Springboot14:集成Shiro
1、Shiro
1.1、什么是Shiro?
- Shiro 是一个Java的安全(权限)框架
- Shiro 可以非常容易开发出足够的应用,其不仅可以用在JavaSE环境,也可以用在JavaEE环境
- Shiro 可以完成认证,授权,加密,会话管理,Web集成,缓存
- 对比 Spring Security,可能没有 Spring Security 做的功能强大,但是在实际工作时可能并不需要那么复杂的东西,所以使用小而简单的 Shiro 就足够了
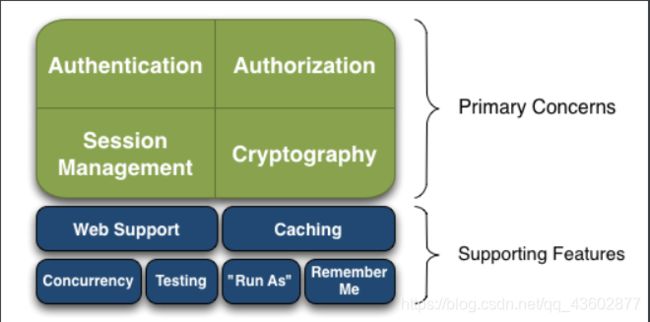
1.2、基本功能
-
Authentication:身份认证 / 登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
-
Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限;即判断用户是否能做事情,常见的如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色。或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限;
-
Session Management:会话管理,即用户登录后就是一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通 JavaSE 环境的,也可以是如 Web 环境的;
-
Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储;
-
Web Support:Web 支持,可以非常容易的集成到 Web 环境;
-
Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息、拥有的角色 / 权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率;
-
Concurrency:shiro 支持多线程应用的并发验证,即如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动传播过去;
-
Testing:提供测试支持;
-
Run As:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
-
Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了。
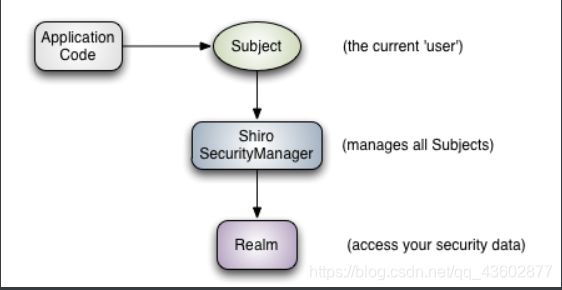
1.3、 Shiro 的架构(外部)
可以看到:应用代码直接交互的对象是 Subject,也就是说 Shiro 的对外 API 核心就是 Subject;其每个 API 的含义:
-
Subject:主体,代表了当前 “用户”,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是 Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等;即一个抽象概念;所有 Subject 都绑定到 SecurityManager,与 Subject 的所有交互都会委托给 SecurityManager;可以把 Subject 认为是一个门面;SecurityManager 才是实际的执行者;
-
SecurityManager:安全管理器;即所有与安全有关的操作都会与 SecurityManager 交互;且它管理着所有 Subject;可以看出它是 Shiro 的核心,它负责与后边介绍的其他组件进行交互,如果学习过 SpringMVC,你可以把它看成 DispatcherServlet 前端控制器;
-
Realm:域,Shiro 从从 Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm 得到用户相应的角色 / 权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把 Realm 看成 DataSource,即安全数据源。
也就是说对于我们而言,最简单的一个 Shiro 应用:
- 应用代码通过 Subject 来进行认证和授权,而 Subject 又委托给 SecurityManager;
- 我们需要给 Shiro 的 SecurityManager 注入 Realm,从而让 SecurityManager 能得到合法的用户及其权限进行判断。
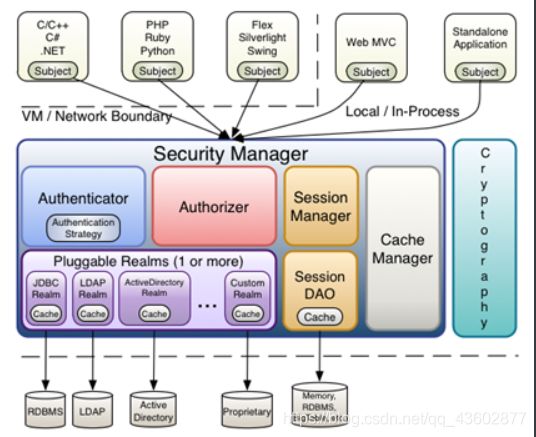
1.4、 Shiro 的架构(内部)
-
Subject:主体,可以看到主体可以是任何可以与应用交互的 “用户”;
-
SecurityManager:相当于 SpringMVC 中的 DispatcherServlet(前端控制器) 或者 Struts2 中的 FilterDispatcher;是 Shiro 的心脏;所有具体的交互都通过 SecurityManager 进行控制;它管理着所有 Subject、且负责进行认证和授权、及会话、缓存的管理。
-
Authenticator:认证器,负责主体认证的,这是一个扩展点,如果用户觉得 Shiro 默认的不好,可以自定义实现;其需要认证策略(Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
-
Authrizer:授权器,或者访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的哪些功能;
-
Realm:可以有 1 个或多个 Realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的;可以是 JDBC 实现,也可以是 LDAP 实现,或者内存实现等等;由用户提供;注意:Shiro 不知道你的用户 / 权限存储在哪及以何种格式存储;所以我们一般在应用中都需要实现自己的 Realm;
-
SessionManager:如果写过 Servlet 就应该知道 Session 的概念,Session 呢需要有人去管理它的生命周期,这个组件就是 SessionManager;而 Shiro 并不仅仅可以用在 Web 环境,也可以用在如普通的 JavaSE 环境、EJB 等环境;所以呢,Shiro 就抽象了一个自己的 Session 来管理主体与应用之间交互的数据;这样的话,比如我们在 Web 环境用,刚开始是一台 Web 服务器;接着又上了台 EJB 服务器;这时想把两台服务器的会话数据放到一个地方,这个时候就可以实现自己的分布式会话(如把数据放到 Memcached 服务器);
-
SessionDAO:DAO 大家都用过,数据访问对象,用于会话的 CRUD,比如我们想把 Session 保存到数据库,那么可以实现自己的 SessionDAO,通过如 JDBC 写到数据库;比如想把 Session 放到 Memcached 中,可以实现自己的 Memcached SessionDAO;另外 SessionDAO 中可以使用 Cache 进行缓存,以提高性能;
-
CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户、角色、权限等的缓存的;因为这些数据基本上很少去改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能
-
Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro 提供了一些常见的加密组件用于如密码加密 / 解密的。
2、Hello-shiro
2.1、官方文档:
- http://shiro.apache.org/10-minute-tutorial.html
2.2、测试
-
导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId> <artifactId>shiro-coreartifactId> <version>1.7.0version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId> <version>1.7.30version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId> <version>1.7.30version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>1.2.17version> dependency> <dependency> -
配置shiro的配置文件:shiro.ini
# # Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one # or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file # distributed with this work for additional information # regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file # to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the # "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance # with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, # software distributed under the License is distributed on an # "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY # KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the # specific language governing permissions and limitations # under the License. # # ============================================================================= # Quickstart INI Realm configuration # # For those that might not understand the references in this file, the # definitions are all based on the classic Mel Brooks' film "Spaceballs". ;) # ============================================================================= # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Users and their assigned roles # # Each line conforms to the format defined in the # org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setUserDefinitions JavaDoc # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [users] # user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role root = secret, admin # user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role guest = guest, guest # user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same combination on # my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president' presidentskroob = 12345, president # user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz' darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz # user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz' lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Roles with assigned permissions # # Each line conforms to the format defined in the # org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [roles] # 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*' admin = * # The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber: schwartz = lightsaber:* # The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with # license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id) goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5 -
Quickstart.java
/** * Simple Quickstart application showing how to use Shiro's API. * * @since 0.9 RC2 */ public class Quickstart { private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class); public static void main(String[] args) { DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager(); IniRealm iniRealm = new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini"); defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(iniRealm); SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager); // Now that a simple Shiro environment is set up, let's see what you can do: // get the currently executing user: //获取当前的用户对象Subject Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!) //通过当前用户拿到session Session session = currentUser.getSession(); session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue"); String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey"); if (value.equals("aValue")) { log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]"); } // let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions: //判断当前的用户是否被认证 if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) { //token : 令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa"); //记住我 token.setRememberMe(true); try { currentUser.login(token); //执行登录 //未知用户 } catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal()); //密码错误 } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) { log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!"); //账号被锁定 } catch (LockedAccountException lae) { log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " + "Please contact your administrator to unlock it."); } // ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application? catch (AuthenticationException ae) { //unexpected condition? error? } } //say who they are: //print their identifying principal (in this case, a username): log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully."); //test a role: if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) { log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!"); } else { log.info("Hello, mere mortal."); } //test a typed permission (not instance-level) //粗粒度 if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) { log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely."); } else { log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only."); } //a (very powerful) Instance Level permission: //细粒度 if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) { log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " + "Here are the keys - have fun!"); } else { log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!"); } //all done - log out! currentUser.logout(); System.exit(0); } } -
运行,没问题
3、shiro-Springboot
3.1、准备好测试环境
1、导入包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-springartifactId>
<version>1.7.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.theborakompanionigroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiroartifactId>
<version>2.0.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8timeartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.16version>
dependency>
2、配置核心配置
-
ShiroConfig
package com.pwx.config; import at.pollux.thymeleaf.shiro.dialect.ShiroDialect; import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean; import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @ Auction:pwx * @ Date:2021/1/29 - 01 - 29 - 11:31 * @ Description:com.pwx.config * @ version:1.0 */ @Configuration public class ShiroConfig { //ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); return bean; } //DefaultWebSecurityManager:2 @Bean(name = "securityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){ DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); //关联userRealm securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return securityManager; } //创建realm对象,需要自定义类:1 @Bean public UserRealm userRealm(){ return new UserRealm(); } } -
UserRealm
@Configuration public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { @Autowired UserService userService; //授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了授权doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } //认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了认证doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } }
我们可以很明显看得出,这个配置相对于Security要复杂一点。都是固定的
然后我们增加一点前端的东西
-
MyController
@Controller public class MyController { @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String toIndex(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","hello,world!"); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/user/add") public String add(){ return "user/add"; } @RequestMapping("/user/update") public String update(){ return "user/update"; } } -
add.html
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>添加h1> body> html> -
update.html
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>修改h1> body> html> -
index.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro" > <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>首页h1> <div> <a th:href="@{/user/add}">adda> div> <div> <a th:href="@{/user/update}">updatea> div> body> html>
简单的初始环境就搭好了,然后我们利用不同的权限对这两个页面进行访问
3.2、 添加shiro的内置过滤器
-
在shiroConfig的第三步进行补充
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //添加shiro的内置过滤器 /* anon:无需认证就可以访问 authc:必须认证才能访问 user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能用 perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问; role:拥有某个角色权限才能访问 */ //添加内置过滤器 Map<String,String>filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //需要认证,没有设置登录页面会报404 filterMap.put("/user/add","authc"); filterMap.put("/user/update","authc"); //支持通配 filterMap.put("/user/*","authc"); bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); //设置登录的请求页面 bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); return bean; } -
login.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>登录h1> <form th:action=""> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username">p> <p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"> p> <p><input type="submit">p> form> body> html> -
MyController
@RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "login"; }
然后运行,我们可以看到,我们点击两个页面跳转的时候,都会被拦截,然后跳转到登录界面。这就证明拦截成功了
3.3、用户认证
既然已经拦截成功了,那就证明前面的都没问题了,那就要进行用户的认证了
1、我们让他登陆后提交到login
<h1>登录h1>
<hr>
<p th:text="${msg}" style="color: red">p>
<form th:action="@{/login}">
<p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username">p>
<p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"> p>
<p><input type="submit">p>
form>
2、我们在Controller进行处理
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username , String password,Model model){
//获取当前的用户对象Subject
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//token : 令牌
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
//这里的几个异常都可以从Quickstart里面看的到
try {
currentUser.login(token); //执行登录
return "index";
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名错误");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
model.addAttribute("msg","密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
3、如果这时候运行,我们会方向他会走到我们的认证,后台会输出执行了认证doGetAuthorizationInfo,这是我们在UserRealm那里写的,所以这时候我们直接过去写我们的账号信息,去处理这个认证
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了认证doGetAuthorizationInfo");
//数据要从数据库中拿,等下再整个MyBatis
String name = "root";
String password = "12345";
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
if(name.equal(usernamePasswordToken.getUsername())){ //如果没有这个人
return null; //抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
//密码认证,shiro做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,"");
}
3.4、连上数据库
1、导入包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.2.4version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.4version>
dependency>
2、配置文件:
-
application.yaml
spring: datasource: username: root password: pwx12345 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500-
application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.pwx.pojo mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
-
3、连接数据库
4、创建pojo实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id; //序号
private String name; //账号
private String pwd; //密码
private String perms; //权限,用户授权要用
}
5、Mapper
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
6、UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.pwx.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserByName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
select * from mybatis.user where name = #{name}
select>
mapper>
7、service
-
UserService
public interface UserService { public User queryUserByName(String name); } -
UserServiceImpl
@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; @Override public User queryUserByName(String name) { return userMapper.queryUserByName(name); } }
8、写完可以测试一下,防止出错。然后我们回到认证那里
@Configuration
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了授权doGetAuthorizationInfo");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了认证doGetAuthorizationInfo");
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
//连接真实的数据库
User user = userService.queryUserByName(usernamePasswordToken.getUsername());
if(user==null){ //如果没有这个人
return null;
}
//密码认证,加密了
//可以加密: MD5 MD5盐值加密:MD5+username
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),"");
}
}
3.5、用户授权
1、小改一个地方测试一下
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
//添加shiro的内置过滤器
/*
anon:无需认证就可以访问
authc:必须认证才能访问
user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能用
perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问;
role:拥有某个角色权限才能访问
*/
//添加内置过滤器
Map<String,String>filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update","authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
//设置登录的请求页面
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
return bean;
}
2、改了之后登录,是不是发现我们自己进不去add页面了,这就是要进行授权了,未授权会跳转401
3、先说说这个401,未授权页面是可以自己定制的
-
MyController
@RequestMapping("/noauth") @ResponseBody public String unauthorized(){ return "未授权"; } -
在上面的代码加一句话
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //添加shiro的内置过滤器 /* anon:无需认证就可以访问 authc:必须认证才能访问 user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能用 perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问; role:拥有某个角色权限才能访问 */ //添加内置过滤器 Map<String,String>filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]"); filterMap.put("/user/update","authc"); bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); //设置登录的请求页面 bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); //自定义未授权页面 bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noauth"); return bean; }
就是这样,定制的操作就好了,甚至还可以自己加一个页面是吧
4、然后我们可以看到在操作的时候,后台有一个执行了授权doGetAuthorizationInfo,我们可以判定他走了授权的那个函数,那就下来我们就对那个函数进行操作
UserRealm
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了授权doGetAuthorizationInfo");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//只是给所有的都添加这个权限,一般一些公共的可以这么写
info.addStringPermission("user:add");
//拿到当前对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
User currentUser = (User) subject.getPrincipal();
//设置当前用户的权限
info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
然后我们再回到我们的认证
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了认证doGetAuthorizationInfo");
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
User user = userService.queryUserByName(usernamePasswordToken.getUsername());
if(user==null){ //如果没有这个人
return null;
}
Subject currentSubject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
Session session = currentSubject.getSession();
session.setAttribute("loginUser",user);
//密码认证,加密了
//可以加密: MD5 MD5盐值加密:MD5+username
//这就实现了授权和认证的联动
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),"");
}
5、最后我们回到我们的前端,处理显示的问题
-
shiroConfig
//整合shiro @Bean public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){ return new ShiroDialect(); } -
index.html
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro" > <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>首页h1> <div th:if="${session.loginUser==null}"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登录a> div> <p th:text="${msg}">p> <hr> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:add" > <a th:href="@{/user/add}">adda> | div> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:update" > <a th:href="@{/user/update}">updatea> div> body> html>