子节点设置为 y的左子节点,并将y的左子节点的父节点设置为 x
* 2.判断 x 是否有父节点,如果有父节点的话,将 y 的父节点设置为 x 的父节点, 并且让 x 的父节点 制定 y
* 3. 将x的左子节点更新为y, 将y的左子节点更新为x
* */
private void leftRotate(RBNode x){
RBNode y = x.right;
//将 x 的右子节点设置为 y的左子节点,并将y的左子节点的父节点设置为 x
if (y!=null){
x.right=y.left;
if (y.left!=null){
y.left.parent=x;
}
}
RBNode parent = x.getParent();
if(parent!=null){
y.parent=parent;
if (x.parent.left == x){
x.parent.left = y;
}else{
x.parent.right = y;
}
}else{
this.root = y;
this.root.parent = null;
}
x.parent = y;
y.left= x;
}
/**
* 右旋方法
* 右旋示意图:右旋y节点
* P P
* | |
* y x
* / \ -----> / \
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \
* lx ly ly ry
*
* 1.将 x 的右子节点设置为 y的左子节点,并将x的右子节点的父节点设置为y
* 2.判断 y 是否有父节点,如果有父节点的话,将 x 的父节点设置为 y 的父节点, 并且让 y 的父节点 绑定 x
* 3.将x的右子节点更新为y, 将y的父子节点更新为x
* */
private void rightRotate(RBNode y){
RBNode x = y.left;
//1.将 x 的右子节点设置为y的左子节点,并将x的右子节点的父节点设置为y
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right!=null){
x.right.parent=y;
}
//2.判断 y 是否有父节点,如果有父节点的话,将 x 的父节点设置为 y 的父节点, 并且让 y 的父节点 绑定 x
if (y.parent!=null) {
x.parent =y.parent;
if (y.parent.left == y) {
y.parent.left = x;
}else{
y.parent.right = x;
}
}else{
this.root = y;
this.root.parent = null;
}
//3.将x的右子节点更新为y, 将y的父子节点更新为x
x.right = y;
y.parent = x;
}
static class RBNode<K extends Comparable<K>,V>{
private RBNode parent;
private RBNode left;
private RBNode right;
private boolean color;
private K key;
private V value;
public RBNode() {
}
public RBNode(RBNode parent, RBNode left, RBNode right, boolean color, K key, V value) {
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.color = color;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isColor() {
return color;
}
public RBNode getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(RBNode parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public RBNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(RBNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public RBNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(RBNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public boolean getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(boolean color) {
this.color = color;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(K key) {
this.key = key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
}
测试类
public class RBTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sacnner = new Scanner(System.in);
RBTree<String,Object> rbt = new RBTree<>();
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入key:");
String key = sacnner.next();
System.out.println();
rbt.insert(key,null);
TreeOperation.show(rbt.getRoot());
}
}
}
代码
public class TreeOperation {
/*
树的结构示例:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
*/
// 用于获得树的层数
public static int getTreeDepth(RBTree.RBNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(root.getLeft()), getTreeDepth(root.getRight())));
}
private static void writeArray(RBTree.RBNode currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// 保证输入的树不为空
if (currNode == null) {return;}
// 先将当前节点保存到二维数组中
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.getKey() + "-" + (currNode.isColor() ? "R" : "B") + "");
// 计算当前位于树的第几层
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// 若到了最后一层,则返回
if (currLevel == treeDepth) {
return;
}
// 计算当前行到下一行,每个元素之间的间隔(下一行的列索引与当前元素的列索引之间的间隔)
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// 对左儿子进行判断,若有左儿子,则记录相应的"/"与左儿子的值
if (currNode.getLeft() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.getLeft(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// 对右儿子进行判断,若有右儿子,则记录相应的"\"与右儿子的值
if (currNode.getRight() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.getRight(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
public static void show(RBTree.RBNode root) {
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("EMPTY!");
}
// 得到树的深度
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(root);
// 最后一行的宽度为2的(n - 1)次方乘3,再加1
// 作为整个二维数组的宽度
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// 用一个字符串数组来存储每个位置应显示的元素
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// 对数组进行初始化,默认为一个空格
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j ++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// 从根节点开始,递归处理整个树
// res[0][(arrayWidth + 1)/ 2] = (char)(root.val + '0');
writeArray(root, 0, arrayWidth/ 2, res, treeDepth);
// 此时,已经将所有需要显示的元素储存到了二维数组中,将其拼接并打印即可
for (String[] line: res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i ++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2: line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}