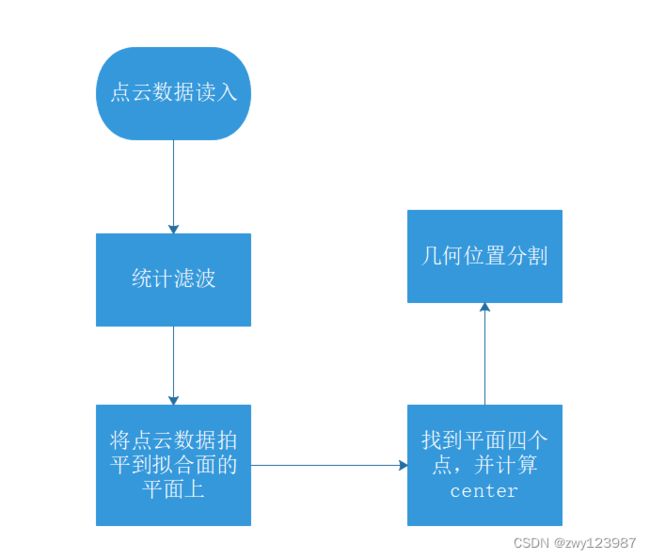
传统方法分割三维点云——几何分割
基于几何特征的分割方法
基于几何特征的分割方法是最早被提出和广泛应用的方法之一。它通过计算点云中的几何属性,如法向量、曲率等,来进行分割。其中,最常用的方法包括:
1.1 基干法向量的分割方法
该方法假设同一区域的法向量相似,通过计算点云中每个点的法向量,将相似法向量的点划分为同一区域。优点是简单易实现,但对于复杂场景或存在噪声的点云效果较差。
1.2 基于曲率的分割方法
该方法通过计算点云中每个点的曲率,将曲率变化较大的点划分为不同区域。优点是对于不同形状的物体有较好的分割效果,但对于噪声点较敏感。
传统方法对于噪声比较多的点云数据处理起来都较为复杂的,而在降噪过程中由于点云的无序性和无规则性,对于去噪后的结果无法保证,因此,传统方法分割点云的困难重重。
本文从几何分割的角度出发,充分利用物体几何特征,对于矩形物体进行了几何分割,以下是算法过程:
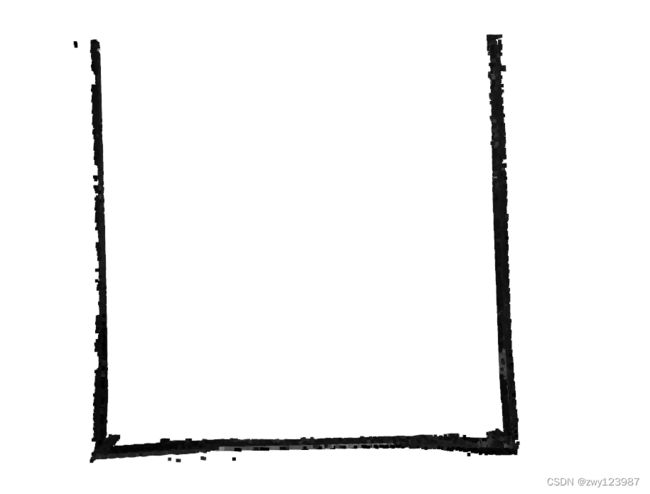
最后得到的数据分割情况如下,可以分割出三个面的点云数据,正上方的点云数据粉色块部分,是该程序也适用于四个面的矩形点云数据。
结果如下:
代码附上:
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
import pyransac3d as pyrsc
def line_fit(pcd,classified_points):
"""
直线拟合
"""
for i, points in classified_points.items():
# 创建点云对象
point_cloud = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
# 将numpy点云数据赋值给点云对象
point_cloud.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points)
print("->正在直线拟合...")
mesh_cylinders = []
line = pyrsc.Line()
# A:直线的斜率,B:直线的截距,inliers:内点索引,
# thresh:内点的距离阈值
# maxIteration:RANSAC算法的拟合次数
A, B, inliers = line.fit(points, thresh=500, maxIteration=500)
print('直线的三维斜率为:', A)
print('直线的截距为:', B)
R = pyrsc.get_rotationMatrix_from_vectors([0, 0, 1], A)
ransac_line = point_cloud.select_by_index(inliers)
mesh_cylinder = o3d.geometry.TriangleMesh.create_cylinder(radius=20, height=10000)
mesh_cylinder.compute_vertex_normals()
mesh_cylinder.paint_uniform_color([1, 0, 0])
mesh_cylinder = mesh_cylinder.rotate(R, center=[0, 0, 0])
mesh_cylinder = mesh_cylinder.translate((B[0], B[1], B[2]))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([point_cloud, ransac_line, mesh_cylinder])
def classifiction_points(pcd,wall_corners):
'''
根据四面墙的四个角点,将四面墙的点云数据分为四块。
'''
# 计算中心点
center_point = np.mean(wall_corners, axis=0)
# 将每个角点向中心点移动1cm
moved_corners = []
for corner in wall_corners:
direction_to_center = center_point - corner
# 单位化方向向量
unit_direction = direction_to_center / np.linalg.norm(direction_to_center)
# 移动1cm
moved_corner = corner + unit_direction * 1
moved_corners.append(moved_corner)
moved_corners = np.array(moved_corners)
# points_cloud是一个Numpy数组,包含点云数据
points_cloud = np.array(pcd.points)
# 分类点云数据
classified_points = {i: [] for i in range(4)}
for point in points_cloud:
# 对每个点,找到最近的延长线
min_distance = float('inf')
min_index = -1
for i in range(4):
corner1 = moved_corners[i]
corner2 = moved_corners[(i + 1) % 4]
# 计算点到延长线的距离
distance = np.linalg.norm(np.cross(corner2 - corner1, corner1 - point)) / np.linalg.norm(corner2 - corner1)
if distance < min_distance:
min_distance = distance
min_index = i
# 添加到对应分类中
classified_points[min_index].append(point)
# 将分类转换为Numpy数组
for i in range(4):
classified_points[i] = np.array(classified_points[i])
# 定义每个分类的颜色 (r, g, b)
colors = [
[1, 0, 0], # 红色
[0, 1, 0], # 绿色
[0, 0, 1], # 蓝色
[1, 1, 0] # 黄色
]
# 创建一个Open3D的点云对象列表
point_cloud_objects = []
for i, points in classified_points.items():
# 创建点云对象
point_cloud = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
# 将numpy点云数据赋值给点云对象
point_cloud.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points)
# 为点云赋予颜色
point_cloud.paint_uniform_color(colors[i])
# 将点云对象添加到列表中
point_cloud_objects.append(point_cloud)
# 可视化所有分类的点云
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries(point_cloud_objects)
return classified_points
def find_farthest_points_in_quadrants(points, center):
# 初始化四个象限的最远点信息
quadrants = {
'upper_left': (-np.inf, None),
'upper_right': (-np.inf, None),
'lower_right': (-np.inf, None),
'lower_left': (-np.inf, None)
}
for point in points:
# 计算点到中心点的角度和距离
angle = np.arctan2(point[1] - center[1], point[0] - center[0])
distance = np.linalg.norm(point - center)
# 确定点所在的象限,并更新该象限的最远点
if -np.pi <= angle < -np.pi / 2:
if distance > quadrants['lower_left'][0]:
quadrants['lower_left'] = (distance, point)
elif -np.pi / 2 <= angle < 0:
if distance > quadrants['lower_right'][0]:
quadrants['lower_right'] = (distance, point)
elif 0 <= angle < np.pi / 2:
if distance > quadrants['upper_right'][0]:
quadrants['upper_right'] = (distance, point)
elif np.pi / 2 <= angle <= np.pi:
if distance > quadrants['upper_left'][0]:
quadrants['upper_left'] = (distance, point)
# 从四个象限中提取最远的点
farthest_points = [quadrants[q][1] for q in quadrants]
return np.array(farthest_points)
def visualize_points_and_lines(pcd_clap,points, lines):
# 从点集创建点云对象
pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points)
# 从点集和线集创建线集对象
line_set = o3d.geometry.LineSet(
points=o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(points),
lines=o3d.utility.Vector2iVector(lines)
)
# 可视化点云和线集
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd_clap,pcd, line_set])
class Ransac_fit():
def __init__(self,pointcloud):
"""
初始化参数
"""
self.pcd = pointcloud # 输入点云
self.NPt = 0 # 输入点云
self.NpPoints = np.asarray(self.pcd.points) # 点云numpy数组
self.min_height = 0 # 点云最小高度
self.max_height = 0 # 点云最大高度
def get_min_max_horizontal_height(self):
"""
求得点云的最低和最高的Z值
"""
obb = self.pcd.get_axis_aligned_bounding_box()
# 从包围盒坐标中获取最高和最低水平高度
obb_points = np.asarray(obb.get_box_points())
self.min_height = np.min(obb_points[:, 2]) # 最低水平高度
self.max_height = np.max(obb_points[:, 2]) # 最高水平高度
def clap_top_bottom(self):
"""
沿着z轴拍平点云数据
"""
pointsID_Window = []
# 遍历所有点,并记录符合条件的点的索引
for idx, point in enumerate(self.NpPoints):
if self.min_height <= point[2] <= self.max_height:
point[2] = 0
pointsID_Window.append(idx)
pcd_clap = self.pcd.select_by_index(pointsID_Window).voxel_down_sample(3)
return pcd_clap
def plane_fit(self,distance_threshold,ransac_n,num_iterations):
"""
拍平平面到原来的平面
"""
distance_threshold = 5 if distance_threshold == 0 else distance_threshold
ransac_n = 5 if ransac_n == 0 else ransac_n
num_iterations = 1000 if num_iterations == 0 else num_iterations
segment_models, inliers = self.pcd.segment_plane(distance_threshold, ransac_n, num_iterations)
# 获取平面的法向量并归一化
normal_vector = np.array(segment_models[:3])
normal_vector /= np.linalg.norm(normal_vector)
# 计算每个点在法向量方向上的分量
dot_products = np.dot(self.NpPoints, normal_vector)
# 计算投影点
projected_points = self.NpPoints - 0.8 * dot_products[:, np.newaxis] * normal_vector
# 创建新的PointCloud对象
projected_pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
projected_pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(projected_points)
return projected_pcd
def main():
# 确保文件路径是正确的
file_path = r"C:\Users\zhaojunzhe\Desktop\点云数据存储\钢梁.pts"
# 读取点云数据
pcd = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(file_path)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
# 点云滤波
cl, ind = pcd.remove_statistical_outlier(nb_neighbors=20, std_ratio=2.0)
pcd = pcd.select_by_index(ind)
# 创建拍平点云数据去拟合
RANSAC = Ransac_fit(pcd)
RANSAC.get_min_max_horizontal_height()
clap_pointcloud = RANSAC.plane_fit(distance_threshold = 0,ransac_n = 0,num_iterations = 0)
# 给点云上色
colored_pcd = clap_pointcloud.paint_uniform_color([0, 0, 1])
# 给定点云数据
points = np.array(colored_pcd.points)
# 计算点云数据的中心
point_cloud_center = np.mean(points,axis = 0)
# 找到相对于中心点在四个象限中距离最远的四个点
farthest_points = find_farthest_points_in_quadrants(points[:, :3], point_cloud_center[:3])
# 点云数据分类
classified_points = classifiction_points(colored_pcd,farthest_points)
# 最后三部分未来得及根据分割后的物体修改完善,请读者自行完善修改!
# RANSAC线拟合
line_fit(colored_pcd,classified_points)
# 定义连接最远点的线集
lines = [[i, (i + 1) % 4] for i in range(4)]
# 可视化中心点、最远点和连接线
visualize_points_and_lines(colored_pcd,farthest_points, lines)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()数据已上传到百度网盘,链接地址如下,自取。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qqX-J3WTecIbWPE6vvvCfw?pwd=142t
提取码:142t
--来自百度网盘超级会员V2的分享