poj 1655 Balancing Act 树的重心
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1655
Consider a tree T with N (1 <= N <= 20,000) nodes numbered 1...N. Deleting any node from the tree yields a forest: a collection of one or more trees. Define the balance of a node to be the size of the largest tree in the forest T created by deleting that node from T.
For example, consider the tree:
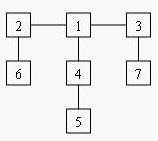
Deleting node 4 yields two trees whose member nodes are {5} and {1,2,3,6,7}. The larger of these two trees has five nodes, thus the balance of node 4 is five. Deleting node 1 yields a forest of three trees of equal size: {2,6}, {3,7}, and {4,5}. Each of these trees has two nodes, so the balance of node 1 is two.
For each input tree, calculate the node that has the minimum balance. If multiple nodes have equal balance, output the one with the lowest number.
题意描述:略。找出重心以及删除重心后两颗子树中结点数大的一颗。
算法分析:重在分析重心问题,一颗树的重心就是所有节点的子节点的数量最大的最小的节点。简而言之,重心就是要让这棵树在节点个数上达到左右子树相对平衡的这样一个节点。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<cmath> 6 #include<algorithm> 7 #include<queue> 8 #include<vector> 9 #define inf 0x7fffffff 10 using namespace std; 11 const int maxn=20000+10; 12 const int M = 20000+10; 13 14 int n; 15 struct node 16 { 17 int v,next; 18 }edge[M*3]; 19 int head[maxn],edgenum; 20 21 void add(int u,int v) 22 { 23 edge[edgenum].v=v ;edge[edgenum].next=head[u] ;head[u]=edgenum++ ; 24 edge[edgenum].v=u ;edge[edgenum].next=head[v] ;head[v]=edgenum++ ; 25 } 26 27 int an[maxn],bn[maxn]; 28 int dfs(int u,int pre) 29 { 30 an[u]=bn[u]=1; 31 for (int i=head[u] ;i!=-1 ;i=edge[i].next) 32 { 33 int v=edge[i].v; 34 if (v != pre) 35 { 36 int k=dfs(v,u); 37 an[u] += k; 38 bn[u]=max(bn[u],k); 39 } 40 } 41 return an[u]; 42 } 43 44 int main() 45 { 46 int t; 47 scanf("%d",&t); 48 while (t--) 49 { 50 scanf("%d",&n); 51 memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); 52 edgenum=0; 53 int a,b; 54 for (int i=1 ;i<n ;i++) 55 { 56 scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); 57 add(a,b); 58 } 59 int k=dfs(1,1); 60 int ans=inf,num=n; 61 for (int i=1 ;i<=n ;i++) 62 { 63 bn[i]=max(bn[i],n-an[i]); 64 if (ans>bn[i] || (ans==bn[i] && n>i)) 65 { 66 ans=bn[i]; 67 num=i; 68 } 69 } 70 printf("%d %d\n",num,ans); 71 } 72 return 0; 73 }