Gin框架: HTML模板渲染之配置与语法详解
Gin的HTML模板配置
1 )单一目录的配置
-
配置模板目录,在与main.go同级下, 新建目录,下面二选一,仅作举例, 这里选择 tpls
templatestpls
-
在 tpls 目录下新建 news.html
<h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p>- 注意,这里加上define和end头尾也可以
{{ define "news.html" }} <h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p> {{ end }}
- 注意,这里加上define和end头尾也可以
-
应用程序示例中配置
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/*")通配设定r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/news.html")逐个指定,多个在字符串中用,分隔
程序示例
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
// 配置模板的文件
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/*")
// r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/news.html") // 逐个指定多个需要使用逗号分隔
// 根路由
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(statusOK, "Welcome to %v", "Home Page")
})
r.GET("/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
r.Run()
}
2 )多目录配置
-
配置模板目录,在与main.go同级下, 新建目录 tpls, 在内部再创建两个目录: web, admin
tpls/webtpls/admin
-
新建 tpls/admin/news.html
{{ define "admin/news.html" }} <h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p> {{ end }}- 这里内容和之前保持一致, 但要注意上下的定义
- 如果不添加,会出现
Error #01: html/template: "admin/news.html" is undefined的错误 - 这里的 define 和 end 非常重要
- define 配置的路径是匹配
c.HTML中的第二个参数
-
应用程序示例中配置
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/*")通配设定r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/admin/news.html")逐个指定,多个在字符串中用,分隔
程序示例
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
// 配置模板的文件
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/*")
// r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/admin/news.html") // 逐个指定多个需要使用逗号分隔
// 根路由
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(statusOK, "Welcome to %v", "Home Page")
})
r.GET("/admin/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "admin/news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
r.Run()
}
3 )多层复杂目录配置
-
首先看下设定的结构
yourGinProject/ ······························· 根目录 ├── go.mod ·································· go mod 文件 ├── go.sum ·································· go sum 文件 ├── main.go ································· main 文件 └── tpls ····································· html模板目录 ├── a │ └── b │ └── c │ └── d │ └── e │ └── news.html ├── admin │ └── news.html │ └── news.html-
tpls/news.html{{ define "news.html" }} <h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p> {{ end }} -
tpls/admin/news.html{{ define "admin/news.html" }} <h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p> {{ end }} -
tpls/a/b/c/d/e/news.html{{ define "a/b/c/d/e/news.html" }} <h1>News Pageh1> <h3>标题:{{.title}}h3> <p>内容:{{.content}}p> {{ end }} -
注意各个 news.html 的define设定
-
程序示例
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
// 配置模板的文件
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/**/**/**/**/*")
// 根路由
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(statusOK, "Welcome to %v", "Home Page")
})
// 这个配置和紧挨着下面的配置一致,只是路由自己设定了一个简洁版的
r.GET("/x/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "a/b/c/d/e/news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
// 多层路由,同上
r.GET("/a/b/c/d/e/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "a/b/c/d/e/news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
// 二级
r.GET("/admin/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
// r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/*") // 这里会 panic 报错
r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/admin/news.html") // 这里正常可以访问,权重会大于顶部的全局配置
c.HTML(statusOK, "admin/news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
// 一级
r.GET("/news", func(c *gin.Context) {
// r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/*") // 这里会 panic 报错
r.LoadHTMLFiles("tpls/news.html") // 这里正常可以访问,权重会大于顶部的全局配置
c.HTML(statusOK, "news.html", gin.H{
"title": "新闻标题",
"content": "这是详细的新闻内容",
})
})
r.Run()
}
- 可以看到,在单个路由中
r.LoadHTMLFiles配置的用处了 - 所以,以上就比较麻烦,一般而言,在一开始设计模板的时候,就要约定好规则
- 特殊的设定只能应用于特殊的场景下
Gin的HTML模板语法
1 )基本渲染
主程序
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
type User struct {
Id int
Name string
Hobby string
}
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
// 配置模板的文件
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/*")
// 根路由
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(statusOK, "Welcome to %v", "Home Page")
})
r.GET("/user", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "user.html", &User{
Id: 1,
Name: " Wang ", // 注意,这里有2个空格
Hobby: "swimming",
})
})
r.Run()
}
html模板
{{ define "user.html" }}
<h1>User Pageh1>
<h3>用户Id:{{.Id}}h3>
{{/* 这里是姓名,本身数据存在空格,但是这个去空格的方式无法去除 */}}
<h3>用户姓名:{{- .Name -}}h3>
<h3>用户爱好:{{.Hobby}}h3>
{{ $xId := .Id }}
<h3>演示变量: {{- $xId -}} h3>
{{ end }}
{{ .x }}x是属性,基于这种方式来输出数据{{/* 这里是注释 */}}注意/*和*/紧贴着{{和}},可以多行,不可嵌套{{ $xId := .Id }}单独设定变量, 变量名只能使用一个${{- $xId -}}这种去除空格,只能去除周围的空格,无法去除属性内包含的空格,且-紧贴{{和}},同时与模板值之间需要使用空格分隔
效果图
2 ) 比较, 判断, range, with
主程序
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type Article struct {
Title string
Content string
}
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
//加载模板 放在配置路由上面
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/*")
//前台
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "web/index.html", gin.H{
"title": "首页",
"msg": " 我是msg",
"score": 89,
"hobby": []string{"吃饭", "睡觉", "写代码"},
"newsList": []interface{}{
&Article{
Title: "新闻标题1",
Content: "新闻详情1",
},
&Article{
Title: "新闻标题2",
Content: "新闻详情2",
},
},
"testSlice": []string{},
"news": &Article{
Title: "新闻标题",
Content: "新闻内容",
},
})
})
r.Run()
}
html模板
{{ define "web/index.html" }}
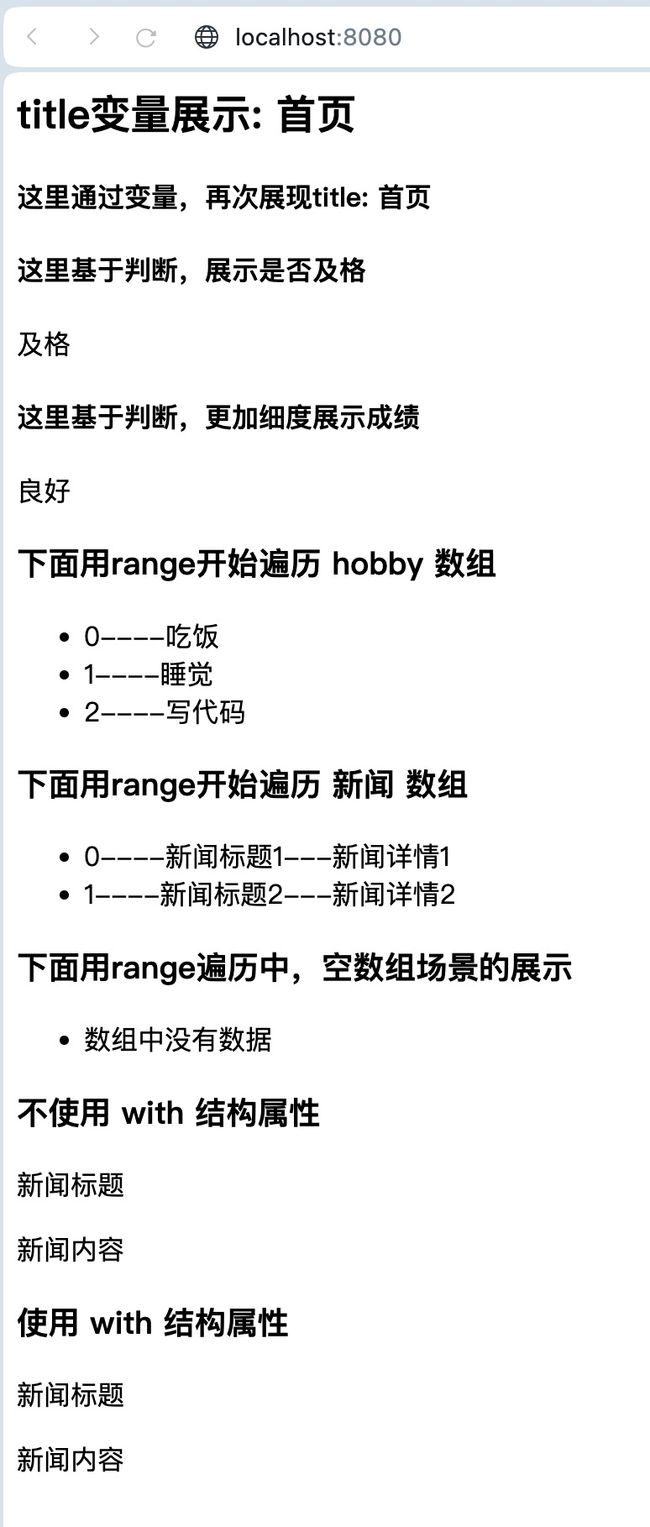
<h2>title变量展示: {{.title}}h2>
{{$t := .title}}
<h4>
这里通过变量,再次展现title: {{$t}}
h4>
<h4>这里基于判断,展示是否及格h4>
{{if ge .score 60}}
<p>及格p>
{{else}}
<p>不及格p>
{{end}}
<h4>这里基于判断,更加细度展示成绩h4>
{{if gt .score 90}}
<p>优秀p>
{{else if gt .score 80}}
<p>良好p>
{{else if gt .score 60}}
<p>及格p>
{{else}}
<p>不及格p>
{{end}}
<h3>下面用range开始遍历 hobby 数组h3>
<ul>
{{range $key,$value:=.hobby}}
<li>{{$key}}----{{$value}}li>
{{end}}
ul>
<h3>下面用range开始遍历 新闻 数组h3>
<ul>
{{range $key,$value:=.newsList}}
<li>{{$key}}----{{$value.Title}}---{{$value.Content}}li>
{{end}}
ul>
<h3>下面用range遍历中,空数组场景的展示h3>
<ul>
{{range $key,$value:=.testSlice}}
<li>{{$key}}----{{$value}}li>
{{else}}
<li>数组中没有数据li>
{{end}}
ul>
<h3>不使用 with 结构属性h3>
<p>{{.news.Title}}p>
<p>{{.news.Content}}p>
<h3>使用 with 结构属性h3>
{{with .news}}
<p>{{.Title}}p>
<p>{{.Content}}p>
{{end}}
{{ end }}
- 关于比较函数中的一些注意事项
eq如果 arg1 == arg2 则返回真ne如果 arg1 != arg2 则返回真lt如果 arg1 < arg2 则返回真le如果 arg1 <= arg2 则返回真gt如果 arg1 > arg2 则返回真ge如果 arg1 >= arg2 则返回真
效果图
3 )高阶用法:预定义函数,自定义模板函数,嵌套模板
- 首先看下设定的结构
yourGinProject/ ······························· 根目录 ├── go.mod ·································· go mod 文件 ├── go.sum ·································· go sum 文件 ├── main.go ································· main 文件 └── tpls ····································· html模板目录 ├── web │ └── index.html └── common └── page_header.html └── page_footer.html
主程序
package main
import (
"html/template"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
type Article struct {
Title string
Content string
}
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
//时间戳转换成日期
func UnixToTime(timestamp int) string {
t := time.Unix(int64(timestamp), 0)
return t.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05") // 这个是按照这个时间来进行格式化, 必须是这个时间点, 据说是go诞生之日
}
func Println(str1 string, str2 string) string {
return str1 + "----" + str2
}
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
//自定义模板函数, 注意要把这个函数放在加载模板前
r.SetFuncMap(template.FuncMap{
"UnixToTime": UnixToTime,
"Println": Println,
})
//加载模板 放在配置路由上面
r.LoadHTMLGlob("tpls/**/*")
// 前台
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(statusOK, "web/index.html", gin.H{
"title": "首页",
"titleEn": "homePage",
"msg": "demo",
"date": 1708344953,
})
})
r.Run()
}
web/index.html模板
{{ define "web/index.html" }}
{{template "common/page_header.html" .}}
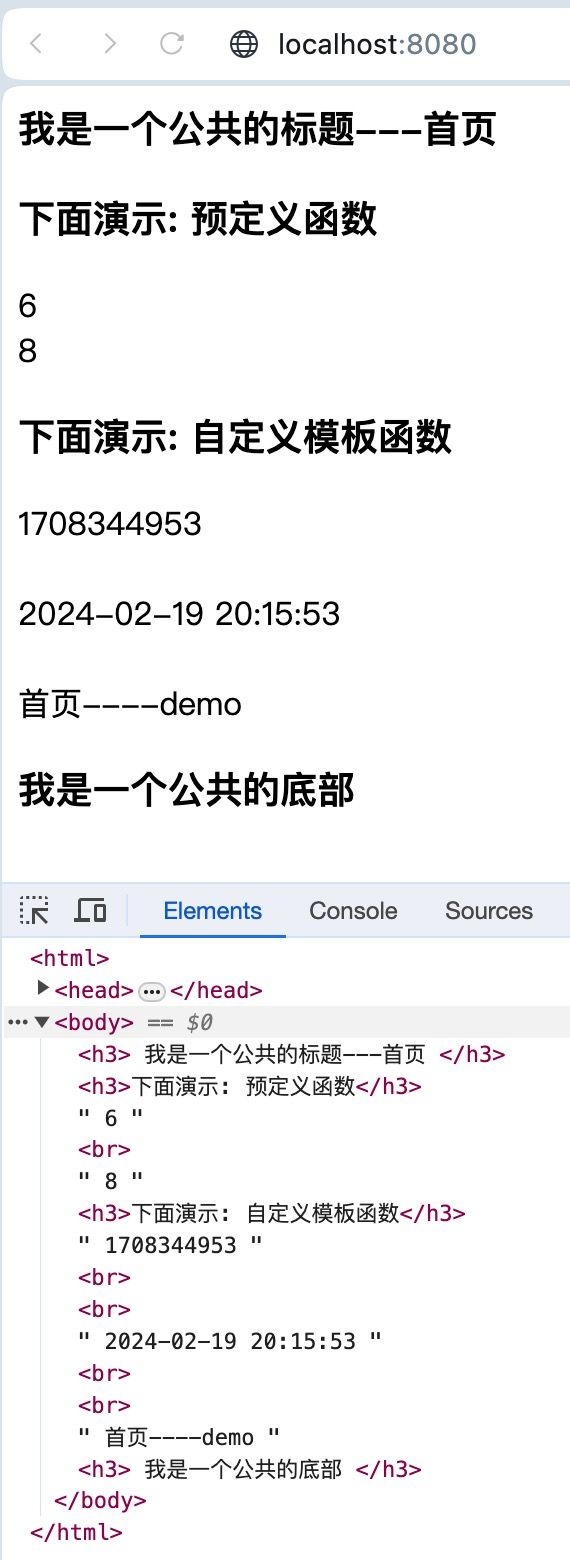
<h3>下面演示: 预定义函数h3>
{{ len .title }}
<br />
{{ len .titleEn }}
<h3>下面演示: 自定义模板函数h3>
{{.date}}
<br />
<br />
{{UnixToTime .date}}
<br>
<br>
{{Println .title .msg}}
{{template "common/page_footer.html" .}}
{{ end }}
common/page_header.html模板
{{ define "common/page_header.html" }}
<h3>
我是一个公共的标题---{{.title}}
h3>
{{end}}
common/page_footer.html模板
{{ define "common/page_footer.html" }}
<h3>
我是一个公共的底部
h3>
{{end}}
-
在 预定义函数 中,执行模板时,函数从两个函数字典中查找
- 首先是模板函数字典,然后是全局函数字典。
- 一般不在模板内定义函数,而是使用 Funcs 方法添加函数到模板里
-
预定义的全局函数如下
and- 函数返回它的第一个 empty 参数或者最后一个参数
- 就是说"and x y"等价于"if x then y else x";所有参数都会执行
or- 返回第一个非 empty 参数或者最后一个参数
- 亦即"or x y"等价于"if x then x else y";所有参数都会执行
not- 返回它的单个参数的布尔值的否定
len- 返回它的参数的整数类型长度
index- 执行结果为第一个参数以剩下的参数为索引/键指向的值
- 如"index x 1 2 3"返回 x[1][2][3]的值;每个被索引的主体必须是数组、切片或者字典
print- 即 fmt.Sprint
printf- 即 fmt.Sprintf
println- 即 fmt.Sprintln
html- 返回与其参数的文本表示形式等效的转义 HTML
- 这个函数在 html/template 中不可用
urlquery- 以适合嵌入到网址查询中的形式返回其参数的文本表示的转义值
- 这个函数在 html/template 中不可用
js- 返回与其参数的文本表示形式等效的转义 JavaScript
call- 执行结果是调用第一个参数的返回值,该参数必须是函数类型,其余参数作为调用该函
数的参数 - 如"call .X.Y 1 2"等价于 go 语言里的 dot.X.Y(1, 2)
- 其中 Y 是函数类型的字段或者字典的值,或者其他类似情况
- call 的第一个参数的执行结果必须是函数类型的值(和预定义函数如 print 明显不同)
- 该函数类型值必须有 1 到 2 个返回值,如果有 2 个则后一个必须是 error 接口类型
- 如果有 2 个返回值的方法返回的 error 非 nil,模板执行会中断并返回给调用模板执行者该错误
- 执行结果是调用第一个参数的返回值,该参数必须是函数类型,其余参数作为调用该函
-
在自定义模板函数中,比如定义了
formatDate方法,有两种用法{{.now | formatDate}}或{{formatDate .now }}
-
在嵌套 template中,注意最后的点(.)
效果图
静态文件服务器的配置
这块比较简单
主程序
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
var statusOK = http.StatusOK
func main() {
// 创建一个默认的路由引擎
r := gin.Default()
//配置静态web目录 第一个参数表示路由, 第二个参数表示映射的目录
r.Static("/static", "./static")
// 前台
r.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(statusOK, "Welcome to %v", "Home Page")
})
r.Run()
}
- 这样就设定好了,在与 main.go 同级新建 static/images 目录,添加 mysql-logo.svg 图片
- 访问该图片: http://localhost:8080/static/images/mysql-logo.svg
- 其他的,如:css, js 这类也同样适用
- 这时候,静态文件服务器就搭建好了