编译原理--实验3-基于-LR(0)方法的语法分析
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.1实验目的
- 1.2 实验任务
- 1.3 实验内容
-
-
- 1.3.1 输入格式:
- 1.3.2 输出格式:
- 1.3.3 样例
-
- 1.4 程序
-
-
- 1.4.1 程序流程图
- 1.4.2 算法描述
- 1.4.3 程序源码
-
前言
编译原理课程实验的实验课内容—构造自底向上LR(0)的语法分析程序。通过本次实验,可以熟练掌握对于LR(0)分析表的构造方法。
1.1实验目的
(1)掌握 LR(0)分析表的构造方法。
(2)掌握设计、编制和调试典型的语法分析程序,进一步掌握常用的语法分析方法。
(3)理解语法分析在编译程序中的作用。
1.2 实验任务
编写一个程序对输入的源代码进行语法分析,并打印分析结果。
自己编写一个基于 LR(0)方法的语法分析程序。语言不限,文法不限。 此时可根据自己的实际情况,选择以下一项实现分析算法中分析表的构造:
(1)直接输入根据已知文法构造的 LR(0)分析表;
(2)输入已知文法的项目集规范族和转换函数,由程序自动生成 LR(0)分析表;
(3)输入已知文法,由程序自动生成 LR(0)分析表。
1.3 实验内容
1.3.1 输入格式:
你的程序输入是一个包含待分析词法单元序列的文本 文件,程序需要能够接收一个输入文件名作为参数,以获得相应的输出结果。
1.3.2 输出格式:
你的程序需要输出语法分析过程(包括 LR(0)分析表和分析过程表,并能够保 存 LR(0)分析表)和相应的分析结果(即此串是否为 LR(0)文法的句子)
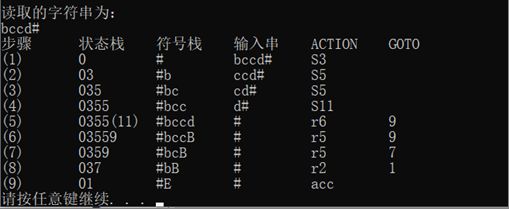
1.3.3 样例

对输入串的分析:
1.4 程序
1.4.1 程序流程图
1.4.2 算法描述
本次LR(0)分析表采用的是课本P136页表6.3的LR(0)分析表。程序的整体设计思路上,首先分为几个主要的函数来实现查找LR(0)分析表,对确定的输入串进行LR(0)分析过程。 同时,还要有出错判断的提示,这个我计划放在对输入串的分析过程中一并实现,另一个是保存当前的LR(0)分析表,这个功能放在输出LR(0)分析表的函数中实现。
1.4.3 程序源码
#include(寒假打算发一下的,结果后来一直拖到现在,忽然想起,还是赶快发一下)
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/wys5wys/article/details/85128812


