Java数组的遍历
目录
- 数组的遍历
-
- 使用for循环遍历数组
- 使用for-each循环遍历数组
- 使用while循环和迭代器遍历数组
- 使用Java 8的流API遍历数组
- 数组遍历的应用
-
- 求数组中的最大值
- 查询数组中指定位置的元素
- 将查指定元素对应的索引的功能提取为方法
- 添加数组元素
- 删除数组元素
数组的遍历
Java数组的遍历可以使用循环结构来实现。以下是一些常见的遍历数组的方法:
使用for循环遍历数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
使用for-each循环遍历数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int element : arr) {
System.out.println(element);
}
使用while循环和迭代器遍历数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Iterator<Integer> iterator = Arrays.asList(arr).iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
使用Java 8的流API遍历数组
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Arrays.stream(arr).forEach(System.out::println);
数组遍历的应用
求数组中的最大值
在Java中,你可以使用一个简单的for循环来遍历数组并找到最大值。以下是一个示例代码:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 5, 9, 3, 7};
int maxValue = arr[0]; // 假设第一个元素是最大的
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > maxValue) {
maxValue = arr[i]; // 如果当前元素大于maxValue,则更新maxValue
}
}
System.out.println(maxValue); // 输出: 9
}
}
在这段代码中,我们假设数组的第一个元素是最大的。然后,我们遍历数组的其余部分,如果当前元素大于maxValue,则更新maxValue。最后,maxValue就是数组中的最大值。
查询数组中指定位置的元素
在Java中,如果你想查询数组中指定位置的元素,你可以使用数组索引。数组索引从0开始,所以如果你想查询第n个元素,你应该使用索引n-1。以下是一个简单的示例:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 5, 9, 3, 7};
int index = 2; // 指定位置
int element = arr[index]; // 查询指定位置的元素
System.out.println(element); // 输出: 9
}
}
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个包含5个元素的整数数组。然后,我们指定要查询的位置(在这个例子中是第2个位置),并使用该位置的索引来获取该位置的元素。最后,我们将元素打印出来,以验证我们的查询结果。
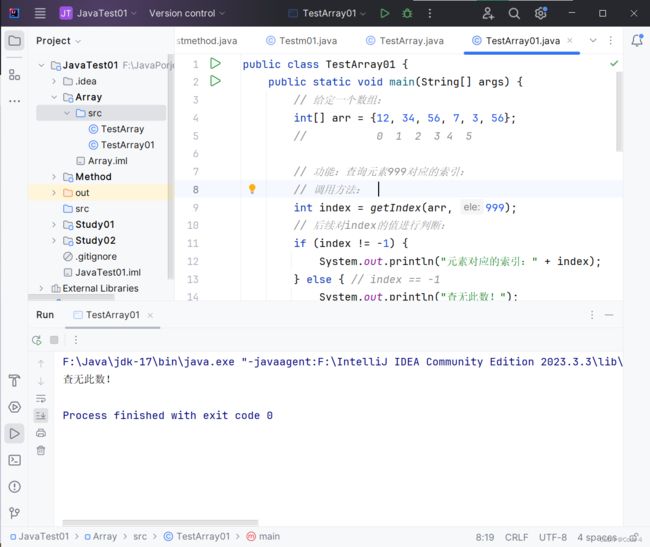
将查指定元素对应的索引的功能提取为方法
public class TestArray01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 给定一个数组:
int[] arr = {12, 34, 56, 7, 3, 56};
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
// 功能:查询元素999对应的索引:
// 调用方法:
int index = getIndex(arr, 999);
// 后续对index的值进行判断:
if (index != -1) {
System.out.println("元素对应的索引:" + index);
} else { // index == -1
System.out.println("查无此数!");
}
}
/*
定义一个方法:查询数组中指定的元素对应的索引:
不确定因素:哪个数组,哪个指定元素 (形参)
返回值:索引
*/
public static int getIndex(int[] arr, int ele) {
int index = -1; // 这个初始值只要不是数组的索引即可
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == ele) {
index = i; // 只要找到了元素,那么index就变成为i
break; // 只要找到这个元素,循环就停止
}
}
return index;
}
}
添加数组元素
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestArray02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 功能:给定一个数组,在数组下标为5的位置上添加一个元素91
// 1. 给定一个数组:
int[] arr = {12, 34, 56, 7, 3, 10, 55, 66, 77, 88, 999, 89};
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
// 2. 输出增加元素前的数组:
System.out.print("增加元素前的数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + ",");
} else { // i == arr.length-1 最后一个元素不用加,
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
// 从键盘接收数据:
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入你要添加元素的指定下标:");
int index = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请录入你要添加的元素:");
int ele = sc.nextInt();
// 3. 增加元素
// 调用方法:
insertEle(arr, index, ele);
// 4. 输出增加元素后的数组:
System.out.print("\n增加元素后的数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i != arr.length - 1) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + ",");
} else { // i == arr.length-1 最后一个元素不用加,
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
}
/*
提取一个添加元素的方法:
在数组的指定位置上添加一个指定的元素。
在哪个数组的哪个位置添加哪个元素!
不确定因素:形参:哪个数组,哪个位置,哪个元素
返回值:无
*/
public static void insertEle(int[] arr, int index, int ele) {
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= index; i--) {
arr[i] = arr[i - 1];
}
arr[index] = ele;
}
}
删除数组元素
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestArray03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 功能:给定一个数组,删除元素4:
// 1. 给定一个数组:
int[] arr = {1, 2, 4, 4, 5, 4, 6, 4, 8, 9};
// 2. 输出删除前的数组:
System.out.println("删除元素前的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
// 找到要删除的元素对应的索引即可:
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == 4) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
// 3. 删除
if (index != -1) {
for (int i = index; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[arr.length - 1] = 0;
} else { // index == -1
System.out.println("根本没有你要删除的元素!");
}
// 4. 输出删除后的数组:
System.out.println("删除元素后的数组:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
这个例子中的数组包含多个重复的元素4,我们将删除第一个出现的元素4。代码执行后,将输出删除元素后的数组。请注意,这里我们使用0来填充删除元素后的位置,以确保数组中的元素数量保持不变。