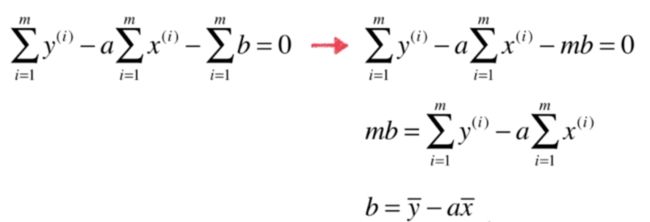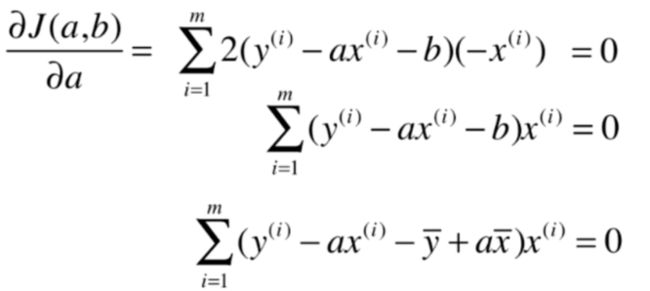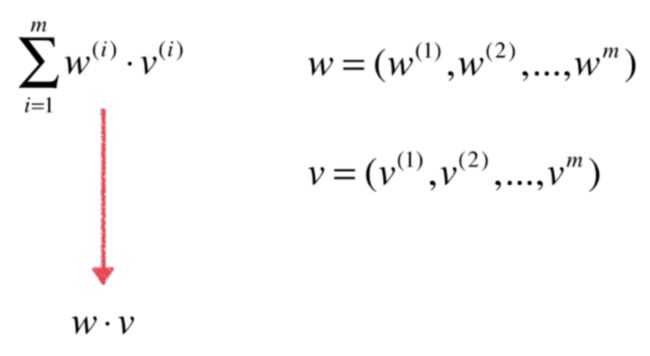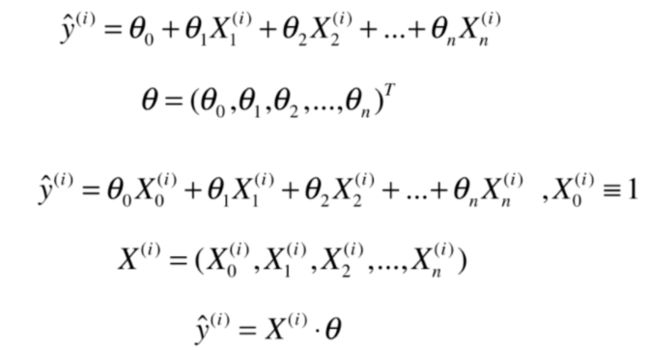机器学习-线性回归法
线性回归算法
- 解决回归问题
- 思想简单,实现容易
- 许多强大的非线性模型的基础
- 结果具有很好的可解释性
- 蕴含机器学习中的很多重要思想

样本特征只有一个,称为:简单线性回归

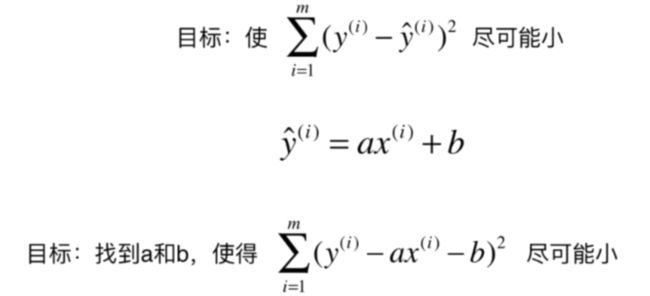

通过分析问题,确定问题的损失函数或者效用函数
通过最优化损失函数或者效用函数,获得机器学习的模型
几乎所有参数学习算法都是这样的套路

最小二乘法
代码实现 简单线性回归法
加载数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([1., 2., 3., 4., 5.])
y = np.array([1., 3., 2., 3., 5.])
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 6])
plt.show()
x_mean = np.mean(x)
y_mean = np.mean(y)
num = 0.0
d = 0.0
for x_i, y_i in zip(x, y):
num += (x_i - x_mean) * (y_i - y_mean)
d += (x_i - x_mean) ** 2
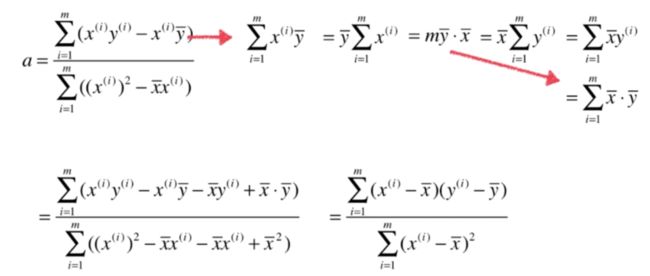
a = num/d
b = y_mean - a * x_mean
y_hat = a * x + b
绘图
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, y_hat, color='r')
plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 6])
plt.show()
import numpy as np
class SimpleLinearRegression1:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Simple Linear Regression 模型"""
self.a_ = None
self.b_ = None
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集x_train,y_train训练Simple Linear Regression模型"""
assert x_train.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert len(x_train) == len(y_train), \
"the size of x_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
x_mean = np.mean(x_train)
y_mean = np.mean(y_train)
num = 0.0
d = 0.0
for x, y in zip(x_train, y_train):
num += (x - x_mean) * (y - y_mean)
d += (x - x_mean) ** 2
self.a_ = num / d
self.b_ = y_mean - self.a_ * x_mean
return self
def predict(self, x_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集x_predict,返回表示x_predict的结果向量"""
assert x_predict.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert self.a_ is not None and self.b_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
return np.array([self._predict(x) for x in x_predict])
def _predict(self, x_single):
"""给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值"""
return self.a_ * x_single + self.b_
def __repr__(self):
return "SimpleLinearRegression1()"
向量化运算
class SimpleLinearRegression2:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Simple Linear Regression模型"""
self.a_ = None
self.b_ = None
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集x_train,y_train训练Simple Linear Regression模型"""
assert x_train.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert len(x_train) == len(y_train), \
"the size of x_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
x_mean = np.mean(x_train)
y_mean = np.mean(y_train)
self.a_ = (x_train - x_mean).dot(y_train - y_mean) / (x_train - x_mean).dot(x_train - x_mean)
self.b_ = y_mean - self.a_ * x_mean
return self
def predict(self, x_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集x_predict,返回表示x_predict的结果向量"""
assert x_predict.ndim == 1, \
"Simple Linear Regressor can only solve single feature training data."
assert self.a_ is not None and self.b_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
return np.array([self._predict(x) for x in x_predict])
def _predict(self, x_single):
"""给定单个待预测数据x_single,返回x_single的预测结果值"""
return self.a_ * x_single + self.b_
def __repr__(self):
return "SimpleLinearRegression2()"
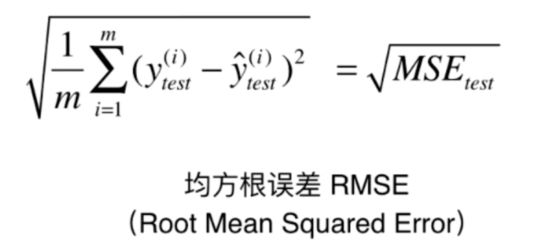
衡量线性回归法的指标:MSE,RMSE和MAE
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
x = boston.data[:,5] # 只使用房间数量这个特征
y = boston.target
可视化
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
x = x[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, seed=666)
from playML.SimpleLinearRegression import SimpleLinearRegression
reg = SimpleLinearRegression()
reg.fit(x_train, y_train)
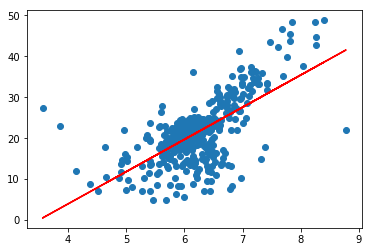
plt.scatter(x_train, y_train)
plt.plot(x_train, reg.predict(x_train), color='r')
plt.show()
y_predict = reg.predict(x_test)
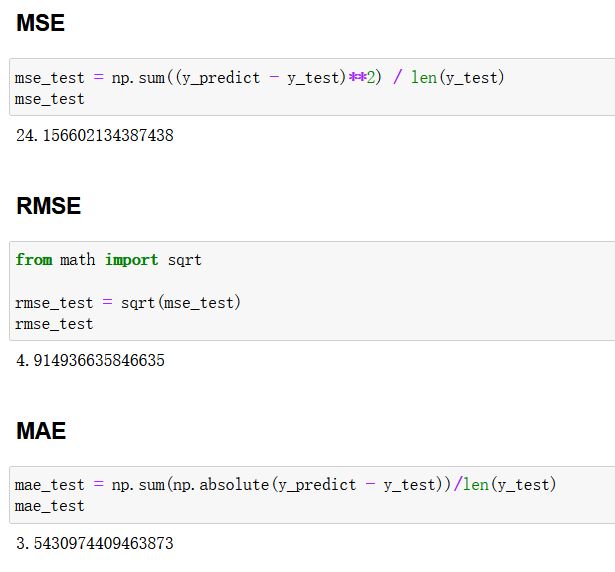
MSE
mse_test = np.sum((y_predict - y_test)**2) / len(y_test)
RMSE
from math import sqrt
rmse_test = sqrt(mse_test)
MAE
mae_test = np.sum(np.absolute(y_predict - y_test))/len(y_test)
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的准确率"""
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict), \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return np.sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true)
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的MSE"""
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict), \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return np.sum((y_true - y_predict)**2) / len(y_true)
def root_mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的RMSE"""
return sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict))
def mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的MAE"""
return np.sum(np.absolute(y_true - y_predict)) / len(y_true)
scikit-learn中的MSE和MAE
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)
mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_predict)
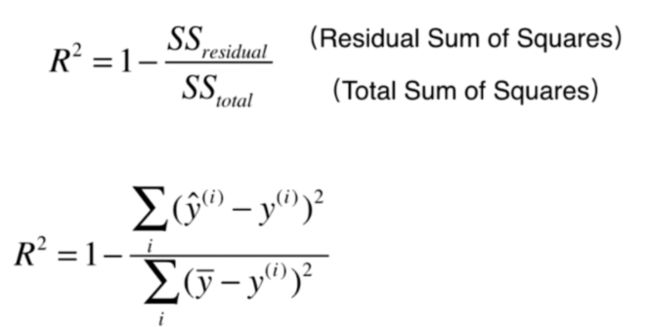
评价回归算法指标:R Square
1 - mean_squared_error(y_test, y_predict)/np.var(y_test)
封装
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的准确率"""
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict), \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return np.sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true)
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的MSE"""
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict), \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return np.sum((y_true - y_predict)**2) / len(y_true)
def root_mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的RMSE"""
return sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict))
def mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的MAE"""
assert len(y_true) == len(y_predict), \
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return np.sum(np.absolute(y_true - y_predict)) / len(y_true)
def r2_score(y_true, y_predict):
"""计算y_true和y_predict之间的R Square"""
return 1 - mean_squared_error(y_true, y_predict)/np.var(y_true)
scikit-learn中的 r2_score
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
r2_score(y_test, y_predict)
多元线性回归
import numpy as np
from .metrics import r2_score
class LinearRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Linear Regression模型"""
self.coef_ = None
self.intercept_ = None
self._theta = None
def fit_normal(self, X_train, y_train):
"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train训练Linear Regression模型"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return X_b.dot(self._theta)
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return r2_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LinearRegression()"
使用
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666)
from playML.LinearRegression import LinearRegression
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit_normal(X_train, y_train)
scikit-learn中的线性回归
加载数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
boston = datasets.load_boston()
X = boston.data
y = boston.target
X = X[y < 50.0]
y = y[y < 50.0]
from playML.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666)
线性回归
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
lin_reg = LinearRegression()
lin_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
standardScaler = StandardScaler()
standardScaler.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_train_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_train)
X_test_standard = standardScaler.transform(X_test)
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsRegressor
knn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor()
knn_reg.fit(X_train_standard, y_train)
knn_reg.score(X_test_standard, y_test)
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = [
{
"weights": ["uniform"],
"n_neighbors": [i for i in range(1, 11)]
},
{
"weights": ["distance"],
"n_neighbors": [i for i in range(1, 11)],
"p": [i for i in range(1,6)]
}
]
knn_reg = KNeighborsRegressor()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(knn_reg, param_grid, n_jobs=-1, verbose=1)
grid_search.fit(X_train_standard, y_train)