c++哈希(哈希表闭散列线性探测实现)
文章目录
- 0. 前言
- 1. 线性探测
- 2. 线性探测的代码实现
-
- 2.0 定义
- 2.1 插入实现--Insert
- 2.2 查找实现--Find
- 2.3 删除实现--Erase
- 2.4 仿函数
- 3. 完整代码实现
- 4. 代码测试并运行结果:
0. 前言
- 闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。那如何寻找下一个空位置呢?
1. 线性探测
- 线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
- 插入
- 通过哈希函数获取待插入元素在哈希表中的位置。
- 如果该位置中没有元素则直接插入新元素,如果该位置中有元素发生哈希冲突,使用线性探测找到下一个空位置,插入新元素。
- 删除
采用闭散列处理哈希冲突时,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有的元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索。比如删除元素4,如果直接删除掉,44查找起来可能会受影响。因此线性探测采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
我们需要借助枚举函数来完成
enum State
{
EMPTY, //空标记
EXIST, //存在
DELETE //删除
};
2. 线性探测的代码实现
2.0 定义
enum State
{
EMPTY, //空标记
EXIST, //存在
DELETE //删除
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashDate
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class K, class V>
class HashTable
{
public:
// 插入
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv);
// 查找
HashDate<K, V>* Find(const K& key);
// 删除
bool Erase(const K& key);
size_t Size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool Empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _size = 0; // 存储有效数据个数
};
2.1 插入实现–Insert
思路::hash(key) = key % capacity;我们根据取模来确定映射的相对位置。
注意:扩容的方法我们采用负载因子的方法

只要负载因子到0.7,我们就扩容;扩容后我们又要重新线性探索太麻烦了,我们可以复用一下Insert;把线性探索任务交给在栈上开辟的类实例化的新对象去作插入重新映射;然后再进行交换即可。具体看下面代码:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//负载因子到了就扩容
if (_tables.size() == 0 || 10 * _size / _tables.size() >= 7) //扩容
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
//旧表数据映射到新表内
for (auto e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();
//线性探测
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXIST)
{
++hashi;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//找到位置了
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._state = EXIST;
++_size;
return true;
}
2.2 查找实现–Find
根据负载因子扩容;我们知道一定有一部分的位置是空也就是被标记为EMPTY。
思路:根据映射关系取查找值的模,找到相对位置;然后往后一次查找知道遇到EMPTY标记的位置。
// 查找
HashDate<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_tables.size()==0)
{
return nullptr;
}
size_t hashi =key % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._state != DELETE && key == _tables[hashi]._kv.first)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
++hashi;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//没找到
return nullptr;
}
2.3 删除实现–Erase
我们这里的删除是标记型删除。
// 删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashDate<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_size;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
2.4 仿函数
- 我们发现我们现在实现的哈希只能存数字,字符串等不行;这个时候我们需要借助仿函数。
template<class k>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const k& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特化--string
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (const auto ch : s) //迭代器
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
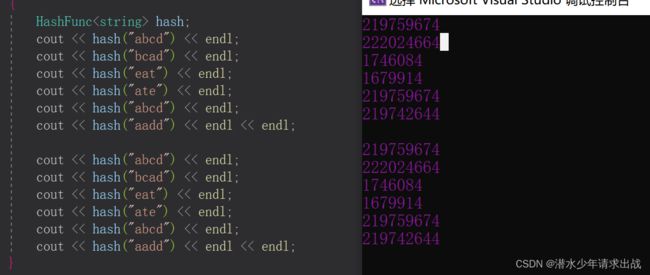
可能大家都很疑惑,string所有字母ASCII值相加理解用来比较;为什么乘于131,大佬经过反复推敲保证它们值稳定,就是下次映射的时候还是原来的数值。
3. 完整代码实现
#pragma once
namespace CloseHash
{
enum State
{
EMPTY, //空标记
EXIST, //存在
DELETE //删除
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashDate
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class k>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const k& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特化--string
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t val = 0;
for (const auto ch : s) //迭代器
{
val *= 131;
val += ch;
}
return val;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//负载因子到了就扩容
if (_tables.size() == 0 || 10 * _size / _tables.size() >= 7) //扩容
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V, Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
//旧表数据映射到新表内
for (auto e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();
//线性探测
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXIST)
{
++hashi;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//找到位置了
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._state = EXIST;
++_size;
return true;
}
// 查找
HashDate<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
if (Empty())
{
return nullptr;
}
Hash hash;
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._state != DELETE && key == _tables[hashi]._kv.first)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
++hashi;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//没找到
return nullptr;
}
// 删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashDate<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
--_size;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
size_t Size()const
{
return _size;
}
//打印一下,用来测试
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i]._state == EXIST)
{
printf("[%d:%d] ", i, _tables[i]._kv.first);
}
else
{
printf("[%d:*] ", i);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<HashDate<K, V>> _tables;
size_t _size = 0; //存储多少个有效数据
};
void TestHT1()
{
//int a[] = { 1, 11, 4, 15, 26, 7, 44, 9 };
int a[] = { 1, 11, 4, 15, 26, 7, 44 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
ht.Print();
ht.Erase(4);
cout << ht.Find(44)->_kv.first << endl;
cout << ht.Find(4) << endl;
ht.Print();
ht.Insert(make_pair(-2, -2));
ht.Print();
cout << ht.Find(-2)->_kv.first << endl;
}
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable countHT;
HashTable<string, int> countHT;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ptr = countHT.Find(str);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
countHT.Insert(make_pair(str, 1));
}
}
for (auto& str : arr)
{
cout << str << ":" << countHT.Find(str)->_kv.second << "---";
}
cout << endl;
}
void TestHT3()
{
HashFunc<string> hash;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("bcad") << endl;
cout << hash("eat") << endl;
cout << hash("ate") << endl;
cout << hash("abcd") << endl;
cout << hash("aadd") << endl << endl;
}
}
