leetcode链表相关题目
文章目录
- 1.移除链表元素
-
- 方法1:
- 方法2
- 2.合并两个有序链表
- 3.链表的中间节点
-
- 方法1
- 方法2
- 4.反转单链表
-
- 方法1
- 方法2
- 5.分割链表
- 6.链表中的倒数第k个节点
-
- 方法1:
- 方法2:
- 7.环形链表的约瑟夫问题
- 8.链表的回文结构
- 9.相交链表
-
- 方法1
- 方法2:
- 10.环形链表
- 11.环形链表Ⅱ
- 12.随机链表的复制

链表学习完以后,来做点相关题目吧
1.移除链表元素
方法1:
在原链表的基础上直接删除指定元素
- 若当前节点是要删除的节点,则将其前驱节点指向当前节点的下一个节点
- 若当前节点不是要删除的节点,前驱节点指向当前节点,当前节点后移
- 特殊情况:
- 循环判断,若头节点是要删除的节点,则将头节点后移
- 头节点不为空
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
//判断头节点
while(head && head->val == val)
{
head = head->next;
}
//链表为空
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//正常情况
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
方法2
创建一个新的链表存放未删除的元素
- 先创建一个虚拟的头节点,指向新链表,同时记录该链表的尾
- 若当前节点是要删除的元素,直接后移
- 若当前节点不是要删除的元素,连接到新链表的尾后
- 将新链表尾节点的next置为空(断开与原链表的连接)
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
//设置新链表的头
struct ListNode* newhead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newhead->val = -1;
newhead->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* tail = newhead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
//将新链表与原链表断开
tail->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* ret = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = tail = NULL;
return ret;
}
2.合并两个有序链表
创建一个新的链表
- 两个指针分别指向两个链表
- 将两指针所指向的元素的较小值连接到新链表的尾
- 若有一个指针走到空,则将另一个指针连接到新链表的尾
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
//定义新链表的头
struct ListNode* newhead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newhead->val = -1;
newhead->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = newhead;
//比较链表元素
while(list1 && list2)
{
if(list1->val < list2->val)
{
tail->next = list1;
tail = tail->next;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
tail = tail->next;
list2 = list2->next;
}
}
//若有一个链表为空,则连接另一个
if(list1)
{
tail->next = list1;
}
else
{
tail->next = list2;
}
struct ListNode* ret = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = tail = NULL;
return ret;
}
3.链表的中间节点
方法1
统计链表长度,计算出中间位置;再寻找中间位置
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
int len = 0;
while(cur)
{
len++;
cur = cur->next;
}
int count = 0;
cur = head;
while(count < (len / 2))
{
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
方法2
快慢指针法:一个指针一次走一步,一个指针一次走两步。当快指针尾空或者快指针的next为空,那么慢指针所指向的元素就是中间元素。

struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
4.反转单链表
方法1
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* newHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newHead->val = -1;
newHead->next = NULL;
while(head)
{
//先记录后继节点
struct ListNode* next = head->next;
//头插
head->next = newHead->next;
newHead->next = head;
//节点后移
head = next;
}
return newHead->next;
}
方法2
原地直接反转
- 先记录当前节点的后继节点,以便节点后移
- 当前节点指向其前驱节点
- 前驱节点后移
- 当前节点后移
- prev即为反转后新的头
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* next = NULL;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
5.分割链表
- 给定两个新的链表,一个放小于X的元素,一个放大于X的元素
- 元素尾插至新链表
- 将两个新链表相连
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){
struct ListNode* minHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* maxHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* minTail = minHead;
struct ListNode* maxTail = maxHead;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val < x)
{
minTail->next = cur;
minTail = minTail->next;
}
else
{
maxTail->next = cur;
maxTail = maxTail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//防止成环
maxTail->next = NULL;
minTail->next = maxHead->next;
struct ListNode* ret = minHead->next;
free(minHead);
free(maxHead);
return ret;
}
6.链表中的倒数第k个节点
方法1:
思路:倒数第k就是正数第n-k+1个(n为链表长度)
特殊情况:
- k应该小于链表长度
- k不能为0
- 链表不能为空
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k) {
struct ListNode* cur = pListHead;
int len = 0;
//求链表的长度
while (cur)
{
len++;
cur = cur->next;
}
//特殊情况判断
//1.k不能大于链表长度
//2.k不能为0
//3.链表不为空
if (k > len || k == 0 || pListHead == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//倒数第k个就是正数第n-k+1个
int n = 1;
len = len - k + 1;
cur = pListHead;
while (n != len)
{
n++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur;
}
方法2:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead;
struct ListNode* slow = pListHead;
//快指针先走k步
while(k--)
{
//fast不能走出链表(k符合)
if(fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
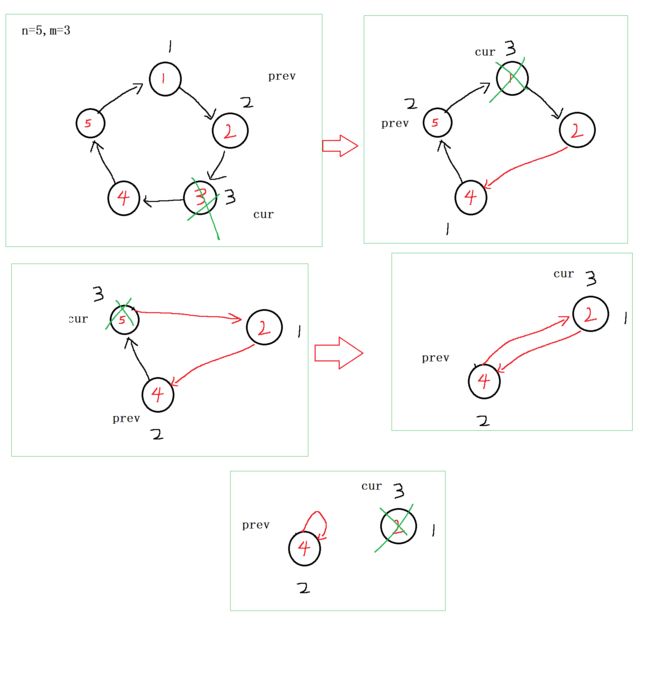
7.环形链表的约瑟夫问题
- 构建环形链表,给每个节点编号
- 逢m就删除节点,再从新报数
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
//创建节点
ListNode* CreatNode(int x)
{
ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//构建环
ListNode* CreatCircle(int n)
{
ListNode* head = CreatNode(1);
ListNode* tail = head;
//连续创建节点
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++)
{
ListNode* newnode = CreatNode(i);
//连接节点
tail->next = newnode;
tail = tail->next;
}
//成环
tail->next = head;
//返回尾节点的目的是:防止第一个元素就是要删除的元素
return tail;
}
int ysf(int n, int m ) {
ListNode* prev = CreatCircle(n);
ListNode* cur = prev->next;
int count = 1;
//有多个节点继续报数,直到剩下一个节点
while(cur->next != cur)
{
//逢m就删除
if(count == m)
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prev->next;
count = 1;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
}
return cur->val;
}
8.链表的回文结构

思路:从链表的中间节点逆置后半段,然后比较前半段与后半段是否相等。
- 快慢指针找链表的中间节点
- 从中间节点反转单链表
- 节点比较
//找中间节点
ListNode* FindMid(ListNode* A)
{
ListNode* fast = A;
ListNode* slow = A;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
//反转
ListNode* Reverse(ListNode* mid)
{
ListNode* cur = mid;
ListNode* prev = NULL;
ListNode* next = NULL;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
ListNode* mid = FindMid(A);
ListNode* midhead = Reverse(mid);
while(midhead)
{
if(A->val == midhead->val)
{
A = A->next;
midhead = midhead->next;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
9.相交链表
方法1
将链表A中的每一个节点与链表B中的每一个节点比较,看是否相等。
- 若相等,则返回相等的节点
- 若所有节点都不相等,则链表不相交。
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode* curA = headA;
struct ListNode* curB = headB;
while(curA)
{
curB = headB;
while(curB)
{
//若节点相等,直接返回相等节点
if(curA == curB)
{
return curA;
}
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = curA->next;
}
//A中每一个节点都与B比较完毕,仍无交点
return NULL;
}
方法2:
分别计算两链表长度,长的先走长度差步,然后再一起走,判断是否相等。
- 再求链表长度的同时,若两链表的最后一个节点相等,则二者一定相交
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode* curA = headA;
struct ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
//先计算链表各自的长度,都少计算一个
while(curA->next)
{
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while(curB->next)
{
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
//若不相交,直接返回空
if(curA != curB)
{
return NULL;
}
//算长度差
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
struct ListNode* longList = headA;
struct ListNode* shortList = headB;
if(lenA < lenB)
{
longList = headB;
shortList = headA;
}
//长的先走长度差步
while(gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
//同时走,找交点
while(longList && shortList)
{
if(longList == shortList)
{
return shortList;
}
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return NULL;
}
10.环形链表
- 一个指针一次走一步,一个指针一次走两步
- 若快指针走到了空,则不带环
- 若快指针与慢指针相遇,则带环
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode * fast = head;
struct ListNode * slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
为什么不是一个走1步一个走3步?一个走1步一个走4步?一个走1步一个走6步?…
若N为奇数,C-1也为奇数则永远追不上(存在这种情况吗?)
11.环形链表Ⅱ

思路:快慢指针,找到二者的相遇点。再使用两指针,从相遇点和链表头开始走,二者相遇点就是入环点
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
struct ListNode* meet = slow;
while(meet != head)
{
meet = meet->next;
head = head->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
原理
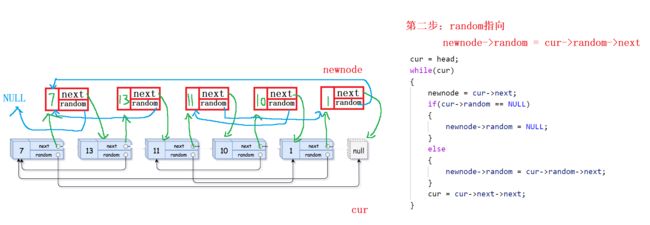
12.随机链表的复制
- 在原链表每个节点的后面尾插一个新的节点
- 根据原链表,找到新链表的random指向
- 将新链表的节点与原链表分离,恢复原链表
第二步:搞清random指向
新链表random就是原链表random的next!!!
第三步:将新链表从原链表上摘下来

struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cur = head;
//插入新节点
while(cur)
{
struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
//连接新节点
newnode->val = cur->val;
newnode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
//原链表后移
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* newnode = cur->next;
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
newnode->random = NULL;
}
else
{
newnode->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//摘新链表
struct Node* newhead = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newhead->next = NULL;
newhead->random = NULL;
struct Node* tail = newhead;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
//尾插新链表
struct Node* newnode = cur->next;
tail->next = newnode;
tail = tail->next;
//恢复原链表
cur->next = newnode->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
return newhead->next;
}