MySQL的函数-窗口函数
mysql8.0窗口函数分类
MySQL的函数-窗口函数
MySQL 8.0 新增窗口函数,窗口函数又被称为开窗函数,与Oracle 窗口函数类似,属于MySQL的一大特点.
非聚合窗口函数是相对于聚函数来说的。聚合函数是对一组数据计算后返回单个值(即分组),非聚合函数一次只会处理一行数据。窗口聚合函数在行记录上计算某个字段的结果时,可将窗口范围内的数据输入到聚合函数中,并不改变行数。

window_function ( expr ) OVER (
PARTITION BY ...
ORDER BY ...
frame_clause
)
其中,window_function 是窗口函数的名称;expr 是参数,有些函数不需要参数;OVER子句包含三个选项:
分区(PARTITION BY)
PARTITION BY选项用于将数据行拆分成多个分区(组),它的作用类似于GROUP BY分组。如果省略了 PARTITION BY,所有的数据作为一个组进行计算
排序(ORDER BY)
OVER 子句中的ORDER BY选项用于指定分区内的排序方式,与 ORDER BY 子句的作用类似
以及窗口大小(frame_clause)。
frame_clause选项用于在当前分区内指定一个计算窗口,也就是一个与当前行相关的数据子集。
1 序号函数
序号函数有三个:ROW_NUMBER()、RANK()、DENSE_RANK(),可以用来实现分组排序,并添加序号。
1.1建表
use mydb4;
create table employee(
dname varchar(20), -- 部门名
eid varchar(20),
ename varchar(20),
hiredate date, -- 入职日期
salary double -- 薪资
);
insert into employee values('研发部','1001','刘备','2021-11-01',3000);
insert into employee values('研发部','1002','关羽','2021-11-02',5000);
insert into employee values('研发部','1003','张飞','2021-11-03',7000);
insert into employee values('研发部','1004','赵云','2021-11-04',7000);
insert into employee values('研发部','1005','马超','2021-11-05',4000);
insert into employee values('研发部','1006','黄忠','2021-11-06',4000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1007','曹操','2021-11-01',2000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1008','许褚','2021-11-02',3000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1009','典韦','2021-11-03',5000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1010','张辽','2021-11-04',6000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1011','徐晃','2021-11-05',9000);
insert into employee values('销售部','1012','曹洪','2021-11-06',6000);
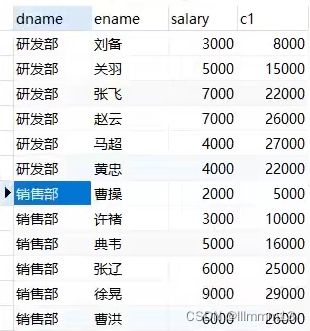
ROW_NUMBER() ,根据分组和条件给出排名,排名不重复
-- 对每个部门的员工按照薪资排序,并给出排名
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
row_number() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn
from employee;
-- 对每个部门的员工按照薪资排序,并给出排名 rank
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
rank() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn
from employee;

dense-rank 根据分组和排序给出排名,可以并列,相对排名
-- 对每个部门的员工按照薪资排序,并给出排名 dense-rank
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
dense_rank() over(partition by dname order by salary desc) as rn
from employee;
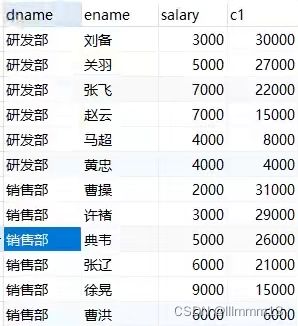
2开窗聚合函数- SUM,AVG,MIN,MAX
在窗口中每条记录动态地应用聚合函数(SUM()、AVG()、MAX()、MIN()、COUNT()),可以动态计算在指定的窗口内的各种聚合函数值。
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as pv1
from employee;-- 累加
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname ) as c1
from employee; -- 如果没有order by排序语句 默认把分组内的所有数据进行sum操作
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as c1
from employee;
-- 从首行到当前行 默认
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between 3 preceding and current row) as c1
from employee;
-- 前三行到当前行
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between 3 preceding and 1 following) as c1
from employee; -- 前三行到当前行的后一行 08
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
sum(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate rows between current row and unbounded following) as c1
from employee; -- 当前行到最后一行
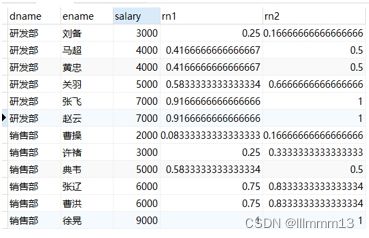
3:CUME_DIST
用途:分组内小于、等于当前rank值的行数 / 分组内总行数
应用场景:查询小于等于当前薪资(salary)的比例
select
dname,
ename,
salary,
cume_dist() over(order by salary) as rn1, -- 没有partition语句 所有的数据位于一组
cume_dist() over(partition by dept order by salary) as rn2
from employee;
/*
rn1: 没有partition,所有数据均为1组,总行数为12,
第一行:小于等于3000的行数为3,因此,3/12=0.25
第二行:小于等于4000的行数为5,因此,5/12=0.4166666666666667
rn2: 按照部门分组,dname='研发部'的行数为6,
第一行:研发部小于等于3000的行数为1,因此,1/6=0.16666666666666666
*/
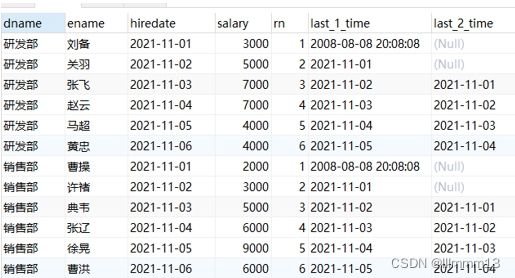
4:前后函数-LAG和LEAD
用途:返回位于当前行的前n行(LAG(expr,n))或后n行(LEAD(expr,n))的expr的值
应用场景:查询前1名同学的成绩和当前同学成绩的差值
-- lag的用法
select
dname,
ename,
hiredate,
salary,
lag(hiredate,1,'2000-01-01') over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last_1_time,
lag(hiredate,2) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last_2_time
from employee;
/*
last_1_time: 指定了往上第1行的值,default为'2000-01-01'
第一行,往上1行为null,因此取默认值 '2000-01-01'
第二行,往上1行值为第一行值,2021-11-01
第三行,往上1行值为第二行值,2021-11-02
last_2_time: 指定了往上第2行的值,为指定默认值
第一行,往上2行为null
第二行,往上2行为null
第四行,往上2行为第二行值,2021-11-01
第七行,往上2行为第五行值,2021-11-02
*/
-- lead的用法
select
dname,
ename,
hiredate,
salary,
lead(hiredate,1,'2000-01-01') over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last_1_time,
lead(hiredate,2) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last_2_time
from employee;
5:头尾函数-FIRST_VALUE和LAST_VALUE
用途:返回第一个(FIRST_VALUE(expr))或最后一个(LAST_VALUE(expr))expr的值
应用场景:截止到当前,按照日期排序查询第1个入职和最后1个入职员工的薪资
-- 注意, 如果不指定ORDER BY,则进行排序混乱,会出现错误的结果
select
dname,
ename,
hiredate,
salary,
first_value(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as first,
last_value(salary) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as last
from employee;
6:其他函数-NTH_VALUE(expr, n)、NTILE(n)NTILE(n)
用途:返回窗口中第n个expr的值。expr可以是表达式,也可以是列名
应用场景:截止到当前薪资,显示每个员工的薪资中排名第2或者第3的薪资
select
dname,
ename,
hiredate,
salary,
nth_value(salary,2) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as second_score,
nth_value(salary,3) over(partition by dname order by hiredate) as third_score
from employee

用途:将分区中的有序数据分为n个等级,记录等级数
应用场景:将每个部门员工按照入职日期分成3组
-- 根据入职日期将每个部门的员工分成3组
select
dname,
ename,
hiredate,
salary,
ntile(3) over(partition by dname order by hiredate ) as rn
from employee;

– 参考黑马程序员MySQL8.0笔记
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iF411z7Pu?p=91&vd_source=35b9993ef3832fde8685bbd472249b91