Go语言实现分布式缓存(一) ——lru淘汰策略和超时过期
我跟着极客兔兔的教程实现了分布式缓存,该系列文章是对实现过程的总结。
详细实现教程:7天用Go从零实现分布式缓存GeeCache
文章目录
- lru淘汰策略
- 超时淘汰
- 代码实现
-
- 实例化缓存
- 添加数据
- 删除缓存
- 获取缓存
- 定期删除
- 测试
lru淘汰策略
缓存的大小是有限的,当添加数据发现剩余缓存不够时,需要淘汰缓存中的部分数据。如何选择性的淘汰缓存中的数据呢?常用方法有以下三种。
-
LRU: 全称Least Recently Use,意为:最近最少使用的。当缓存到达最大值时,就会淘汰最近最久未使用的数据。
-
LFU: 全称Least Frequently User,意为:最少使用。注意与LRU的区别,LFU强调使用次数最少的。当缓存到达最大值时,就会淘汰最近最少使用的。
-
FIFO: 全称First In First Out,意为:最先进的最先出去。当缓存到达最大值时,就会淘汰最先进入缓存的那个数据。
这里我们只实现LRU淘汰策略。
lru的实现需要用到两个数据结构:双向循环链表和一个字典map,双向循环链表是缓存内容的主要存放位置,并且借助双向循环链表 来实现数据淘汰。字典map存放的是指向链表节点的指针,便于在链表中查询缓存。
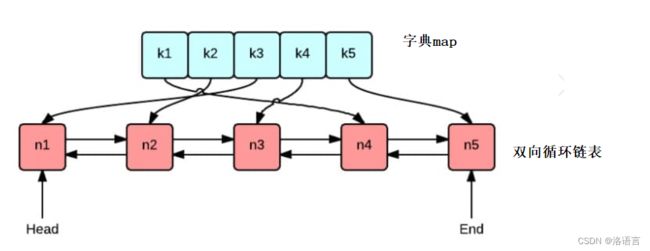
每当我们添加数据时,将数据插入链表头部,同时将节点的指针存储到map中。当我们查询数据时,通过key在map中获取对应节点的指针,然后将该节点放到链表的头部,并返回数据。当缓存淘汰数据时,只需要将链表尾部的数据剔除,并删除map中对应节点的指针。
通过以上方案可以实现lru淘汰策略。但是lru淘汰策略还存在很大问题,数据的剔除是由lru算法决定的,使用者并不能决定何时淘汰。如果旧数据一直不被剔除,就可能造成数据并不一致问题。所以接下来在lru的基础上实现超时淘汰。
超时淘汰
实现超时淘汰我们需要增加一个字典map来维护,当我们添加数据时需要指定数据的过期时间,设置为负数表示永不过期。设置了过期时间的数据(过期时间为非负数)也要加入这个map。
接下来要考略的就是什么时候剔除过期数据,这里有三种方案:
- 定时剔除: 为设置了过期时间的值绑定定时事件,时间一到就触发事件将数据删除。
缺点: 当很多数据同时过期时会占用大量cpu,使缓存的效率降低。 - 惰性删除: 数据过期时并不会立刻删除,当过期的数据被获取时,才会删除。
缺点: 若数据一直未被获取,会占用内存。 - 定期删除: 同样也是数据过期不会被立刻删除,缓存会每隔一段时间从map中抽取部分数据,删除其中过期的数据。
缺点: 时间间隔很难确定,若时间间隔太短,会跟定时删除一样,占用大量CPU资源。若时间间隔太长, 缓存中的数据不能被及时删除,浪费大量内存资源。
这里为参考了Redis的超时淘汰策略,将惰性删除和定期删除结合使用。每当获取数据时会查看该数据是否过期,如果过期就将该数据删除。与此同时,会另外开启一个协程,定期的从缓存中抽取部分数据,删除过期数据。
代码实现
my-cache2/evict/cache.go
type Value interface {
Len() int
}
type entity struct {
key string
v Value
ddl int64
}
type Cache struct {
maxBytes uint64
uBytes uint64
ll *list.List
allDataMap map[string]*list.Element
expireDataMap map[string]*list.Element
}
- Value 是缓存存储的数据类型接口。
- entity 是将缓存数据、key,以及过期时间ddl封装成的数据类型。key用于从两个map中查找数据并删除。
- Cache 是 实现lru和超时过期的核心数据结构。
- maxBytes 是缓存的最大内存。
- uBytes是已经使用的缓存大小。
- ll 是双向循环链表,是存储缓存数据和实现lru的主要数据结构。
- allDataMap 是缓存中所有数据的映射字典,可以通过key获取该数据在ll中对应节点的指针。
- expireDataMap 与allDataMap类似,它是缓存中所有设置了过期时间的数据的映射字典。
实例化缓存
func NewCache(maxBytes uint64) *Cache {
return &Cache{
maxBytes: maxBytes,
ll: new(list.List),
allDataMap: make(map[string]*list.Element),
}
}
在实例化缓存时并没有初始化expireDataMap,是因为这里会使用延迟加载,当第一个设置了过期时间的数据被添加时,这个map才会被初始化。
添加数据
func (c *Cache) Add(key string, v Value, expire int64) error {
if c.allDataMap[key] != nil{
c.remove(key)
}
vBytes := uint64(v.Len()) + uint64(len([]byte(key)))
if vBytes > c.maxBytes-c.uBytes {
if vBytes > c.maxBytes {
return fmt.Errorf("%s is not find in cache", key)
}
c.RemoveOldest()
return c.Add(key, v, expire)
}
var ddl int64 = -1
if expire > 0 {
ddl = time.Now().Unix() + expire
}
e := c.ll.PushFront(&entity{key, v, ddl})
c.uBytes += vBytes
c.allDataMap[key] = e
if expire > 0 {
if c.expireDataMap == nil {
c.expireDataMap = make(map[string]*list.Element)
}
c.expireDataMap[key] = e
}
return nil
}
- 添加的数据若已经存在,需要先删掉旧数据(实现更新)。
- 添加数据首先要检查缓存的内存大小是否足够,不够的话就需要剔除缓存中的一些旧数据。
- 添加数据时需要指定expire(数据多少秒后过期)。若expire小于0,表示永不过期;expire大于0会在指定秒数后过期然后Add函数会根据这个expire获取数据的过期时间。
删除缓存
func (c *Cache) RemoveOldest() {
back := c.ll.Back()
c.ll.Remove(back)
e := back.Value.(*entity)
delete(c.allDataMap, e.key)
delete(c.expireDataMap, e.key)
c.uBytes -= uint64(back.Value.(*entity).v.Len()) + uint64(len(e.key))
}
func (c *Cache) remove(key string) {
element := c.allDataMap[key]
c.ll.MoveToBack(element)
c.RemoveOldest()
}
- RemoveOldest() 函数用来移除最久未使用的缓存。
- remove() 函数用来移除指定key对应的缓存。
获取缓存
func (c *Cache) Get(key string) (Value, error) {
element := c.allDataMap[key]
if element == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s is not find in cache", key)
}
entity := element.Value.(*entity)
if entity.ddl > 0 && entity.ddl < time.Now().Unix() {
c.remove(key)
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s is not find in cache", key)
}
c.ll.MoveToFront(element)
return entity.v, nil
}
- 在获取缓存时,若被获取的缓存过期,就会将该缓存删除,并返回nil和异常。若被获取的数据未过期或未设置过期时间,就会将该数据放到链表首部。
定期删除
func (c *Cache) DeleteExpired() {
go func() {
for true {
if c.expireDataMap == nil {
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
continue
}
count := 20
expired := 0
for _, v := range c.expireDataMap {
if count <= 0 {
break
}
e := v.Value.(*entity)
if e.ddl <= time.Now().Unix() {
expired++
c.remove(e.key)
}
count--
}
if expired < 5 {
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
}
}
}()
}
- go语言中,range遍历map每次的顺序都是随机的,我们可以借助range来随机获取map中的部分键。
- 调用该函数会启动一个协程,该协程每秒会随机获取expiredDataMap中的二十个缓存数据,并检查它们是否过期,若二十个数据中有五个以上的数据已经过期,那么会立刻再次获取二十个缓存数据重复该操作(不会进行等待)。
测试
func (c *Cache) Print() {
fmt.Println("allDataMap:")
for _, v := range c.allDataMap {
fmt.Printf("%v ", v.Value.(*entity).key)
}
fmt.Println("\nexpireDataMap")
for _, v := range c.expireDataMap {
fmt.Printf("%v ", v.Value.(*entity).key)
}
fmt.Println()
}
func (c *Cache) Len() int {
return len(c.allDataMap)
}
在cache.go中实现这两个函数是为了更好的进行测试。
my-cache2/test/cache_test.go
type v struct {
s string
}
func (v v) Len() int {
return len(v.s)
}
// 测试对url剔除、对设置超时时间和未设置超时时间进行分组
func TestCache1(t *testing.T) {
cache := evict.NewCache(20)
cache.Add("12", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("34", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("56", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("78", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("90", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("91", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("92", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("93", v{"ab"}, -1)
cache.Add("94", v{"ab"}, -1)
cache.Add("95", v{"ab"}, -1)
cache.Print()
}
// 测式定时随机剔除
func TestCache2(t *testing.T) {
cache := evict.NewCache(20)
cache.DeleteExpired()
cache.Add("12", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("34", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("56", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("78", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("90", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("95", v{"ab"}, -1)
cache.Print()
time.Sleep(4 * time.Second)
cache.Print()
}
//测试Get不会删除未过期数据,但是会删除过期数据
func TestCache3(t *testing.T) {
cache := evict.NewCache(20)
cache.Add("12", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("34", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("56", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("78", v{"ab"}, 2)
cache.Add("90", v{"ab"}, 2)
fmt.Println(cache.Get("12"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("34"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("56"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("78"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("90"))
time.Sleep(4 * time.Second)
fmt.Println(cache.Get("12"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("34"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("56"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("78"))
fmt.Println(cache.Get("90"))
cache.Print()
}
=== RUN TestCache1
allDataMap:
93 94 95 91 92
expireDataMap
91 92
--- PASS: TestCache1 (0.00s)
PASS
=== RUN TestCache2
allDataMap:
56 78 90 95 34
expireDataMap
34 56 78 90
allDataMap:
95
expireDataMap
--- PASS: TestCache2 (4.00s)
PASS
=== RUN TestCache3
{ab}
{ab}
{ab}
{ab}
{ab}
12 is not find in cache
34 is not find in cache
56 is not find in cache
78 is not find in cache
90 is not find in cache
allDataMap:
expireDataMap
--- PASS: TestCache3 (4.01s)
PASS