- 《STL基础之hashtable》
边城梦溪
c++开发语言stlhashtable面试
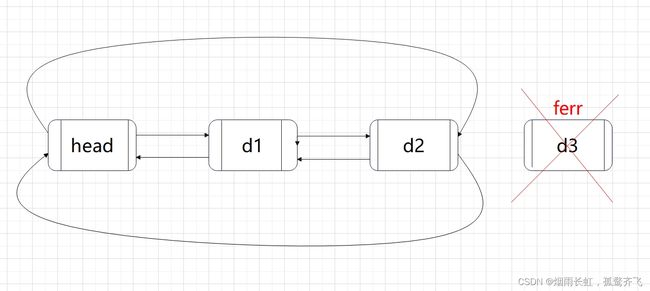
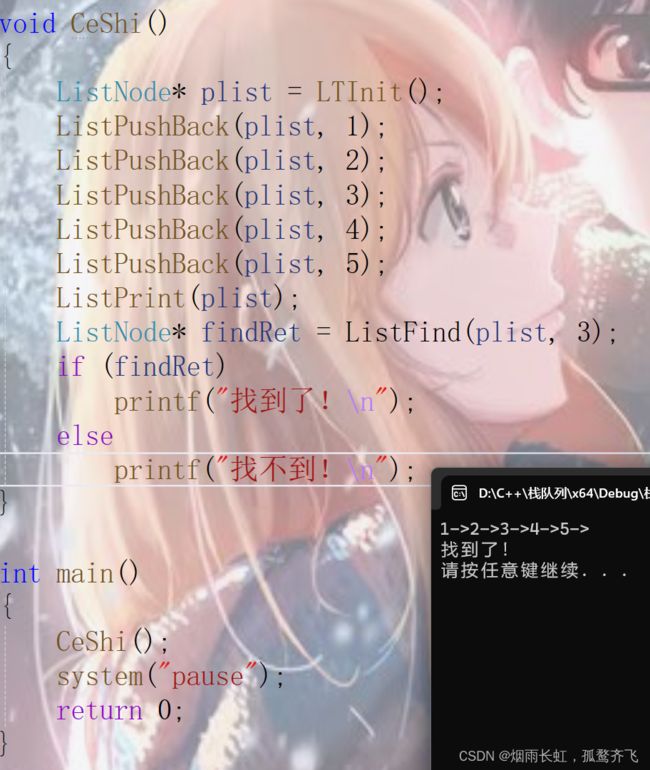
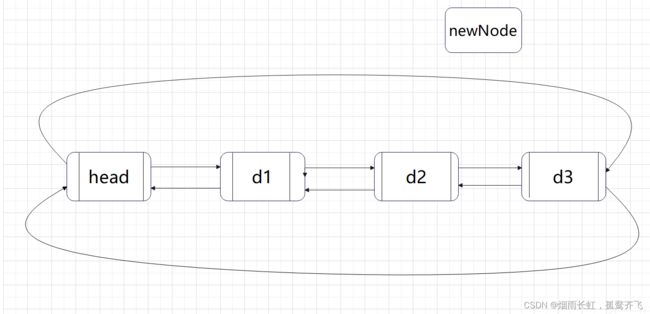
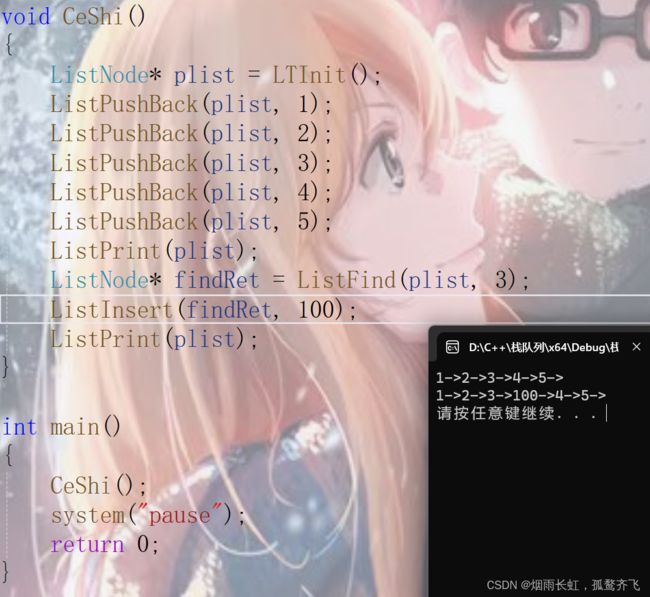
【hashtable导读】STL为大家提供了丰富的容器,hashtable也是值得大家学习和掌握的基础容器,而且面试官经常会把它和hashmap混在一起,让同学们做下区分。因此关于hashtable的一些特性,比如:底层的数据结构、插入、查找元素的时间复杂度,这些很有必要和大家一起分享下。开门见山,hashtable设计的初衷就是为了方便元素的快速插入、查找,到底有多快速呢?查找、删除元素的时间复
- 【C语言】常用字符串函数大盘点
橘猫.exe
C语言c语言算法开发语言
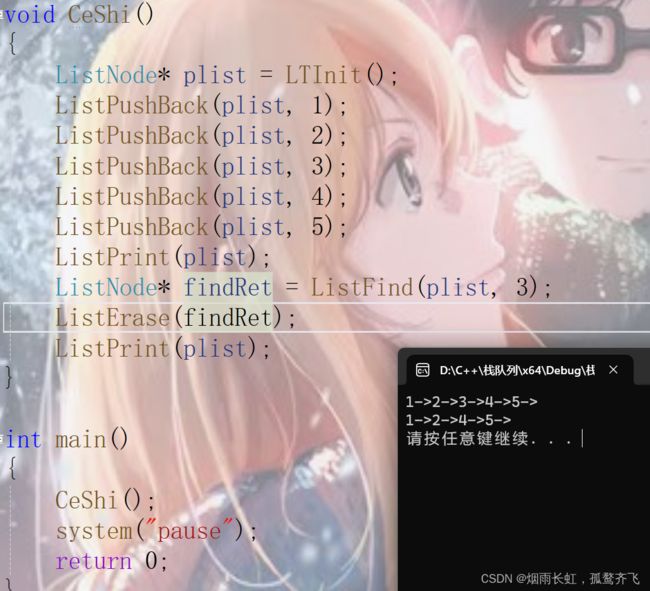
【C语言】常用字符串函数大盘点文章目录【C语言】常用字符串函数大盘点1.字符串的基本概念2.常用字符串函数2.1字符串长度和复制2.2字符串连接2.3字符串比较2.4字符串搜索2.5字符串修改2.6字符串到数字的转换-atoi,atol,strtol2.7数字到字符串的转换-`itoa`(非标准,需要自定义实现)3.使用字符串函数的注意事项C语言提供了一组标准库函数,用于处理字符串,这些函数定义在
- 21. Ubuntu 交叉编译工具链安装
lljss2020
Linux
交叉编译器安装ARM裸机、Uboot移植、Linux移植这些都需要在Ubuntu下进行编译,编译就需要编译器,我们在第三章“LinuxC编程入门”里面已经讲解了如何在Liux进行C语言开发,里面使用GCC编译器进行代码编译,但是Ubuntu自带的gcc编译器是针对X86架构的!而我们现在要编译的是ARM架构的代码,所以我们需要一个在X86架构的PC上运行,可以编译ARM架构代码的GCC编译器,这个
- 生成树生成森林c语言中文网,生成树协议(STP)基本知识及实验(使用eNSP)
飞翔的十号
生成树生成森林c语言中文网
1、基本知识--摘至《网络之路--交换专题》(1)生成树的作用:在链路层消除环路上可能出现的广播风暴。(2)生成树的工作由三部分组成:选举过程、拓扑计算、端口行为确定。选举过程:在二层网络中选举一个网桥作为根桥,用于指挥整网设备协同工作。根桥只是负责统一计算的规则。根桥统一网络中所有网桥的行为准则的原理:通过在某个恰当位置阻塞端口来阻止环路的发生。从一台网桥的角度来说,它通过这样的法则进行判断,如
- .cc扩展名是什么语言?C语言必须用.c为扩展名吗?主流编程语言扩展名?Java为什么不能用全数字的文件名?
程序员小迷
编程语言小话c语言Javac语言开发语言javaswiftobjective-cc++扩展名
.cc扩展名是什么语言?.cc是C++语言使用的扩展名,一种说法是它是cwithclass的简写,当然C++语言使用的扩展名不止.cc和.cpp,还包含.cxx,.c++,.C等,这些在不同编译器系统采用的默认设定不同,需要区分使用。当然,编译器提供编译选项将源代码指定为特定编程语言的方式,例如gcc提供-xc++将源代码指定为c++代码,哪怕源代码扩展名是.java也会被当做c++代码。关于.c
- Effective Objective-C 2.0 读书笔记
chidu8866
内存管理移动开发c/c++
EffectiveObjective-C2.0编写高质量iOS与OSX代码的52个有效方法第1章熟悉Objective-C第1条:了解Objective-C语言的起源第2条:在类的头文件中尽量少引入其他头文件需要引入许多用不到的内容,增加编译时间循环引用,使用import不会像include那样发生编译死循环,但是会导致两个类中有一个类无法被正确编译第3条:多用字面量好处缩减代码长度,更易读使用下
- 8644 堆排序
软工在逃男大学生
SCAU_OJ_DS算法数据结构c++c语言
SCAU数据结构OJ第六章文章目录8644堆排序8644堆排序Description用函数实现堆排序,并输出每趟排序的结果输入格式第一行:键盘输入待排序关键的个数n第二行:输入n个待排序关键字,用空格分隔数据输出格式第一行:初始建堆后的结果其后各行输出交换堆顶元素并调整堆的结果,数据之间用一个空格分隔输入样例105480932671输出样例97864325018736412509763541208
- 【C语言基础习题】C语言练习题——bite 寒假班作业(8)
拾贰_C
【bite就业课】作业习题c语言算法开发语言
你是如何克服编程学习中的挫折感的?编程学习之路上,挫折感就像一道道难以逾越的高墙,让许多人望而却步。然而,真正的编程高手都曾在这条路上跌倒过、迷茫过,却最终找到了突破的方法。你是如何在Bug的迷宫中找到出口的?面对复杂的算法时,你用什么方法让自己保持冷静?让我们一起分享那些克服挫折的经验,为彼此的编程之路点亮希望之光!2024-01-31_debug和release的区别等_作业文章目录你是如何克
- 【C语言基础习题】C语言练习题——bite 寒假班作业(7)
拾贰_C
【bite就业课】作业习题c语言算法开发语言
如何高效记录并整理编程学习笔记?在编程学习的海洋中,高效的笔记记录和整理方法就像一张珍贵的航海图,能够帮助我们在浩瀚的知识中找到方向。如何建立一个既能快速记录又易于回顾的笔记系统?如何在繁忙的学习中保持笔记的条理性?让我们一起探讨如何打造属于自己的编程学习“知识宝库”!2024-01-28_函数的概念等_作业文章目录如何高效记录并整理编程学习笔记?2024-01-28_函数的概念等_作业习题第1题
- 【C语言基础习题】C语言练习题——bite 寒假班作业(3)
拾贰_C
c语言开发语言
AI是在帮助开发者还是取代他们?在软件开发领域,生成式人工智能(AIGC)正在改变开发者的工作方式。无论是代码生成、错误检测还是自动化测试,AI工具正在成为开发者的得力助手。然而,这也引发了对开发者职业前景和技能需求变化的讨论。AI究竟是在帮助开发者还是取代他们?提醒:在发布作品前,请把不需要的内容删掉。方向一:AI工具现状提示:介绍当前市场上的主要AI开发工具,如GitHubCopilot、Ta
- 【C语言基础习题】C语言练习题——bite 寒假班作业(4)
拾贰_C
c语言算法开发语言
C语言练习题——bite寒假班作业(4)题目第1题(单选题)题目名称:下面代码执行的结果是:()#includeintmain(){inti=0;for(i=0;iintmain(){intcount=0;//打印1-100之间所有3的倍数的数字for(inti=1;iintmain(){inta,b,c,tmp;scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);//max=a>b?a,a=b:b
- 【C语言基础习题】C语言练习题——bite 寒假班作业(2)
拾贰_C
【bite就业课】作业习题c语言人工智能大数据
GPT-5一年半后发布?对此你有何期待?IT之家6月22日消息,在美国达特茅斯工程学院周四公布的采访中,OpenAI首席技术官米拉·穆拉蒂被问及GPT-5是否会在明年发布,给出了肯定答案并表示将在一年半后发布。此外,穆拉蒂在采访中还把GPT-4到GPT-5的飞跃描述为高中生到博士生的成长。“像GPT-4这样的系统则更像是聪明的高中生智力水平,在接下来的几年里,我们期待在特定任务上达到博士的智力水平
- 刷题前必学!栈与队列!用JavaScript学数据结构与算法
JavaScript数据结构与算法-HowieCong务必要熟悉JavaScript使用再来学!一、数组增删操作在了解栈和队列前,明确数组中的增删操作具有什么样的特性、对应的方法有哪些:灵活增删的数组数组增加元素的三种方法:unshift方法,添加元素到数组的头部constarr=[1,2]arr.unshift(0)//[0,1,2]push方法,添加元素到数组的尾部constarr=[1,2
- 揭秘C语言中的堆:构建与管理艺术
就爱学编程
新星杯c语言数据结构
大家好,这里是小编的博客频道小编的博客:就爱学编程很高兴在CSDN这个大家庭与大家相识,希望能在这里与大家共同进步,共同收获更好的自己!!!本文目录正文一、堆的基本概念二、堆的存储表示三、堆的基本操作1.插入元素(Insert)2.删除最大/最小值(ExtractMax/Min)3.构建堆(BuildHeap)四、源码(1)heap.h(2)heap.c(3)Test.c五、堆的应用1.优先队列2
- 7个改变python金融分析神奇库
python茶水实验室
python金融开发语言数据结构beautifulsoupscikit-learnscrapy
理解几个常用的Python金融分析库对于金融数据处理和分析非常重要。以下是几个常用的Python金融分析库的介绍和理解方法:1.Pandas用途:用于数据操作和分析。功能:提供数据结构和数据分析工具,尤其适用于时间序列数据。如何学习:基础知识:熟悉DataFrame和Series,学习如何导入和导出数据。数据操作:掌握数据清洗、数据变换、数据聚合等操作。时间序列分析:了解如何处理和分析时间序列数据
- C语言之降序数
CAFE~BABE
刷题纪录
C语言之降序数一到考试就紧张,之前写过的题都过不去了。这里做一下提醒。代码#include#includeintmain(void){intn;scanf("%d",&n);intb=n%10;inta=n;while((a/10)>0)//这里卡了半天。最开始直接写的是n,太傻了。{a=a/10;if(a%10<=b){printf("NO");exit(0);//exit可以直接跳出,要加st
- redis的内部编码和数据结构类型
Chsavvy
redisredis数据结构nosql
1.redis原理reids使用了单线程架构和I/O多路复用模型来实现性能的内存数据库服务2.简化的工作流程发送命令,执行命令,返回结果3.单线程处理但处理快速的原因纯内存访问非阻塞I/O,redis使用epoll作为I/O多路复用技术单线程避免了线程切换和竞态产生的消耗redis内部编码1)string内部编辑raw:大于的39个字节的字符串int:8个字节的长整型embstr:小于等于39个字
- 【某大厂一面】JDK1.8中对HashMap数据结构进行了哪些优化
冰糖心158
2025Java面试系列数据结构java
在JDK1.8中,HashMap数据结构进行了重要的优化。相较于之前版本,JDK1.8引入了许多改进,提升了性能,尤其是在高负载的情况下。以下是JDK1.8中HashMap数据结构的关键优化。1.链表转化为红黑树在JDK1.8之前,HashMap使用链表来解决哈希冲突,即多个元素哈希值相同时,它们会被存储在同一个桶中,并通过链表(LinkedList)来连接。这个设计虽然简单,但当哈希冲突非常严重
- Java基础知识总结(二十二)--List接口
a18007931080
javalist开发语言
List本身是Collection接口的子接口,具备了Collection的所有方法。现在学习List体系特有的共性方法,查阅方法发现List的特有方法都有索引,这是该集合最大的特点。List:有序(元素存入集合的顺序和取出的顺序一致),元素都有索引。元素可以重复。|--ArrayList:底层的数据结构是数组,线程不同步,ArrayList替代了Vector,查询元素的速度非常快。|--Link
- C++,STL 简介:历史、组成、优势
智驾
C/C++c++开发语言STL
文章目录引言一、STL的历史STL的核心组成三、STL的核心优势四、结语进一步学习资源:引言C++是一门强大且灵活的编程语言,但其真正的魅力之一在于其标准库——尤其是标准模板库(StandardTemplateLibrary,STL)。STL提供了一系列高效的数据结构和算法,极大地简化了开发者的工作。无论是处理复杂的数据操作,还是优化代码性能,STL都已成为C++开发中不可或缺的工具。本文将带您了
- C 语言中的 char 关键字详解
嘻嘻爱编码
开发语言c语言
1.char类型char类型用于存储单个字符,占用1个字节的内存空间。在C语言中,char类型可以用于存储ASCII码表中的任意字符,包括大小写字母、数字、标点符号等。例如:charch='A';在这个例子中,变量ch存储了字符'A'的ASCII码值。需要注意的是,在C语言中,字符常量实际上是整型常量,因此可以进行数学运算和比较操作。2.char类型的存储范围char类型占用1个字节的内存空间,它
- 深入探索数据库世界:SQLite、Redis、MySQL 与数据库设计范式
巴依老爷coder
数据库数据库sqliteredis网络安全mysqlsqldatabase
数据库深入探索数据库世界:SQLite、Redis、MySQL与数据库设计范式一、SQLite数据库全方位解析(一)创建与基本操作(二)数据存储与表结构设计(三)数据操作:增删改查(四)与C语言联合使用(五)防止SQL注入二、Redis数据库深度剖析(一)数据存储类型与独特结构(二)数据持久化策略(三)卓越性能表现与应用场景三、MySQL数据库概览(一)创建数据库与表(二)数据操作与C语言交互四、
- 类加载的过程
码农小旋风
后端
类加载的过程类加载过程包括5个阶段:加载、验证、准备、解析和初始化。加载加载的过程“加载”是“类加载”过程的一个阶段,不能混淆这两个名词。在加载阶段,虚拟机需要完成3件事:通过类的全限定名获取该类的二进制字节流。将二进制字节流所代表的静态结构转化为方法区的运行时数据结构。在内存中创建一个代表该类的java.lang.Class对象,作为方法区这个类的各种数据的访问入口。获取二进制字节流对于Clas
- .rds 文件数据结构 和内容 查看方法
Bio Coder
空间转录组&单细胞数据结构R语言.rds数据格式内容
要查看.rds文件中的数据结构和内容,可以按照以下步骤操作:1.加载.rds文件:使用readRDS()函数将.rds文件加载到R环境中:#加载.rds文件my_data<-readRDS("path/to/yourfile.rds")2.检查数据结构:加载文件后,可以使用几种常见的R函数来检查其数据结构:str():用于查看对象的结构和类型。该函数会显示对象的内部结构,包括类型、变量及其内容的摘
- Objective-C语言的软件工程
慕璃嫣
包罗万象golang开发语言后端
Objective-C语言的软件工程引言在软件工程的领域中,编程语言的选择至关重要。随着技术的不断进步,开发者面临着各种编程语言的选择。其中,Objective-C作为一种成熟且广泛应用的编程语言,尤其是在苹果生态系统中,仍然扮演着重要的角色。本文将从多个方面探讨Objective-C语言在软件工程中的应用,包括历史背景、核心特性、开发流程及其在现代开发环境中的地位。一、Objective-C的历
- 第十七题:电话号码的字母组合
冰魄雕狼
leetcode算法leetcodec语言pythonjava数据结构
题目描述给定一个仅包含数字2-9的字符串,返回所有可能的由它组成的字母组合。你可以假设输入字符串至少包含一个数字,并且不超过3位数字。实现思路使用哈希表或数组存储每个数字对应的字符,然后通过递归或迭代的方式生成所有可能的组合。如果字符串长度为n,则可以看作是n层循环,每层循环可以选择对应数字的所有字符之一。算法实现C语言实现#include#include#includevoidbacktrack
- 数据结构【时间复杂度、空间复杂度--1】
北方留意尘
数据结构c语言后端数据结构算法
目录数据结构前言1.算法的复杂度2.时间复杂度2.1时间复杂度的概念2.2大O的渐进表示法2.3时间复杂度存在最好、平均和最坏情况2.4常见时间复杂度计算举例3.空间复杂度注意:时间累积(一去不复返),空间不累计(可重复利用)4.常见时间复杂度以及复杂度oj练习数据结构前言什么是数据结构?数据结构(DataStructure)是计算机存储、组织数据的方式,指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素
- TensorFlow 简介
九月十九
tensorflow人工智能python
TensorFlow是一个开源的机器学习框架,由Google开发。它提供了一个强大的工具集,用于构建和训练各种机器学习模型。TensorFlow的基本概念和使用场景包括:1.张量(Tensor):TensorFlow中的核心数据结构是张量,它是一个多维数组,可以表示标量、向量、矩阵等。2.计算图(Graph):TensorFlow使用计算图来表示机器学习模型的计算过程。计算图由一系列的操作节点和数
- python——格式化输出
pumpkin84514
python相关python
Python提供了多种格式化输出的方法,常见的有以下几种:百分号(%)格式化str.format()方法f-string(格式化字符串字面量)模板字符串每种方法都有其独特的用法和适用场景。下面我们逐一详细讲解并举例说明。1.百分号(%)格式化这种方法类似于C语言中的printf格式,使用百分号(%)作为占位符。用法%s:字符串%d:整数%f:浮点数%%:百分号示例name="Alice"age=3
- 指针(C语言)从0到1掌握指针,为后续学习c++打下基础
Hou'
c语言开发语言
目录一,指针二,内存地址和指针1,什么是内存地址2,指针在不同系统下所占内存三,指针的声明和初始化以及类型1,指针的声明2,指针的初始化1,初始化方式优点及适用场景4,指针的声明初始化类型四,野指针(永远都要避免)1,野指针的定义2,野指针产生的原因1,指针没有初始化2,释放内存后未置空3.局部变量超出作用域3,野指针的危害4,如何避免野指针五,取地址符和解引用1,取地址符&2,解引用*六,指针的
- 解读Servlet原理篇二---GenericServlet与HttpServlet
周凡杨
javaHttpServlet源理GenericService源码
在上一篇《解读Servlet原理篇一》中提到,要实现javax.servlet.Servlet接口(即写自己的Servlet应用),你可以写一个继承自javax.servlet.GenericServletr的generic Servlet ,也可以写一个继承自java.servlet.http.HttpServlet的HTTP Servlet(这就是为什么我们自定义的Servlet通常是exte
- MySQL性能优化
bijian1013
数据库mysql
性能优化是通过某些有效的方法来提高MySQL的运行速度,减少占用的磁盘空间。性能优化包含很多方面,例如优化查询速度,优化更新速度和优化MySQL服务器等。本文介绍方法的主要有:
a.优化查询
b.优化数据库结构
- ThreadPool定时重试
dai_lm
javaThreadPoolthreadtimertimertask
项目需要当某事件触发时,执行http请求任务,失败时需要有重试机制,并根据失败次数的增加,重试间隔也相应增加,任务可能并发。
由于是耗时任务,首先考虑的就是用线程来实现,并且为了节约资源,因而选择线程池。
为了解决不定间隔的重试,选择Timer和TimerTask来完成
package threadpool;
public class ThreadPoolTest {
- Oracle 查看数据库的连接情况
周凡杨
sqloracle 连接
首先要说的是,不同版本数据库提供的系统表会有不同,你可以根据数据字典查看该版本数据库所提供的表。
select * from dict where table_name like '%SESSION%';
就可以查出一些表,然后根据这些表就可以获得会话信息
select sid,serial#,status,username,schemaname,osuser,terminal,ma
- 类的继承
朱辉辉33
java
类的继承可以提高代码的重用行,减少冗余代码;还能提高代码的扩展性。Java继承的关键字是extends
格式:public class 类名(子类)extends 类名(父类){ }
子类可以继承到父类所有的属性和普通方法,但不能继承构造方法。且子类可以直接使用父类的public和
protected属性,但要使用private属性仍需通过调用。
子类的方法可以重写,但必须和父类的返回值类
- android 悬浮窗特效
肆无忌惮_
android
最近在开发项目的时候需要做一个悬浮层的动画,类似于支付宝掉钱动画。但是区别在于,需求是浮出一个窗口,之后边缩放边位移至屏幕右下角标签处。效果图如下:
一开始考虑用自定义View来做。后来发现开线程让其移动很卡,ListView+动画也没法精确定位到目标点。
后来想利用Dialog的dismiss动画来完成。
自定义一个Dialog后,在styl
- hadoop伪分布式搭建
林鹤霄
hadoop
要修改4个文件 1: vim hadoop-env.sh 第九行 2: vim core-site.xml <configuration> &n
- gdb调试命令
aigo
gdb
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/hanchaoman/article/details/5517362
一、GDB常用命令简介
r run 运行.程序还没有运行前使用 c cuntinue
- Socket编程的HelloWorld实例
alleni123
socket
public class Client
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Client c=new Client();
c.receiveMessage();
}
public void receiveMessage(){
Socket s=null;
BufferedRea
- 线程同步和异步
百合不是茶
线程同步异步
多线程和同步 : 如进程、线程同步,可理解为进程或线程A和B一块配合,A执行到一定程度时要依靠B的某个结果,于是停下来,示意B运行;B依言执行,再将结果给A;A再继续操作。 所谓同步,就是在发出一个功能调用时,在没有得到结果之前,该调用就不返回,同时其它线程也不能调用这个方法
多线程和异步:多线程可以做不同的事情,涉及到线程通知
&
- JSP中文乱码分析
bijian1013
javajsp中文乱码
在JSP的开发过程中,经常出现中文乱码的问题。
首先了解一下Java中文问题的由来:
Java的内核和class文件是基于unicode的,这使Java程序具有良好的跨平台性,但也带来了一些中文乱码问题的麻烦。原因主要有两方面,
- js实现页面跳转重定向的几种方式
bijian1013
JavaScript重定向
js实现页面跳转重定向有如下几种方式:
一.window.location.href
<script language="javascript"type="text/javascript">
window.location.href="http://www.baidu.c
- 【Struts2三】Struts2 Action转发类型
bit1129
struts2
在【Struts2一】 Struts Hello World http://bit1129.iteye.com/blog/2109365中配置了一个简单的Action,配置如下
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configurat
- 【HBase十一】Java API操作HBase
bit1129
hbase
Admin类的主要方法注释:
1. 创建表
/**
* Creates a new table. Synchronous operation.
*
* @param desc table descriptor for table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the table name is res
- nginx gzip
ronin47
nginx gzip
Nginx GZip 压缩
Nginx GZip 模块文档详见:http://wiki.nginx.org/HttpGzipModule
常用配置片段如下:
gzip on; gzip_comp_level 2; # 压缩比例,比例越大,压缩时间越长。默认是1 gzip_types text/css text/javascript; # 哪些文件可以被压缩 gzip_disable &q
- java-7.微软亚院之编程判断俩个链表是否相交 给出俩个单向链表的头指针,比如 h1 , h2 ,判断这俩个链表是否相交
bylijinnan
java
public class LinkListTest {
/**
* we deal with two main missions:
*
* A.
* 1.we create two joined-List(both have no loop)
* 2.whether list1 and list2 join
* 3.print the join
- Spring源码学习-JdbcTemplate batchUpdate批量操作
bylijinnan
javaspring
Spring JdbcTemplate的batch操作最后还是利用了JDBC提供的方法,Spring只是做了一下改造和封装
JDBC的batch操作:
String sql = "INSERT INTO CUSTOMER " +
"(CUST_ID, NAME, AGE) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
- [JWFD开源工作流]大规模拓扑矩阵存储结构最新进展
comsci
工作流
生成和创建类已经完成,构造一个100万个元素的矩阵模型,存储空间只有11M大,请大家参考我在博客园上面的文档"构造下一代工作流存储结构的尝试",更加相信的设计和代码将陆续推出.........
竞争对手的能力也很强.......,我相信..你们一定能够先于我们推出大规模拓扑扫描和分析系统的....
- base64编码和url编码
cuityang
base64url
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
- web应用集群Session保持
dalan_123
session
关于使用 memcached 或redis 存储 session ,以及使用 terracotta 服务器共享。建议使用 redis,不仅仅因为它可以将缓存的内容持久化,还因为它支持的单个对象比较大,而且数据类型丰富,不只是缓存 session,还可以做其他用途,一举几得啊。1、使用 filter 方法存储这种方法比较推荐,因为它的服务器使用范围比较多,不仅限于tomcat ,而且实现的原理比较简
- Yii 框架里数据库操作详解-[增加、查询、更新、删除的方法 'AR模式']
dcj3sjt126com
数据库
public function getMinLimit () { $sql = "..."; $result = yii::app()->db->createCo
- solr StatsComponent(聚合统计)
eksliang
solr聚合查询solr stats
StatsComponent
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2169134
http://eksliang.iteye.com/ 一、概述
Solr可以利用StatsComponent 实现数据库的聚合统计查询,也就是min、max、avg、count、sum的功能
二、参数
- 百度一道面试题
greemranqq
位运算百度面试寻找奇数算法bitmap 算法
那天看朋友提了一个百度面试的题目:怎么找出{1,1,2,3,3,4,4,4,5,5,5,5} 找出出现次数为奇数的数字.
我这里复制的是原话,当然顺序是不一定的,很多拿到题目第一反应就是用map,当然可以解决,但是效率不高。
还有人觉得应该用算法xxx,我是没想到用啥算法好...!
还有觉得应该先排序...
还有觉
- Spring之在开发中使用SpringJDBC
ihuning
spring
在实际开发中使用SpringJDBC有两种方式:
1. 在Dao中添加属性JdbcTemplate并用Spring注入;
JdbcTemplate类被设计成为线程安全的,所以可以在IOC 容器中声明它的单个实例,并将这个实例注入到所有的 DAO 实例中。JdbcTemplate也利用了Java 1.5 的特定(自动装箱,泛型,可变长度
- JSON API 1.0 核心开发者自述 | 你所不知道的那些技术细节
justjavac
json
2013年5月,Yehuda Katz 完成了JSON API(英文,中文) 技术规范的初稿。事情就发生在 RailsConf 之后,在那次会议上他和 Steve Klabnik 就 JSON 雏形的技术细节相聊甚欢。在沟通单一 Rails 服务器库—— ActiveModel::Serializers 和单一 JavaScript 客户端库——&
- 网站项目建设流程概述
macroli
工作
一.概念
网站项目管理就是根据特定的规范、在预算范围内、按时完成的网站开发任务。
二.需求分析
项目立项
我们接到客户的业务咨询,经过双方不断的接洽和了解,并通过基本的可行性讨论够,初步达成制作协议,这时就需要将项目立项。较好的做法是成立一个专门的项目小组,小组成员包括:项目经理,网页设计,程序员,测试员,编辑/文档等必须人员。项目实行项目经理制。
客户的需求说明书
第一步是需
- AngularJs 三目运算 表达式判断
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境众观千象AngularJS
事件回顾:由于需要修改同一个模板,里面包含2个不同的内容,第一个里面使用的时间差和第二个里面名称不一样,其他过滤器,内容都大同小异。希望杜绝If这样比较傻的来判断if-show or not,继续追究其源码。
var b = "{{",
a = "}}";
this.startSymbol = function(a) {
- Spark算子:统计RDD分区中的元素及数量
superlxw1234
sparkspark算子Spark RDD分区元素
关键字:Spark算子、Spark RDD分区、Spark RDD分区元素数量
Spark RDD是被分区的,在生成RDD时候,一般可以指定分区的数量,如果不指定分区数量,当RDD从集合创建时候,则默认为该程序所分配到的资源的CPU核数,如果是从HDFS文件创建,默认为文件的Block数。
可以利用RDD的mapPartitionsWithInd
- Spring 3.2.x将于2016年12月31日停止支持
wiselyman
Spring 3
Spring 团队公布在2016年12月31日停止对Spring Framework 3.2.x(包含tomcat 6.x)的支持。在此之前spring团队将持续发布3.2.x的维护版本。
请大家及时准备及时升级到Spring
- fis纯前端解决方案fis-pure
zccst
JavaScript
作者:zccst
FIS通过插件扩展可以完美的支持模块化的前端开发方案,我们通过FIS的二次封装能力,封装了一个功能完备的纯前端模块化方案pure。
1,fis-pure的安装
$ fis install -g fis-pure
$ pure -v
0.1.4
2,下载demo到本地
git clone https://github.com/hefangshi/f