倒计时61天
M-智乃的36倍数(normal version)_2024牛客寒假算法基础集训营3 (nowcoder.com)
//非ac代码,超时了,54.17/100
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+5;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
#define int long long
int n;
string s1[N];
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>s1[i];
}
int cn=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
{
string s=s1[i]+s1[j];
string ss=s1[j]+s1[i];
int b,c;
b=strtoll(s.c_str(),NULL,10);
if(s==ss)c=b;
else c=strtoll(ss.c_str(),NULL,10);
if(b%36==0)cn++;
if(c%36==0)cn++;
}
}
cout<>t;
t=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
} ac代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+5;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
#define int long long
int a[N],b[37];
void solve()
{
int n,cn=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
b[a[i]%36]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int r=a[i];
int c=1;
while(r)
{
c*=10;
r/=10;
}
for(int j=0;j<=35;j++)
{
if(((j*(c%36))%36+a[i]%36)%36==0)
{
cn+=b[j]-(a[i]%36==j);
}
}
}
cout<>t;
t=1;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
} 笔记:(来源:b站杭电acm刘老师)
并查集:不相交集合。
1.实现方法:
每个集合用一颗“有根树”表示
定义数组 set[1..n]
set[i]=i;则i表示本集合,并是集合对应树的根
set[i]=j,则表示j不等于i,则j是i的父节点
set[i]:1 2 3 2 1 3 4 3 3 4
i: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
#define int long long
int a[110];
int find(int x) {
int r = x;
while (a[r] != r) {
r = a[r];
}
return r;
}
void solve() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int x;
cin >> x;
cout << find(x);
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
//cin>>t;
t = 1;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
} (碎碎念,,,好像考过这个,刚开学那会儿。。。。。。
把1,2班合并:让set[1]=2;
即:set[i]:1 2 3 2 1 3 4 3 3 4
i: 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
优化:路径压缩:如果树的高度很大,查找路径就会较长,当查找量很大的时候,就很容易tle,
解决方法:每次查找的时候,如果路径较长,则修改信息,以便下次查找的时候速度更快。
具体方案:1)找到根节点。2)修改查找路径上的所有结点,将它们都指向根节点
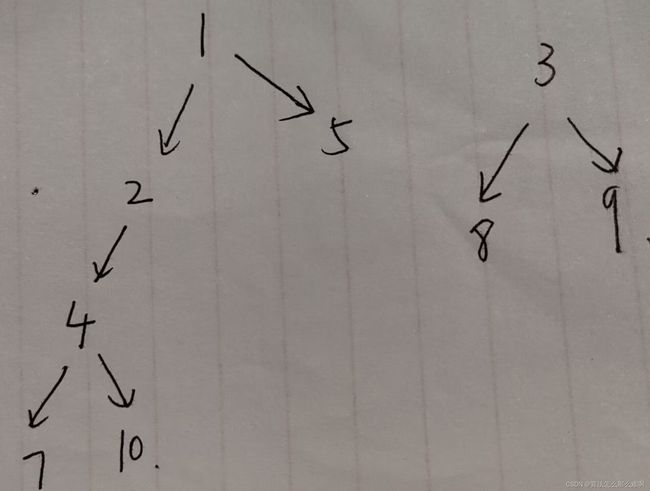
例子:
优化后的代码:
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
#define int long long
int a[110];
/*
int find(int x) {
int r = x;
while (a[r] != r) {
r = a[r];
}
return r;
}
*/
int find1(int x) {
if (a[x] != x) {
a[x] = find1(a[x]);
}
return a[x];
}
void solve() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int x;
cin >> x;
cout << find1(x);
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
//cin>>t;
t = 1;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
} 例题:(来源:浙大研究生复试
“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个城镇间可以实现交通(不一定要有直接的道路),问最少还需要建设多少条道路?
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
#define int long long
int a[110];
int find(int x) {
int r = x;
while (a[r] != r) {
r = a[r];
}
return r;
}
int find1(int x, int y) {
int fx, fy;
fx = find(x);
fy = find(y);
if (fx != fy) {
a[fx] = fy;
}
}
void solve() {
int n, m, x, y, cn = -1;
while (cin >> n, n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = i;
}
for (cin >> m; m > 0; m--) {
cin >> x >> y;
find1(x, y);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i] == i)
cn++;
}//求老大的数量
cout << cn << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
//cin>>t;
t = 1;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/*
5 3
1 2
3 4
2 5
*/ 经典应用——最小生成树
重点!!:一定包含最短的那一条边:1-3这条
所以先把最短的这边选上,之后再选第二短的遍,如果这条边对应的顶点还没有联通(构成环)就加上,所以之后就是:4-6,2-5,3-6,之后就是3-4但因为3-4再加上就成环了,所以跳过,1-4同理跳过,然后2-3,可以,至此,最小生成树生成o(* ̄▽ ̄*)ブ,加起来等于15,所以输出15!
例题:
地图上有n个城市,现在想给这n个城市之间造路,希望让城市之间两两可达,给出了m种供选择的道路,每种选择是一个三元组(u,v,w),代表u,v城市之间建造一条长度为w的道路。希望总长越小越好。