二十、K8S-1-权限管理RBAC详解
目录
k8s RBAC 权限管理详解
一、简介
二、用户分类
1、普通用户
2、ServiceAccount
三、k8s角色&角色绑定
1、授权介绍:
1.1 定义角色:
1.2 绑定角色:
1.3主体(subject)
2、角色(Role和ClusterRole)
1、Role示例:
2、ClusterRole示例:
3、面向用户的默认的ClusterRole
3、角色绑定 (RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding)
1、RoleBinding示例:
2、ClusterRoleBinding 示例
4、对主体的引用
1、RoleBinding示例:角色绑定主体
5、对ServiceAccount的授权管理
1、为应用程序特定的服务帐户授予角色 (最佳实践)
2、在命名空间中为“默认”服务帐户(service account)授予角色
3、为命名空间中的所有服务帐户授予角色
4、对集群范围内的所有服务帐户(不鼓励)授予权限(role)
5、将超级用户权限授予集群内的所有服务帐户(强烈反对)
6、命令行工具
1、kubectl create role
2、kubectl create clusterrole
3、kubectl create rolebinding
4、kubectl create clusterrolebinding
k8s RBAC 权限管理详解
一、简介
基于角色(Role)的访问控制(RBAC Role Base Access Control)是一种基于组织中用户的角色来调节控制对计算机或者网络资源的访问的方法。RBAC鉴权机制使用 rbac.authorization.k8s.io API组来驱动鉴权决定, 允许你通过 Kubernetes API 动态配置策略。
k8s 集群相关所有的交互都通过apiserver来完成,对应这样集中式管理的系统来说,权限管理尤为重要,在1.5版本时候引入了RBAC的权限控制机制
让一个用户(Users)扮演一个角色(Role),角色拥有权限,从而让用户拥有这样的权限,随后在 授权机制当中,只需要将权限授予某个角色,此时用户将获取对应角色的权限,从而实现角色的访问 控制
在 k8s 的授权机制当中,采用 RBAC 的方式进行授权,其工作逻辑是,把对对象的操作权限定义到 一个角色当中,再将用户绑定到该角色,从而使用户得到对应角色的权限。如果通过 rolebinding 绑定 role,只能对 rolebingding 所在的名称空间的资源有权限。另外,k8s 为此还有一种集群级别的授权机制,就是定义一个集群角色(ClusterRole),对集群内 的所有资源都有可操作的权限,从而将 User2 通过 ClusterRoleBinding 到 ClusterRole,从而使 User2 拥有集群的操作权限。
启用RBAC,需要在 apiserver 中添加参数–authorization-mode=RBAC,如果使用的kubeadm安装的集群,1.6+版本都默认开启了RBAC。
[root@k8s-master-1 cfg]# cat kube-apiserver.conf | grep authorization
--authorization-mode=RBAC,Node \API Server 目前支持一下集中授权策略
- Webhook:通过调用外部REST服务对用户进行授权。
- RBAC:Role-Based Access Control,基于角色的访问控制(本章讲解)。
- Node:是一种专用模式,用于对kubelet发出的请求进行访问控制。
二、用户分类
k8s的用户分两种,一种是普通用户,一种是ServiceAccount(服务账户)
1、普通用户
- 普通用户是假定被外部或独立服务管理的,管理员分配私钥,平时常用的kubectl命令都是普通用户执行的
- 如果是用户需求权限,则将Role与User(或Group)绑定(需要创建User/Group),是给用户使用的。
2、ServiceAccount
- ServiceAccount(服务帐户)是由Kubernetes API管理的用户。它们绑定到特定的命名空间,并由API服务器自动创建或通过API调用手动创建。服务帐户与存储为Secrets的一组证书相关联,这些凭据被挂载到pod中,以便集群进程与Kubernetes API通信。(登录dashboard时我们使用的就是ServiceAccount)
- 如果是程序需求权限,将Role与ServiceAccount指定(这需要创建ServiceAccount并且在deployment中指定ServiceAccount),是给程序使用的。
工作流程图:
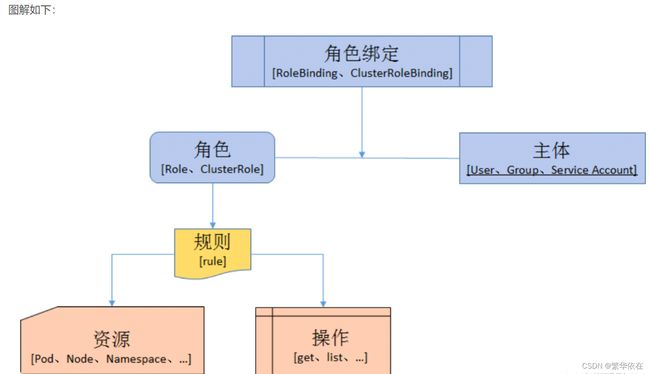
三、k8s角色&角色绑定
k8s引入了4个资源对象:Role、ClusterRole、RoleBinding、ClusterRoleBinding
1、授权介绍:
在RBAC API中,通过如下步骤进行授权
1.1 定义角色:
在定义角色时会指定此角色对于资源的访问控制规则
Role:角色,包含一组权限的规则,没有拒绝规则,只是附加运行,namespaces隔离,只作用于命名空间。授权特定命名空间的访问权限
ClusterRole:和Role的区别,Role只作用于命名空间内,ClusterRole作用于整个集群,也就是所有Namespace
1.2 绑定角色:
将主体与角色进行绑定,对用户进行访问授权
RoleBinding:作用于命名空间内,将ClusterRole或Role绑定于主体(User、Group或ServiceAccount)
ClusterRoleBinding:作用于整个集群,将ClusterRole或Role绑定于主体(User、Group或ServiceAccount)
1.3主体(subject)
User:用户
Group:用户组
ServiceAccount:服务账户
2、角色(Role和ClusterRole)
角色Role是权限的定义,在k8s中角色分为两种,
1、Role针对特定的命名空间的访问权限,
2、ClusterRole在整个集群范围内都生效。为啥要用两种资源?因为k8s对象作用域已经被划分为集群和命名空间两部分了。
需要注意:角色只有授权,没有禁止。
| 授权词 |
说明 |
| get |
列出单个资源 |
| list |
列出资源类型的集合 |
| create |
创建 |
| update |
修改全部资源 |
| patch |
修改部分资源 |
| watch |
动态监控 |
| proxy |
代理 |
| redirect |
重定向 |
| use |
调用 |
| delete |
删除 |
| deletecollection |
级联删除 |
相关参数:构成一个role 需要三部分
- Verbs:设置允许对资源对象操作的方法列表,如:{“get”, “list”, “watch”, “create”, “update”, “patch”, “delete”, “exec”}
- resources:需要操作的资源类型列表,如:{“services”, “endpoints”, “pods”,“secrets”,“configmaps”,“crontabs”,“deployments”,“jobs”,“nodes”,“rolebindings”,“clusterroles”,“daemonsets”,“replicasets”,“statefulsets”,“horizontalpodautoscalers”,“replicationcontrollers”,“cronjobs”}
- apiGroups:资源对象的API组列表:"" 缺省为 core 组资源,如: “”,“apps”, “autoscaling”, “batch”
1、Role示例:
1、命令行方式创建
kubectl create role [options]
常用的options 如上
示例:创建一个名为pod-role的role,可以操作的资源为pod,可以进行的操作为get, watch, list
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl create role pod-role --resource=pod --verb=get,watch,list
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-role created
2、yaml文件方式创建
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# vim role.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: pod-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl apply -f role.yaml
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-role created
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl get role
NAME CREATED AT
pod-role 2023-06-19T07:51:55Z
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe role pod-role
Name: pod-role
Labels:
Annotations:
PolicyRule:
Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs
--------- ----------------- -------------- -----
pods [] [] [get watch list]
- - - - - - -对资源的引用 - - - - - - - - -
kubernetes API中,大多数资源都是使用对象名称的字符串表示来呈现与访问的。例如pod 应使用"pods",有一些kubernetes API涉及子资源,
在RBAC角色表达资资源时,使用斜线(/)来分隔资源和子资源。
1、要允许某主体读取pod 同时访问这些pod的log子资源
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
2、对于某些请求,也可以通过resourceNames列表按名称引用资源,在指定时,可以将请求限定为资源的单个实例,
下面的例子中可以get和update 一个名为my-configmap 的 ConfigMap
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: default
name: configmap-updater
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
# 在 HTTP 层面,用来访问 ConfigMap 资源的名称为 "configmaps"
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["my-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"] 注意:
如果resources:填写的资源是["pods", "services"]等,apiGroups:可以直接用空来表示所有 [""],但是如果resources中添加了["deployments"],绑定的用户在创建deployment时候就会报错,没有权限。这是为啥?
因为apiGroups 为空的话,他只是针对单级的资源生效,
比方说 xx 例如 apiServer: v1,就是单级的,有pod、svc、ep...
还有两级的 比如:xx/yy 例如apiServer: apps/v1 他的父级就是apps 包括 :deployment、ds...
可以使用如下命令查看资源
kubectl apiresources 查看
示例:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: pod-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: ["","apps"] #因为deployments 的父级是apps ,添加了apps才会生效。
resources: ["pods","deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
或者deployment可以单独写个规则
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: pod-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]2、ClusterRole示例:
1、命令行方式创建
kubectl create clusterrole [options]
常用的options 如上
示例:创建一个名为pod-clusterrole的ClusterRole,可以操作的资源为pod,可以进行的操作为get, watch, list
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl create clusterrole pod-clusterrole --resource=pod --verb=get,watch,list
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-clusterrole created
2、通过yaml文件方式创建
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# vim clusterrole.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: pod-clusterrole
namespace: default #被忽略,因为clusterRole不收命名空间限制
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl apply -f clusterrole.yaml
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-clusterrole created
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl get clusterrole |grep pod
pod-clusterrole 2023-06-19T07:57:37Z
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe clusterrole pod-clusterrole
Name: pod-clusterrole
Labels:
Annotations:
PolicyRule:
Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs
--------- ----------------- -------------- -----
pods [] [] [get watch list] 3、面向用户的默认的ClusterRole
有些系统 的默认角色不是以“system”为前缀的,这部分角色时面向用户设置的,他们包含超级用户角色 (cluster-admin), 使用 ClusterRoleBinding 的集群范围的角色 (cluster-status), 以及是用RoleBding 的具体某个 namespace中的角色 (admin, edit, view)。
| 默认的ClusterRole |
默认的ClusterRoleBinding |
描述 |
| cluster-admin |
system:masters group |
允许在任何资源上执行任何操作,当通过ClusterRoleBinding 使用此角色时,授权所有民命空间下的所有资源,当使用 Rolebinding 时,授权rolebingding 所在的 命名空间下的所有资源,并包含命名空间自身所代表的资源 |
| admin |
None |
允许管理员访问,一般与Rolebinding搭配使用,绑定到一个命名空间中,可以读写大多数命名空间中的资源,并且可以在命名空间中创建 role 和 rolebinding,不允许访问命名空间中的资源配额,和命名空间自身 |
| edit |
None |
允许读写命名空间中的大多数资源,不过不允许查看和修改角色 (role)和角色绑定 (role binding) |
| view |
None |
允许读命名空间中的大多数资源,不过不允许查看和修改角色 (role)和角色绑定 (role binding),不允许查看secrets 资源 |
3、角色绑定 (RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding)
上边代码块 我们定义了角色,下一步就是将角色关联到用户,角色绑定是将我们创建的角色中定义好的权限赋予给一个或者一组用户,即主体(subject),RoleBinding 在指定的命名空间中执行授权,而 ClusterRoleBinding 在集群范围执行授权。
一个 RoleBinding 可以引用同一名字空间中的任何 Role。 或者,一个 RoleBinding 可以引用某 ClusterRole 并将该 ClusterRole 绑定到 RoleBinding 所在的名字空间。 如果你希望将某 ClusterRole 绑定到集群中所有名字空间,你要使用 ClusterRoleBinding。
注意:
在集群角色绑定(ClusterRoleBinding)中引用的角色只能是集群级别的角色(ClusterRole),而不能是命名空间级别的Role。
一旦通过创建RoleBinding或者ClusterRoleBinding与某个Role或者ClusterRole完成了绑定,用户就无法修改与之绑定的Role和ClusterRole了。只有删除了RoleBinding或者ClusterRoleBinding,才能修改Role和ClusterRole。
1、RoleBinding示例:
1、命令行方式创建
1.1 先创建serviceaccount服务账户
# kubectl create sa 或 kubectl create serviceAccount
# 例如
# kubectl create serviceaccount zhangsan
创建完serviceaccount服务账户之后,可以根据账户信息,查询到相应的token
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe serviceaccount zhangsan
Name: zhangsan
Namespace: default
Labels:
Annotations:
Image pull secrets: #自动添加到所有与该SA绑定的pod
Mountable secrets: zhangsan-token-8n48m
Tokens: zhangsan-token-8n48m #认证需要的token
Events:
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe secrets zhangsan-token-8n48m
Name: zhangsan-token-8n48m
Namespace: default
Labels:
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: zhangsan
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: fdae783b-aa7d-42f5-a5e0-3856c0f50c0e
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1143 bytes
namespace: 7 bytes
token: 太长删掉了
1.2创建rolebinding
# kubectl create rolebinding [options]
#常用options:
--role='':要进行绑定的role的name
--serviceaccount=[]:要进行绑定的clusterrole的name
--clusterrole='':要进行绑定的serviceaccount的name
# 例如 将read-pods和zhangsan进行绑定,绑定后zhangsana就拥有了role中定义的规则,需要指定命名空间--serviceaccount=namespaces:zhangsan
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl create rolebinding read-pods --role=pod-role --serviceaccount=default:zhangsan
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-pods created
2、通过yaml文件方式创建
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# vim rolebinding.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
# 此角色绑定允许 "zhangsan" 读取 "default" 命名空间中的 Pod
。你需要在该命名空间中有一个名为 “pod-role” 的 Role
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
# 你可以指定不止一个“subject(主体)”
- kind: ServiceAccount/User/Group
name: zhangsan # "name" 是区分大小写的
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io #ServiceAccount 不需要添加这行,User 需要添加 Group没试
roleRef:
# "roleRef" 指定与某 Role 或 ClusterRole 的绑定关系
kind: Role # 此字段必须是 Role 或 ClusterRole
name: pod-role # 此字段必须与你要绑定的 Role 或 ClusterRole 的名称匹配
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl apply -f rolebinding.yaml
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-pods created
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl get RoleBinding
NAME ROLE AGE
read-pods Role/pod-role 5s
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe RoleBinding read-pods
Name: read-pods
Labels:
Annotations:
Role:
Kind: Role
Name: pod-role
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
User zhangsan
- - - - - - - roleBinding也可以引用clusterRole - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# vim rolebinding2.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
# 此角色绑定允许 "zhangsan" 读取 "default" 名字空间中的 Pod
。你需要在该名字空间中有一个名为 “pod-clusterrole” 的 ClusterRole
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-secrets
namespace: default
subjects:
# 你可以指定不止一个“subject(主体)”
- kind: User
name: zhangsan # "name" 是区分大小写的
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
# "roleRef" 指定与某 Role 或 ClusterRole 的绑定关系
kind: ClusterRole # 此字段必须是 Role 或 ClusterRole
name: pod-clusterrole # 此字段必须与你要绑定的 Role 或 ClusterRole 的名称匹配
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl apply -f rolebinding2.yaml
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-secrets created
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl get RoleBinding
NAME ROLE AGE
read-pods Role/pod-role 13m
read-secrets ClusterRole/pod-clusterrole 9s
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl describe RoleBinding read-secrets
Name: read-secrets
Labels:
Annotations:
Role:
Kind: ClusterRole
Name: pod-clusterrole
Subjects:
Kind Name Namespace
---- ---- ---------
User zhangsan 2、ClusterRoleBinding 示例
1、命令行创建
# 此集群角色绑定允许 “manager” 组中的任何人访问任何名字空间中的 Secret 资源
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding read-secrets-global --clusterrole=pod-clusterrole --group=manager -n 命名空间
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-secrets-global created
2、yaml文件方式
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# vim clusterRoleBinding.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: read-secrets-global
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: manager # 'name' 是区分大小写的
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: pod-clusterrole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl apply -f clusterRoleBinding.yaml
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-secrets-global created
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl get clusterRoleBinding
NAME ROLE AGE
read-secrets-global ClusterRole/pod-clusterrole 10s
4、对主体的引用
RoleBinding或者ClusterRoleBinding 可绑定角色到某“主体(Subject)”上。主体可以是用户、组或者服务账户。
1、RoleBinding示例:角色绑定主体
下面示例是RoleBinding中的片段,仅展示subject的部分
1、对于名称为 [email protected] 的用户:
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "[email protected]"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
2、对于名称为frontend-admins 的用户组:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: "frontend-admins"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3、对于kube-system 命名空间中的默认服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: kube-system
4、对于 "qa" 命名空间中的所有服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts:qa
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
5、对于在任何名字空间中的服务账户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:serviceaccounts
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
6、对于所有已经过身份认证的用户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
7、对于所有未通过身份认证的用户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
8、对于所有用户:
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io5、对ServiceAccount的授权管理
默认RBAC策略向控制平面(controll plane),节点和控制器授予拥有范围限制的权限,但不向“kube-system”命名空间之外的服务帐户(service account)授予权限(超出所有已验证用户的发现权限)
从最安全到最不安全的方法是:
1、为应用程序特定的服务帐户授予角色 (最佳实践)
这要求应用程序在其pod规范中指定serviceAccountName,并且要在之前创建好服务帐户(通过API,应用程序清单【application manifest】,kubectl 等方式创建)。
例如,将“my-namespace”中的只读权限授予“my-sa”服务帐户:
kubectl create rolebinding my-sa-view --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=my-namespace:my-sa --namespace=my-namespace2、在命名空间中为“默认”服务帐户(service account)授予角色
例如,将“my-namespace”中的只读权限授予“默认”服务帐户:
kubectl create rolebinding default-view --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=my-namespace:default --namespace=my-namespace3、为命名空间中的所有服务帐户授予角色
例如,将“my-namespace”中的只读权限授予该命名空间中的所有服务帐户:所有用户 肯定是个组啊
kubectl create rolebinding test --clusterrloe=view --group=system:serviceaccounts:my-namespace --namespace=my-namespace4、对集群范围内的所有服务帐户(不鼓励)授予权限(role)
例如,将所有命名空间中的只读权限授予群集中的所有服务帐户:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding serviceaccounts-view --clusterrole=view --group=system:serviceaccounts5、将超级用户权限授予集群内的所有服务帐户(强烈反对)
在此不做演示
目录
k8s RBAC 权限管理详解
一、简介
二、用户分类
1、普通用户
2、ServiceAccount
三、k8s角色&角色绑定
1、授权介绍:
1.1 定义角色:
1.2 绑定角色:
1.3主体(subject)
2、角色(Role和ClusterRole)
1、Role示例:
2、ClusterRole示例:
3、面向用户的默认的ClusterRole
3、角色绑定 (RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding)
1、RoleBinding示例:
2、ClusterRoleBinding 示例
4、对主体的引用
1、RoleBinding示例:角色绑定主体
5、对ServiceAccount的授权管理
1、为应用程序特定的服务帐户授予角色 (最佳实践)
2、在命名空间中为“默认”服务帐户(service account)授予角色
3、为命名空间中的所有服务帐户授予角色
4、对集群范围内的所有服务帐户(不鼓励)授予权限(role)
5、将超级用户权限授予集群内的所有服务帐户(强烈反对)
6、命令行工具
1、kubectl create role
2、kubectl create clusterrole
3、kubectl create rolebinding
4、kubectl create clusterrolebinding
6、命令行工具
1、kubectl create role
创建Role对象,定义在某一命名空间中的权限
1、创建名称为 “pod-reader” 的 Role 对象,允许用户对 Pods 执行get、watch 和 list 操作:并创建a.yaml文件
[root@k8s-master-1 rbac]# kubectl create role pod-reader --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods -oyaml > a.yaml
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-reader created
2创建名称为 “pod-reader” 的 Role 对象并指定resourceNames:
kubectl create role pod-reader --verb=get --resource=pods --resource-name=readablepod --resource-name=anotherpod
3、创建名为 “foo” 的 Role 对象并指定 apiGroups:
kubectl create role foo --verb=get,list,watch --resource=replicasets.apps
4、创建名为 “foo” 的 Role 对象并指定子资源权限:
kubectl create role foo --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods,pods/status
5、创建名为 “my-component-lease-holder” 的 Role 对象,使其具有对特定名称的资源执行 get/update 的权限:
kubectl create role my-component-lease-holder --verb=get,list,watch,update --resource=lease --resource-name=my-component2、kubectl create clusterrole
1、创建名称为 “pod-reader” 的 ClusterRole 对象,允许用户对 Pods 对象执行 get、 watch 和 list 操作:并创建a.yaml文件
kubectl create clusterrole pod-reader --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods -oyaml > a.yaml
2、创建名为 “pod-reader” 的 ClusterRole 对象并指定 resourceNames:
kubectl create clusterrole pod-reader --verb=get --resource=pods --resource-name=readablepod --resource-name=anotherpod
3、创建名为 “foo” 的 ClusterRole 对象并指定 apiGroups:
kubectl create clusterrole foo --verb=get,list,watch --resource=replicasets.apps
4、创建名为 “foo” 的 ClusterRole 对象并指定子资源:
kubectl create clusterrole foo --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods,pods/status
5、创建名为 “foo” 的 ClusterRole 对象并指定 nonResourceURL:
kubectl create clusterrole "foo" --verb=get --non-resource-url=/logs/*
6、创建名为 “monitoring” 的 ClusterRole 对象并指定 aggregationRule:
kubectl create clusterrole monitoring --aggregation-rule="rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring=true"3、kubectl create rolebinding
在特定的命名空间中对Role或者ClusterRole授权
1、在名字空间 “acme” 中,将名为 admin 的 ClusterRole 中的权限授予名称 “bob” 的用户: 并创建a.yaml文件
kubectl create rolebinding bob-admin-binding --clusterrole=admin --user=bob --namespace=acme -oyaml > a.yaml
2、在名字空间 “acme” 中,将名为 view 的 ClusterRole 中的权限授予名字空间 “acme” 中名为 myapp 的服务账户:
kubectl create rolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myapp --namespace=acme
3、在名字空间 “acme” 中,将名为 view 的 ClusterRole 对象中的权限授予名字空间 “myappnamespace” 中名称为 myapp 的服务账户:
kubectl create rolebinding myappnamespace-myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=myappnamespace:myapp --namespace=acme4、kubectl create clusterrolebinding
在整个集群(所有命名空间)中用ClusterRole授权
1、在整个集群范围,将名为 cluster-admin 的 ClusterRole 中定义的权限授予名为 “root” 用户:并创建a.yaml文件
kubectl create clusterrolebinding root-cluster-admin-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=root -oyaml > a.yaml
2、在整个集群范围内,将名为 system:node-proxier 的 ClusterRole 的权限授予名为 “system:kube-proxy” 的用户:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding kube-proxy-binding --clusterrole=system:node-proxier --user=system:kube-proxy
3、在整个集群范围内,将名为 view 的 ClusterRole 中定义的权限授予 “acme” 名字空间中名为 “myapp” 的服务账户:
kubectl create clusterrolebinding myapp-view-binding --clusterrole=view --serviceaccount=acme:myapp