leetcode 918. Maximum Sum Circular Subarray
Given a circular array C of integers represented by A, find the maximum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of C.
Here, a circular array means the end of the array connects to the beginning of the array. (Formally, C[i] = A[i] when 0 <= i < A.length, and C[i+A.length] = C[i] when i >= 0.)
Also, a subarray may only include each element of the fixed buffer A at most once. (Formally, for a subarray C[i], C[i+1], …, C[j], there does not exist i <= k1, k2 <= j with k1 % A.length = k2 % A.length.)
Example 1:
Input: [1,-2,3,-2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarray [3] has maximum sum 3
Example 2:
Input: [5,-3,5]
Output: 10
Explanation: Subarray [5,5] has maximum sum 5 + 5 = 10
Example 3:
Input: [3,-1,2,-1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Subarray [2,-1,3] has maximum sum 2 + (-1) + 3 = 4
Example 4:
Input: [3,-2,2,-3]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarray [3] and [3,-2,2] both have maximum sum 3
Example 5:
Input: [-2,-3,-1]
Output: -1
Explanation: Subarray [-1] has maximum sum -1
Note:
-30000 <= A[i] <= 30000
1 <= A.length <= 30000
给定一个数组,把这个数组看作一个环,则有一个序列为:从选定位置到选定位置的前一位,求这个序列的最大连续子列和。
首先,可以想到的一个很朴素的算法,即枚举数组每一位作为序列的开始,求出最大连续子列和。
但是这样算法复杂度为O(n2),仅在数据量较小的时候可行
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubarraySumCircular(vector& A) {
if(A.size()==0)
return 0;
if(A.size()==1)
return A[0];
int len=A.size();
int sum=0;
int ans=INT_MIN;
for(int i=0;i 除了这暴力的算法外,还有没有一个更好的设计思路。
在这里,可以分析一下,有如下两种情况:
-
最大连续子列同时包含了数组尾与数组头
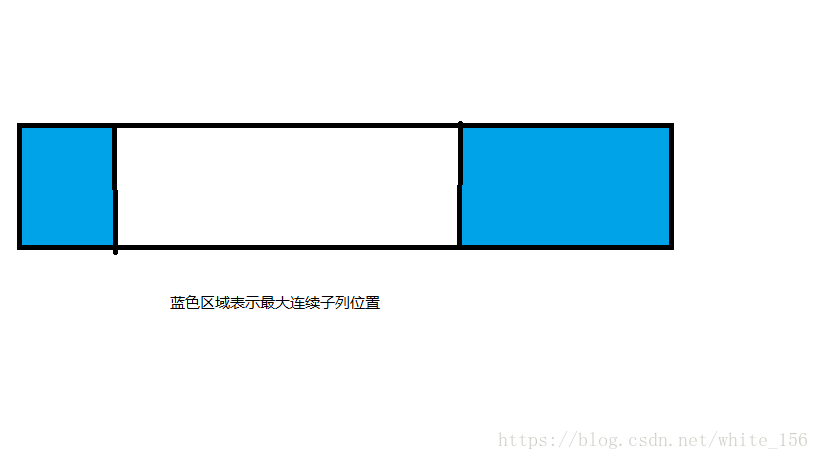
对于上图,已知蓝色部分为最大连续子列的位置,可以思考一下能否将白色的部分加入到蓝色部分?
答案很显然是不能的,不难发现,白色的部分有这样的性质:从端点到白色区间的任意位置的序列和均为负根据这一性质,可以得出,白色区间就是数组序列的最小连续子列和。
综上所述,只需要在遍历数组时求出数组的最大连续子列和 与 最下连续子列和进行比较即可
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubarraySumCircular(vector& A) {
if(A.size()==0)
return 0;
if(A.size()==1)
return A[0];
int ans=INT_MIN;
int tol=0;
int least=0;
int num=INT_MAX;
int sum=0;
for(auto ele : A){
tol+=ele;
sum+=ele;
if(sum<0){
ans=max(ans,ele);
sum=0;
}else{
ans=max(sum,ans);
}
least+=ele;
if(least>0)
least=0;
else
num=min(least,num);
}
if(ans<=0)
return ans;
else
return max(ans,tol-num);
}
};
