Spring 面试必考:Spring Bean 的生命周期和作用域
目录
一. 前言
二. Spring Bean 作用域
2.1. Spring Bean 五大作用域
2.2. request 请求作用域
2.3. session 会话作用域
三. Spring Bean 生命周期流程
四. Spring Bean 生命周期案例
一. 前言
Spring 只帮我们管理单例模式 Bean 的完整生命周期,对于 prototype 的 Bean ,Spring 在创建好交给使用者之后则不会再管理后续的生命周期。Spring 容器可以管理 singleton 作用域 Bean 的生命周期,在此作用域下,Spring 能够精确地知道该 Bean 何时被创建,何时初始化完成,以及何时被销毁。
而对于 prototype 作用域的 Bean,Spring 只负责创建,当容器创建了 Bean 的实例后,Bean 的实例就交给客户端代码管理,Spring 容器将不再跟踪其生命周期。每次客户端请求 prototype 作用域的 Bean 时,Spring 容器都会创建一个新的实例,并且不会管那些被配置成 prototype 作用域的 Bean 的生命周期。
了解 Spring 生命周期的意义就在于,可以利用 Bean 在其存活期间的指定时刻完成一些相关操作。这种时刻可能有很多,但一般情况下,会在 Bean 被初始化后和被销毁前执行一些相关操作。
二. Spring Bean 作用域
2.1. Spring Bean 五大作用域
Spring Bean 支持五个作用域:singleton、prototype、request、session、global session。
1. singleton:默认作用域, Spring IoC 容器仅存在一个 Bean 实例,Bean 以单例方式存在,在创建容器时就同时自动创建了一个 Bean 对象。作用域范围是 ApplicationContext 中。
2. prototype:每次从容器中调用 Bean 时,都会返回一个新的实例,即每次调用 getBean 时。作用域返回的是 getBean 方法调用直至方法结束。相当于执行 new XxxBean().Prototype 是原型类型,在我们创建容器的时候并没有实例化,而是当我们获取 Bean 的时候才会去创建一个对象,而且我们每次获取到的对象都不是同一个对象。
3.request:每次 HTTP 请求都会创建一个新的 Bean,作用域范围是每次发起 HTTP 请求直至拿到相应结果。该作用域仅适用于 WebApplicationContext 环境。
4. session:首次 HTTP 请求创建一个实例,作用域是浏览器首次访问直至浏览器关闭。同一个HTTP Session 共享一个 Bean,不同 Session 使用不通的 Bean,仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境。
5. global-session:作用域范围是 WebApplicationContext 中。一般用于 Portlet 应用环境,该运用域仅适用于 WebApplicationContext 环境。
作用域范围比较:prototype < request < session < global-session < singleton。
为什么要定义作用域:可以通过 Spring 配置的方式限定 Spring Bean 的作用范围,可以起到对Bean 使用安全的保护作用。
2.2. request 请求作用域
request 请求作用域(有如下定义):
// 第二种
@Scope("request")
@Controller
public class LoginController {
private int flag = 0;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public int login() {
return flag++;
}
}// 第三种
@RestController
@RequestScope
public class LoginController {
private int flag = 0;
@RequestMapping("/login")
public int login() {
return flag++;
}
}对于每个 HTTP 请求,Spring 容器会创建一个 LoginController Bean 的新实例。也就是说,LoginController Bean 的作用域限于 HTTP 请求范围。 你可以在请求内随意修改这个 Bean 实例的状态,因为其他 LoginController Bean 实例看不到这些变化,Bean 实例是与特定的请求相关的。 当请求处理完毕,对应的 Bean 实例也就销毁(被回收)了。
2.3. session 会话作用域
session 会话作用域(有如下定义):
// 第二种
@RestController
@Scope("session")
public class UserController {
private int flag = 0;
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public int getUser() {
return flag++;
}
}// 第三种
@RestController
@SessionScope
public class UserController {
private int flag = 0;
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public int getUser() {
return flag++;
}
}在每个 HTTP Session 的生命周期内,Spring 容器会根据 id 为 UserController 的 Bean 定义创建一个 UserController Bean 的新实例。也就是说,UserController Bean 的作用域限于 HTTP Session 范围。和请求作用域 request-scoped Bean 类似,因为每个会话域 session-scoped Bean的范围限于特定的 HTTP Session 内部,所以一个 Session 内的 UserController Bean 也是可以被随意修改, 而不会影响到其他 Session 中的 UserController Bean。当一个 HTTP Session 最终用完被 JVM 回收时,相关的会话域 session-scoped Bean 也被一起回收。
三. Spring Bean 生命周期流程
在 Spring 中,Bean 的生命周期是一个很复杂的执行过程,我们可以利用 Spring 提供的方法定制 Bean 的创建过程。
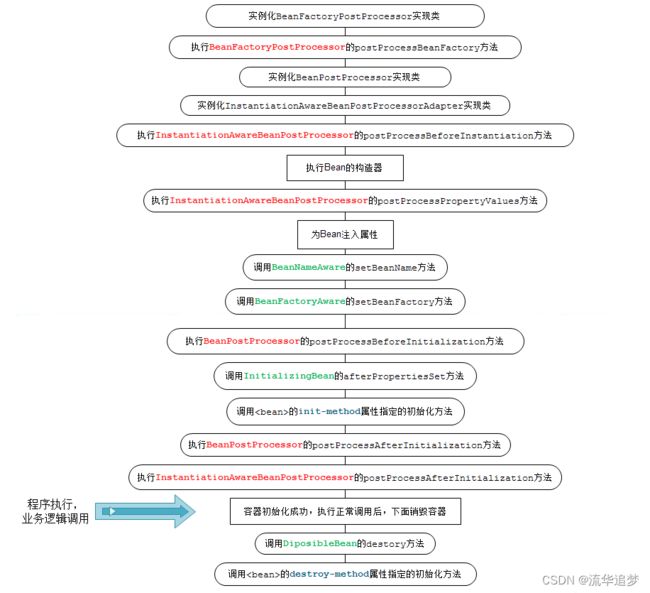
Spring 容器中 Bean 的生命周期流程:
1. 如果 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则调用 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。(即首先尝试从 Bean 工厂中获取 Bean)。
2. 如果 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法。
3. 根据配置情况调用 Bean 构造方法实例化 Bean。
4. 利用依赖注入完成 Bean 中所有属性值的配置注入。
5. 如果 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则调用postProcessAfterInstantiation 方法和 postProcessProperties。
6. 调用 xxxAware 接口(上图只是给了几个例子)
- 第一类 Aware 接口:
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 Bean 的 setBeanName() 方法传入当前 Bean 的 id 值。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setBeanFactory() 方法传入当前工厂实例的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanClassLoaderAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setBeanClassLoader() 方法传入 classLoader 的引用。
- 第二类 Aware 接口:
- 如果 Bean 实现了 EnvironmentAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setEnvironment() 方法传入当前 Environment 实例的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法传入当前 StringValueResolver 实例的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setApplicationContext() 方法传入当前 ApplicationContext 实例的引用。
- ...
7. 如果 BeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则 Spring 将调用该接口的预初始化方法 postProcessBeforeInitialzation() 对 Bean 进行加工操作,此处非常重要,Spring 的 AOP 就是利用它实现的。
8. 如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,则 Spring 将调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。(或者有执行 @PostConstruct 注解的方法)。
9. 如果在配置文件中通过 init-method 属性指定了初始化方法,则调用该初始化方法。
10. 如果 BeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则 Spring 将调用该接口的初始化方法 postProcessAfterInitialization()。此时,Bean 已经可以被应用系统使用了。
11. 如果在
12. 如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,则 Spring 会调用 destory() 方法将 Spring 中的 Bean 销毁;(或者有执行 @PreDestroy 注解的方法)。
13. 如果在配置文件中通过 destory-method 属性指定了 Bean 的销毁方法,则 Spring 将调用该方法对 Bean 进行销毁。
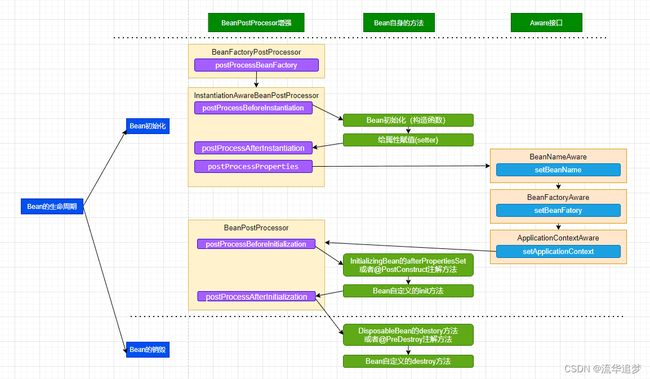
Bean 的完整生命周期经历了各种方法调用,这些方法可以划分为以下几类:(结合上图,需要有如下顶层思维)
- Bean 自身的方法:这个包括了 Bean 本身调用的方法和通过配置文件中
的 init-method 和 destroy-method 指定的方法。 - Bean 级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了 BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware;当然也包括 InitializingBean 和 DiposableBean 这些接口的方法(可以被 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注解替代)。
- 容器级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor 这两个接口实现,一般称它们的实现类为后处理器。
- 工厂后处理器接口方法:这个包括了 AspectJWeavingEnabler、 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor、CustomAutowireConfigurer 等等非常有用的工厂后处理器接口的方法。工厂后处理器也是容器级的。在应用上下文装配配置文件之后立即调用。
四. Spring Bean 生命周期案例
我们通过一个例子来验证上面的整个流程。
定义Bean(这里是 User),并让它实现BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware 接口和 InitializingBean、DisposableBean 接口:
package com.lm.it.springframework.entity;
import lombok.ToString;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**
* User
*/
@Slf4j
@ToString
public class User implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware,
InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
/**
* user's name.
*/
private String name;
/**
* user's age.
*/
private int age;
/**
* bean factory.
*/
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
/**
* application context.
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* bean name.
*/
private String beanName;
public User() {
log.info("execute User#new User()");
}
public void setName(String name) {
log.info("execute User#setName({})", name);
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
log.info("execute User#setAge({})", age);
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
log.info("execute BeanNameAware#setBeanName");
this.beanName = s;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext");
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
log.info("execute DisposableBean#destroy");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("execute InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet");
}
public void doInit() {
log.info("execute User#doInit");
}
public void doDestroy() {
log.info("execute User#doDestroy");
}
}定义 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类:
/**
* MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory");
}
}定义 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的实现类:
/**
* MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation for {}", beanName);
return InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation for {}", beanName);
return InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties for {}", beanName);
return InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessProperties(pvs, bean, beanName);
}
}定义 BeanPostProcessor 的实现类:
/**
* MyBeanPostProcessor
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization for {}", beanName);
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("execute BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization for {}", beanName);
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}通过 Java 配置方式初始化 Bean:
/**
* BeansConfig
*/
@Configuration
public class BeansConfig {
@Bean(name = "user", initMethod = "doInit", destroyMethod = "doDestroy")
public User create() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("pdai");
user.setAge(18);
return user;
}
}测试主方法:
/**
* Cglib proxy demo.
*/
@Slf4j
public class App {
/**
* main interface.
*
* @param args args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("Init application context");
// create and configure beans
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(
"com.lm.it.springframework");
// retrieve configured instance
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
// print info from beans
log.info(user.toString());
log.info("Shutdown application context");
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}输出结果(剔除无关输出):
12:44:42.547 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.App - Init application context
...
12:44:43.134 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor - execute BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory
...
12:44:43.216 [main] DEBUG org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory - Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'user'
12:44:43.216 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor - execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation for user
12:44:43.236 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute User#new User()
12:44:43.237 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute User#setName(pdai)
12:44:43.237 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute User#setAge(18)
12:44:43.237 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor - execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation for user
12:44:43.237 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor - execute InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties for user
12:44:43.242 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute BeanNameAware#setBeanName
12:44:43.242 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory
12:44:43.242 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
12:44:43.242 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyBeanPostProcessor - execute BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization for user
12:44:43.242 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
12:44:43.243 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute User#doInit
12:44:43.243 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.processor.MyBeanPostProcessor - execute BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization for user
12:44:43.270 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.App - User(name=pdai, age=18)
12:44:43.270 [main] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.App - Shutdown application context
12:44:43.276 [SpringContextShutdownHook] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute DisposableBean#destroy
12:44:43.276 [SpringContextShutdownHook] INFO com.lm.it.springframework.entity.User - execute User#doDestroy