Charles抓不到python的请求,代理无效怎么办
有一天兄弟发现配置了Charles,电脑上各个应用抓包都抓到了,就是python代码一跑,不仅抓不到包,而且连网络都不通了。咋办?
原因是Charles代理开启以后,是个虚拟网卡,和本地ip不一致。
故可以通过配http_proxy环境变量解决,但不方便测试,当关闭Charles后,还得改回去,否则又连不了网。
所以,折中方案是在python代码中配置一下临时环境变量:
http.verify = False
# proxies配置代理设置无效,连不上时,使用环境变量配置代理
# http.proxies = {
# "http": 'http://172.31.192.1:8888',
# "https": 'http://172.31.192.1:8888',
# }
# 使用环境变量临时配置代理
os.environ["http_proxy"] = 'http://172.31.192.1:8888'
os.environ["https_proxy"] = 'http://172.31.192.1:8888'
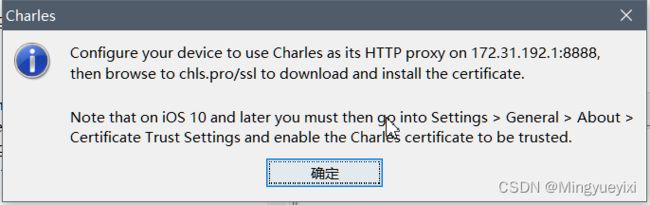
http://172.31.192.1:8888 即Charles代理服务器地址,可通过以下方式获取
test_hsl.py:43 (test_play_list)
self = <urllib3.connectionpool.HTTPSConnectionPool object at 0x0000020D8BF0C9D0>
method = 'GET', url = '/', body = None
headers = {'User-Agent': 'python-requests/2.27.1', 'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate', 'Accept': '*/*', 'Connection': 'keep-alive'}
retries = Retry(total=0, connect=None, read=False, redirect=None, status=None)
redirect = False, assert_same_host = False
timeout = Timeout(connect=None, read=None, total=None), pool_timeout = None
release_conn = False, chunked = False, body_pos = None
response_kw = {'decode_content': False, 'preload_content': False}
parsed_url = Url(scheme=None, auth=None, host=None, port=None, path='/', query=None, fragment=None)
destination_scheme = None, conn = None, release_this_conn = True
http_tunnel_required = True, err = None, clean_exit = False
def urlopen(
self,
method,
url,
body=None,
headers=None,
retries=None,
redirect=True,
assert_same_host=True,
timeout=_Default,
pool_timeout=None,
release_conn=None,
chunked=False,
body_pos=None,
**response_kw
):
"""
Get a connection from the pool and perform an HTTP request. This is the
lowest level call for making a request, so you'll need to specify all
the raw details.
.. note::
More commonly, it's appropriate to use a convenience method provided
by :class:`.RequestMethods`, such as :meth:`request`.
.. note::
`release_conn` will only behave as expected if
`preload_content=False` because we want to make
`preload_content=False` the default behaviour someday soon without
breaking backwards compatibility.
:param method:
HTTP request method (such as GET, POST, PUT, etc.)
:param url:
The URL to perform the request on.
:param body:
Data to send in the request body, either :class:`str`, :class:`bytes`,
an iterable of :class:`str`/:class:`bytes`, or a file-like object.
:param headers:
Dictionary of custom headers to send, such as User-Agent,
If-None-Match, etc. If None, pool headers are used. If provided,
these headers completely replace any pool-specific headers.
:param retries:
Configure the number of retries to allow before raising a
:class:`~urllib3.exceptions.MaxRetryError` exception.
Pass ``None`` to retry until you receive a response. Pass a
:class:`~urllib3.util.retry.Retry` object for fine-grained control
over different types of retries.
Pass an integer number to retry connection errors that many times,
but no other types of errors. Pass zero to never retry.
If ``False``, then retries are disabled and any exception is raised
immediately. Also, instead of raising a MaxRetryError on redirects,
the redirect response will be returned.
:type retries: :class:`~urllib3.util.retry.Retry`, False, or an int.
:param redirect:
If True, automatically handle redirects (status codes 301, 302,
303, 307, 308). Each redirect counts as a retry. Disabling retries
will disable redirect, too.
:param assert_same_host:
If ``True``, will make sure that the host of the pool requests is
consistent else will raise HostChangedError. When ``False``, you can
use the pool on an HTTP proxy and request foreign hosts.
:param timeout:
If specified, overrides the default timeout for this one
request. It may be a float (in seconds) or an instance of
:class:`urllib3.util.Timeout`.
:param pool_timeout:
If set and the pool is set to block=True, then this method will
block for ``pool_timeout`` seconds and raise EmptyPoolError if no
connection is available within the time period.
:param release_conn:
If False, then the urlopen call will not release the connection
back into the pool once a response is received (but will release if
you read the entire contents of the response such as when
`preload_content=True`). This is useful if you're not preloading
the response's content immediately. You will need to call
``r.release_conn()`` on the response ``r`` to return the connection
back into the pool. If None, it takes the value of
``response_kw.get('preload_content', True)``.
:param chunked:
If True, urllib3 will send the body using chunked transfer
encoding. Otherwise, urllib3 will send the body using the standard
content-length form. Defaults to False.
:param int body_pos:
Position to seek to in file-like body in the event of a retry or
redirect. Typically this won't need to be set because urllib3 will
auto-populate the value when needed.
:param \\**response_kw:
Additional parameters are passed to
:meth:`urllib3.response.HTTPResponse.from_httplib`
"""
parsed_url = parse_url(url)
destination_scheme = parsed_url.scheme
if headers is None:
headers = self.headers
if not isinstance(retries, Retry):
retries = Retry.from_int(retries, redirect=redirect, default=self.retries)
if release_conn is None:
release_conn = response_kw.get("preload_content", True)
# Check host
if assert_same_host and not self.is_same_host(url):
raise HostChangedError(self, url, retries)
# Ensure that the URL we're connecting to is properly encoded
if url.startswith("/"):
url = six.ensure_str(_encode_target(url))
else:
url = six.ensure_str(parsed_url.url)
conn = None
# Track whether `conn` needs to be released before
# returning/raising/recursing. Update this variable if necessary, and
# leave `release_conn` constant throughout the function. That way, if
# the function recurses, the original value of `release_conn` will be
# passed down into the recursive call, and its value will be respected.
#
# See issue #651 [1] for details.
#
# [1]
def connect(self):
# Add certificate verification
self.sock = conn = self._new_conn()
hostname = self.host
tls_in_tls = False
if self._is_using_tunnel():
if self.tls_in_tls_required:
> self.sock = conn = self._connect_tls_proxy(hostname, conn)
C:\Python310\lib\site-packages\urllib3\connection.py:364:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
self =
hostname = ' 127.0.0.1'
conn =
def _connect_tls_proxy(self, hostname, conn):
"""
Establish a TLS connection to the proxy using the provided SSL context.
"""
proxy_config = self.proxy_config
ssl_context = proxy_config.ssl_context
if ssl_context:
# If the user provided a proxy context, we assume CA and client
# certificates have already been set
return ssl_wrap_socket(
sock=conn,
server_hostname=hostname,
ssl_context=ssl_context,
)
ssl_context = create_proxy_ssl_context(
self.ssl_version,
self.cert_reqs,
self.ca_certs,
self.ca_cert_dir,
self.ca_cert_data,
)
# If no cert was provided, use only the default options for server
# certificate validation
> socket = ssl_wrap_socket(
sock=conn,
ca_certs=self.ca_certs,
ca_cert_dir=self.ca_cert_dir,
ca_cert_data=self.ca_cert_data,
server_hostname=hostname,
ssl_context=ssl_context,
)
C:\Python310\lib\site-packages\urllib3\connection.py:499:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
sock =
keyfile = None, certfile = None, cert_reqs = None, ca_certs = None
server_hostname = ' 127.0.0.1', ssl_version = None, ciphers = None
ssl_context = <ssl.SSLContext object at 0x0000020D8BEC5EC0>, ca_cert_dir = None
key_password = None, ca_cert_data = None, tls_in_tls = False
def ssl_wrap_socket(
sock,
keyfile=None,
certfile=None,
cert_reqs=None,
ca_certs=None,
server_hostname=None,
ssl_version=None,
ciphers=None,
ssl_context=None,
ca_cert_dir=None,
key_password=None,
ca_cert_data=None,
tls_in_tls=False,
):
"""
All arguments except for server_hostname, ssl_context, and ca_cert_dir have
the same meaning as they do when using :func:`ssl.wrap_socket`.
:param server_hostname:
When SNI is supported, the expected hostname of the certificate
:param ssl_context:
A pre-made :class:`SSLContext` object. If none is provided, one will
be created using :func:`create_urllib3_context`.
:param ciphers:
A string of ciphers we wish the client to support.
:param ca_cert_dir:
A directory containing CA certificates in multiple separate files, as
supported by OpenSSL's -CApath flag or the capath argument to
SSLContext.load_verify_locations().
:param key_password:
Optional password if the keyfile is encrypted.
:param ca_cert_data:
Optional string containing CA certificates in PEM format suitable for
passing as the cadata parameter to SSLContext.load_verify_locations()
:param tls_in_tls:
Use SSLTransport to wrap the existing socket.
"""
context = ssl_context
if context is None:
# Note: This branch of code and all the variables in it are no longer
# used by urllib3 itself. We should consider deprecating and removing
# this code.
context = create_urllib3_context(ssl_version, cert_reqs, ciphers=ciphers)
if ca_certs or ca_cert_dir or ca_cert_data:
try:
context.load_verify_locations(ca_certs, ca_cert_dir, ca_cert_data)
except (IOError, OSError) as e:
raise SSLError(e)
elif ssl_context is None and hasattr(context, "load_default_certs"):
# try to load OS default certs; works well on Windows (require Python3.4+)
context.load_default_certs()
# Attempt to detect if we get the goofy behavior of the
# keyfile being encrypted and OpenSSL asking for the
# passphrase via the terminal and instead error out.
if keyfile and key_password is None and _is_key_file_encrypted(keyfile):
raise SSLError("Client private key is encrypted, password is required")
if certfile:
if key_password is None:
context.load_cert_chain(certfile, keyfile)
else:
context.load_cert_chain(certfile, keyfile, key_password)
try:
if hasattr(context, "set_alpn_protocols"):
context.set_alpn_protocols(ALPN_PROTOCOLS)
except NotImplementedError: # Defensive: in CI, we always have set_alpn_protocols
pass
# If we detect server_hostname is an IP address then the SNI
# extension should not be used according to RFC3546 Section 3.1
use_sni_hostname = server_hostname and not is_ipaddress(server_hostname)
# SecureTransport uses server_hostname in certificate verification.
send_sni = (use_sni_hostname and HAS_SNI) or (
IS_SECURETRANSPORT and server_hostname
)
# Do not warn the user if server_hostname is an invalid SNI hostname.
if not HAS_SNI and use_sni_hostname:
warnings.warn(
"An HTTPS request has been made, but the SNI (Server Name "
"Indication) extension to TLS is not available on this platform. "
"This may cause the server to present an incorrect TLS "
"certificate, which can cause validation failures. You can upgrade to "
"a newer version of Python to solve this. For more information, see "
"https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/1.26.x/advanced-usage.html"
"#ssl-warnings",
SNIMissingWarning,
)
if send_sni:
ssl_sock = _ssl_wrap_socket_impl(
sock, context, tls_in_tls, server_hostname=server_hostname
)
else:
> ssl_sock = _ssl_wrap_socket_impl(sock, context, tls_in_tls)
C:\Python310\lib\site-packages\urllib3\util\ssl_.py:453:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
sock =
ssl_context = , tls_in_tls = False
server_hostname = None
def _ssl_wrap_socket_impl(sock, ssl_context, tls_in_tls, server_hostname=None):
if tls_in_tls:
if not SSLTransport:
# Import error, ssl is not available.
raise ProxySchemeUnsupported(
"TLS in TLS requires support for the ' ssl' module"
)
SSLTransport._validate_ssl_context_for_tls_in_tls(ssl_context)
return SSLTransport(sock, ssl_context, server_hostname)
if server_hostname:
return ssl_context.wrap_socket(sock, server_hostname=server_hostname)
else:
> return ssl_context.wrap_socket(sock)
C:\Python310\lib\site-packages\urllib3\util\ssl_.py:495:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
self =
sock =
server_side = False, do_handshake_on_connect = True, suppress_ragged_eofs = True
server_hostname = None, session = None
def wrap_socket(self, sock, server_side=False,
do_handshake_on_connect=True,
suppress_ragged_eofs=True,
server_hostname=None, session=None):
# SSLSocket class handles server_hostname encoding before it calls
# ctx._wrap_socket()
> return self.sslsocket_class._create(
sock=sock,
server_side=server_side,
do_handshake_on_connect=do_handshake_on_connect,
suppress_ragged_eofs=suppress_ragged_eofs,
server_hostname=server_hostname,
context=self,
session=session
)
C:\Python310\lib\ssl.py:512:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
cls = ssl.SSLSocket'>
sock =
server_side = False, do_handshake_on_connect = True, suppress_ragged_eofs = True
server_hostname = None, context =
session = None
@classmethod
def _create(cls, sock, server_side=False, do_handshake_on_connect=True,
suppress_ragged_eofs=True, server_hostname=None,
context=None, session=None):
if sock.getsockopt(SOL_SOCKET, SO_TYPE) != SOCK_STREAM:
raise NotImplementedError("only stream sockets are supported")
if server_side:
if server_hostname:
raise ValueError("server_hostname can only be specified "
"in client mode")
if session is not None:
raise ValueError("session can only be specified in "
"client mode")
if context.check_hostname and not server_hostname:
raise ValueError("check_hostname requires server_hostname")
kwargs = dict(
family=sock.family, type=sock.type, proto=sock.proto,
fileno=sock.fileno()
)
self = cls.__new__(cls, **kwargs)
super(SSLSocket, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.settimeout(sock.gettimeout())
sock.detach()
self._context = context
self._session = session
self._closed = False
self._sslobj = None
self.server_side = server_side
self.server_hostname = context._encode_hostname(server_hostname)
self.do_handshake_on_connect = do_handshake_on_connect
self.suppress_ragged_eofs = suppress_ragged_eofs
# See if we are connected
try:
self.getpeername()
except OSError as e:
if e.errno != errno.ENOTCONN:
raise
connected = False
else:
connected = True
self._connected = connected
if connected:
# create the SSL object
try:
self._sslobj = self._context._wrap_socket(
self, server_side, self.server_hostname,
owner=self, session=self._session,
)
if do_handshake_on_connect:
timeout = self.gettimeout()
if timeout == 0.0:
# non-blocking
raise ValueError("do_handshake_on_connect should not be specified for non-blocking sockets")
> self.do_handshake()
C:\Python310\lib\ssl.py:1070:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
self =
block = False
@_sslcopydoc
def do_handshake(self, block=False):
self._check_connected()
timeout = self.gettimeout()
try:
if timeout == 0.0 and block:
self.settimeout(None)
> self._sslobj.do_handshake()
E ssl.SSLError: [SSL: WRONG_VERSION_NUMBER] wrong version number (_ssl.c:997)
C:\Python310\lib\ssl.py:1341: SSLError
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
self =
request = , stream = False
timeout = Timeout(connect=None, read=None, total=None), verify = False
cert = None
proxies = OrderedDict([(' http', 'http://127.0.0.1:8888'), ('https', 'https://127.0.0.1:8888')])
def send(self, request, stream=False, timeout=None, verify=True, cert=None, proxies=None):
"""Sends PreparedRequest object. Returns Response object.
:param request: The :class:` PreparedRequest <PreparedRequest>` being sent.
:param stream: (optional) Whether to stream the request content.
:param timeout: (optional) How long to wait for the server to send
data before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout,
read timeout) <timeouts>` tuple.
:type timeout: float or tuple or urllib3 Timeout object
:param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether
we verify the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it
must be a path to a CA bundle to use
:param cert: (optional) Any user-provided SSL certificate to be trusted.
:param proxies: (optional) The proxies dictionary to apply to the request.
:rtype: requests.Response
"""
try:
conn = self.get_connection(request.url, proxies)
except LocationValueError as e:
raise InvalidURL(e, request=request)
self.cert_verify(conn, request.url, verify, cert)
url = self.request_url(request, proxies)
self.add_headers(request, stream=stream, timeout=timeout, verify=verify, cert=cert, proxies=proxies)
chunked = not (request.body is None or 'Content-Length' in request.headers)
if isinstance(timeout, tuple):
try:
connect, read = timeout
timeout = TimeoutSauce(connect=connect, read=read)
except ValueError as e:
# this may raise a string formatting error.
err = ("Invalid timeout {}. Pass a (connect, read) "
"timeout tuple, or a single float to set "
"both timeouts to the same value".format(timeout))
raise ValueError(err)
elif isinstance(timeout, TimeoutSauce):
pass
else:
timeout = TimeoutSauce(connect=timeout, read=timeout)
try:
if not chunked:
> resp = conn.urlopen(
method=request.method,
url=url,
body=request.body,
headers=request.headers,
redirect=False,
assert_same_host=False,
preload_content=False,
decode_content=False,
retries=self.max_retries,
timeout=timeout
)
C:\Python310\lib\site-packages\requests\adapters.py:440:
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
self =
method = ' GET', url = '/', body = None
headers = {'User-Agent': 'python-requests/2.27.1', 'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate', 'Accept': '*/*', 'Connection': 'keep-alive'}
retries = Retry(total=0, connect=None, read=False, redirect=None, status=None)
redirect = False, assert_same_host = False
timeout = Timeout(connect=None, read=None, total=None), pool_timeout = None
release_conn = False, chunked = False, body_pos = None
response_kw = {'decode_content': False, 'preload_content': False}
parsed_url = Url(scheme=None, auth=None, host=None, port=None, path='/', query=None, fragment=None)
destination_scheme = None, conn = None, release_this_conn = True
http_tunnel_required = True, err = None, clean_exit = False
def urlopen(
self,
method,
url,
body=None,
headers=None,
retries=None,
redirect=True,
assert_same_host=True,
timeout=_Default,
pool_timeout=None,
release_conn=None,
chunked=False,
body_pos=None,
**response_kw
):
"""
Get a connection from the pool and perform an HTTP request. This is the
lowest level call for making a request, so you'll need to specify all
the raw details.
.. note::
More commonly, it's appropriate to use a convenience method provided
by :class:`.RequestMethods`, such as :meth:`request`.
.. note::
`release_conn` will only behave as expected if
`preload_content=False` because we want to make
`preload_content=False` the default behaviour someday soon without
breaking backwards compatibility.
:param method:
HTTP request method (such as GET, POST, PUT, etc.)
:param url:
The URL to perform the request on.
:param body:
Data to send in the request body, either :class:`str`, :class:`bytes`,
an iterable of :class:`str`/:class:`bytes`, or a file-like object.
:param headers:
Dictionary of custom headers to send, such as User-Agent,
If-None-Match, etc. If None, pool headers are used. If provided,
these headers completely replace any pool-specific headers.
:param retries:
Configure the number of retries to allow before raising a
:class:`~urllib3.exceptions.MaxRetryError` exception.
Pass ``None`` to retry until you receive a response. Pass a
:class:`~urllib3.util.retry.Retry` object for fine-grained control
over different types of retries.
Pass an integer number to retry connection errors that many times,
but no other types of errors. Pass zero to never retry.
If ``False``, then retries are disabled and any exception is raised
immediately. Also, instead of raising a MaxRetryError on redirects,
the redirect response will be returned.
:type retries: :class:`~urllib3.util.retry.Retry`, False, or an int.
:param redirect:
If True, automatically handle redirects (status codes 301, 302,
303, 307, 308). Each redirect counts as a retry. Disabling retries
will disable redirect, too.
:param assert_same_host:
If ``True``, will make sure that the host of the pool requests is
consistent else will raise HostChangedError. When ``False``, you can
use the pool on an HTTP proxy and request foreign hosts.
:param timeout:
If specified, overrides the default timeout for this one
request. It may be a float (in seconds) or an instance of
:class:`urllib3.util.Timeout`.
:param pool_timeout:
If set and the pool is set to block=True, then this method will
block for ``pool_timeout`` seconds and raise EmptyPoolError if no
connection is available within the time period.
:param release_conn:
If False, then the urlopen call will not release the connection
back into the pool once a response is received (but will release if
you read the entire contents of the response such as when
`preload_content=True`). This is useful if you're not preloading
the response's content immediately. You will need to call
``r.release_conn()`` on the response ``r`` to return the connection
back into the pool. If None, it takes the value of
``response_kw.get('preload_content', True)``.
:param chunked:
If True, urllib3 will send the body using chunked transfer
encoding. Otherwise, urllib3 will send the body using the standard
content-length form. Defaults to False.
:param int body_pos:
Position to seek to in file-like body in the event of a retry or
redirect. Typically this won't need to be set because urllib3 will
auto-populate the value when needed.
:param \\**response_kw:
Additional parameters are passed to
:meth:`urllib3.response.HTTPResponse.from_httplib`
"""
parsed_url = parse_url(url)
destination_scheme = parsed_url.scheme
if headers is None:
headers = self.headers
if not isinstance(retries, Retry):
retries = Retry.from_int(retries, redirect=redirect, default=self.retries)
if release_conn is None:
release_conn = response_kw.get("preload_content", True)
# Check host
if assert_same_host and not self.is_same_host(url):
raise HostChangedError(self, url, retries)
# Ensure that the URL we're connecting to is properly encoded
if url.startswith("/"):
url = six.ensure_str(_encode_target(url))
else:
url = six.ensure_str(parsed_url.url)
conn = None
# Track whether `conn` needs to be released before
# returning/raising/recursing. Update this variable if necessary, and
# leave `release_conn` constant throughout the function. That way, if
# the function recurses, the original value of `release_conn` will be
# passed down into the recursive call, and its value will be respected.
#
# See issue #651 [1] for details.
#
# [1]