内核回调 之 一"读"到底
小小地跟踪下read函数,从 ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count) 到 DATASHEET 一调到底,见证内核的分层模块化。
--内核服务例程开始提供服务--
--fs/read_write.c--
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, unsigned int, fd, char __user *, buf, size_t, count)
{
struct file *file;
ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
int fput_needed;
file = fget_light(fd, &fput_needed);
if (file) {
loff_t pos = file_pos_read(file);
ret = vfs_read(file, buf, count, &pos); //-->
file_pos_write(file, pos);
fput_light(file, fput_needed);
}
return ret;
}
--进入vfs层--
ssize_t vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
... ...
if (ret >= 0) {
count = ret;
if (file->f_op->read)
ret = file->f_op->read(file, buf, count, pos); //-->
... ...
return ret;
}
发现回调函数,file->f_op->read
static const struct file_operations yaffs_file_operations = {
.read = do_sync_read, //-->
.write = do_sync_write,
.aio_read = generic_file_aio_read,
.aio_write = generic_file_aio_write,
.mmap = generic_file_mmap,
.flush = yaffs_file_flush,
.fsync = yaffs_sync_object,
.sendfile = generic_file_sendfile,
}
又是何时给回调函数挂上的钩子?
file = fget_light(fd, &fput_needed)
通过fd得出file。是谁将fd与file有了联系,是read之前的open。
--fs/open.c--
669 static struct file *__dentry_open(struct dentry *dentry, struct vfsmount *mnt,
670 struct file *f,
671 int (*open)(struct inode *, struct file *),
672 const struct cred *cred)
673 {
684 inode = dentry->d_inode;
704 f->f_op = fops_get(inode->i_fop); //-->
734 return f;
735 }
我们发现:f->f_op等同了inode->i_fop。
--include/linux/fs.h--
1862 /* Alas, no aliases. Too much hassle with bringing module.h everywhere */
1863 #define fops_get(fops) \
1864 (((fops) && try_module_get((fops)->owner) ? (fops) : NULL))
1865 #define fops_put(fops) \
1866 do { if (fops) module_put((fops)->owner); } while(0)
继续追踪inode,发现这么一个函数:yaffs_fill_inode_from_obj 。
inode->i_fop在这里赋值。函数名说的很清楚,通过yaffs_obj结构体来填充inode。填充inode就是该函数的使命。
--fs/yaffs2/yaffs_vfs.c--
1273 static void yaffs_fill_inode_from_obj(struct inode *inode,
1274 struct yaffs_obj *obj)
1354 case S_IFREG: /* file */
1355 inode->i_op = &yaffs_file_inode_operations;
1356 inode->i_fop = &yaffs_file_operations;
1357 inode->i_mapping->a_ops =
1358 &yaffs_file_address_operations;
1359 break;
1378 }
看来这里还给inode->i_op 和 inode->i_mapping->a_ops 挂上了钩子,以后会用到。
紧接之前回调到do_sync_read。
ssize_t do_sync_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
... ...
for (;;) {
ret = filp->f_op->aio_read(&kiocb, &iov, 1, kiocb.ki_pos); -->
if (ret != -EIOCBRETRY)
break;
wait_on_retry_sync_kiocb(&kiocb);
}
... ...
}
这里又转向了aio_read? 是异步读取的意思。原有的read为同步读取,异步读写后被patch上。
From: Marco Stornelli <[email protected]> If a filesystem in the file operations specifies for read and write operations only do_sync_read and do_sync_write without init aio_read and aio_write, there will be a kernel oops, because the vfs code check the presence of (to read for example) read OR aio_read method, then it calls read if it's pointer is not null. It's not sufficient because if the read function is actually a do_sync_read, it calls aio_read but without checking the presence. I think a BUG_ON check can be more useful. Signed-off-by: Marco Stornelli <[email protected]>
回调到generic_file_aio_read。
1292 ssize_t
1293 generic_file_aio_read(struct kiocb *iocb, const struct iovec *iov,
1294 unsigned long nr_segs, loff_t pos)
1295 {
1369 do_generic_file_read(filp, ppos, &desc, file_read_actor); -->
1380 }
开始真正的读操作。
不管是读还是写,都会优先考虑cache。若无法命中,再进行传统意义上的actual read。
975 /**
976 * do_generic_file_read - generic file read routine
977 * @filp: the file to read
978 * @ppos: current file position
979 * @desc: read_descriptor
980 * @actor: read method
981 *
982 * This is a generic file read routine, and uses the
983 * mapping->a_ops->readpage() function for the actual low-level stuff.
984 *
985 * This is really ugly. But the goto's actually try to clarify some
986 * of the logic when it comes to error handling etc.
987 */
988 static void do_generic_file_read(struct file *filp, loff_t *ppos,
989 read_descriptor_t *desc, read_actor_t actor)
990 {
991 struct address_space *mapping = filp->f_mapping;
1134 /* Start the actual read. The read will unlock the page. */
1135 error = mapping->a_ops->readpage(filp, page); //假设cache没有命中,就继续向下读,没有命中真是一种糟糕的情况
1203 }
又见回调。
static struct address_space_operations yaffs_file_address_operations = {
.readpage = yaffs_readpage, //-->
.writepage = yaffs_writepage,
#if (YAFFS_USE_WRITE_BEGIN_END > 0)
.write_begin = yaffs_write_begin,
.write_end = yaffs_write_end,
#else
.prepare_write = yaffs_prepare_write,
.commit_write = yaffs_commit_write,
#endif
};
struct address_space_operations 为struct address_space的操作函数。
struct address_space 用于管理文件(struct inode)映射到内存的页面(struct page);
与之对应,address_space_operations 就是用来操作该文件映射到内存的页面,比如把内存中的修改写回文件、从文件中读入数据到页面缓冲等。
也就是说address_space结构与文件的对应:一个具体的文件在打开后,内核会在内存中为之建立一个struct inode结构,其中的i_mapping域指向一个address_space结构。这样,一个文件就对应一个address_space结构,一个 address_space与一个偏移量能够确定一个page cache 或swap cache中的一个页面。因此,当要寻址某个数据时,很容易根据给定的文件及数据在文件内的偏移量而找到相应的页面。
-- fs/yaffs2/yaffs_vfs.c --
static int yaffs_readpage(struct file *f, struct page *pg)
{
int ret;
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_OS, "yaffs_readpage");
ret = yaffs_readpage_unlock(f, pg); //-->
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_OS, "yaffs_readpage done");
return ret;
}
看样子要读page:
static int yaffs_readpage_unlock(struct file *f, struct page *pg)
{
int ret = yaffs_readpage_nolock(f, pg); //-->
UnlockPage(pg);
return ret;
}
这里出现了file指针,我们知道file是个vfs逻辑上的概念,可能多个file对应一个inode。看来逻辑file就快转化为相应的文件物理地址。
static int yaffs_readpage_nolock(struct file *f, struct page *pg)
{
... ...
/* FIXME: Can kmap fail? */
pg_buf = kmap(pg);
/********************************
void *kmap(struct page *page)
{
might_sleep();
if (!PageHighMem(page))
return page_address(page);
return kmap_high(page);, //将高端内存页映射到内核地址空间,返回映射的虚拟地址
}
********************************/
yaffs_gross_lock(dev);
ret = yaffs_file_rd(obj, pg_buf,
pg->index << PAGE_CACHE_SHIFT, PAGE_CACHE_SIZE); //-->
yaffs_gross_unlock(dev);
... ...
}
--文件系统:yaffs--
终于进入了yaffs_guts.c文件,该文件涉及到了yaffs的操作细节。
-- fs/yaffs2/yaffs_guts.c --
int yaffs_file_rd(struct yaffs_obj *in, u8 * buffer, loff_t offset, int n_bytes)
{
... ...
int n = n_bytes; //page size: 4k(arm)
while (n > 0) {
yaffs_addr_to_chunk(dev, offset, &chunk, &start);
//chunk = (u32) (addr >> dev->chunk_shift);
chunk++;
/* OK now check for the curveball where the start and end are in
* the same chunk.
*/
if ((start + n) < dev->data_bytes_per_chunk)
n_copy = n;
else
n_copy = dev->data_bytes_per_chunk - start;
cache = yaffs_find_chunk_cache(in, chunk);
/* If the chunk is already in the cache or it is less than
* a whole chunk or we're using inband tags then use the cache
* (if there is caching) else bypass the cache.
*/
if (cache || n_copy != dev->data_bytes_per_chunk ||
dev->param.inband_tags) {
/*先考虑是否在高缓中*/
} else {
/* A full chunk. Read directly into the buffer. */
yaffs_rd_data_obj(in, chunk, buffer); //-->
}
n -= n_copy;
offset += n_copy;
buffer += n_copy;
n_done += n_copy;
}
return n_done;
}
-->
/*inode_chunk:yaffs中的chunk下标*/
static int yaffs_rd_data_obj(struct yaffs_obj *in, int inode_chunk, u8 * buffer)
{
int nand_chunk = yaffs_find_chunk_in_file(in, inode_chunk, NULL);
if (nand_chunk >= 0)
return yaffs_rd_chunk_tags_nand(in->my_dev, nand_chunk, buffer, NULL); //-->
else {
... ...
}
}
有必要了解下:
int nand_chunk = yaffs_find_chunk_in_file(in, inode_chunk, NULL);
第二个参数inode_chunk是逻辑地址,在这里chunk是以512字节为单位排序后的下标。
YAFFS2文件系统使用树结点结构来完成逻辑chunk地址与物理地址的映射。显然,经过此函数的处理,找到物理下标对应的逻辑下标。树结点用Tnode表示。
关于Tnode,涉及读yaffs的细节的理解,总之,yaffs作为文件系统就要管理物理页面,物理页面对应着逻辑chunk,出于文件寻找,文件扩大等效率方面的考虑,采用了数据结构——树。具体可参考有关yaffs的论文。
-->
--fs/yaffs2/yaffs_nand.c--
int yaffs_rd_chunk_tags_nand(struct yaffs_dev *dev, int nand_chunk,
u8 *buffer, struct yaffs_ext_tags *tags)
{
... ...
if (dev->param.read_chunk_tags_fn)
result =
dev->param.read_chunk_tags_fn(dev, realigned_chunk, buffer, tags); //-->
... ...
}
一个看似不一样的回调,赋值在这里:
--yaffs_vfs.c--
static struct super_block *yaffs_internal_read_super(int yaffs_version,
struct super_block *sb,
void *data, int silent)
{
param->read_chunk_tags_fn = nandmtd2_read_chunk_tags;
}
进入yaffs_mtdif2.c文件,看来要到mtd层咯。
--fs/yaffs2/yaffs_mtdif2.c--
int nandmtd2_read_chunk_tags(struct yaffs_dev *dev, int nand_chunk,
u8 *data, struct yaffs_ext_tags *tags)
{
... ...
if (dev->param.inband_tags || (data && !tags))
retval = mtd->read(mtd, addr, dev->param.total_bytes_per_chunk,
&dummy, data); //-->进入mtd层
else if (tags) {
ops.mode = MTD_OOB_AUTO;
ops.ooblen = packed_tags_size;
ops.len = data ? dev->data_bytes_per_chunk : packed_tags_size;
ops.ooboffs = 0;
ops.datbuf = data;
ops.oobbuf = yaffs_dev_to_lc(dev)->spare_buffer;
retval = mtd->read_oob(mtd, addr, &ops);
}
... ...
}
在进入mtd层之前,简单的提下yaffs中的各种回调是在何时挂好的呢?yaffs又是如何注册进的内核?
--------------------
注册文件系统:
--------------------
--fs/yaffs2/yaffs_vfs.c--
static int __init init_yaffs_fs(void)
{
int error = 0;
struct file_system_to_install *fsinst;
... ...
fsinst = fs_to_install; //创建文件系统进程入口
/***********************************************************
static struct file_system_to_install fs_to_install[] = {
{&yaffs_fs_type, 0},
{&yaffs2_fs_type, 0},
{NULL, 0}
};
************************************************************/
while (fsinst->fst && !error) {
error = register_filesystem(fsinst->fst); //注册文件系统
if (!error)
fsinst->installed = 1;
fsinst++;
}
... ...
return error;
}
注册文件系统后,yaffs2挂上fs list,开始超级块操作:
static struct file_system_type yaffs2_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "yaffs2",
.get_sb = yaffs2_read_super, //-->
.kill_sb = kill_block_super,
.fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV,
};
读取超级块。
static int yaffs2_read_super(struct file_system_type *fs,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
return get_sb_bdev(fs, flags, dev_name, data,
yaffs2_internal_read_super_mtd, mnt); //-->
}
----> mount_bdev函数中调用 fill_super, 也就是 yaffs2_internal_read_super_mtd
int get_sb_bdev(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int),
struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
struct dentry *root;
//获得了超级块指针,如果s->s_root,也就是目录挂载点为空的化,那就要填充超级块
root = mount_bdev(fs_type, flags, dev_name, data, fill_super); //-->
if (IS_ERR(root))
return PTR_ERR(root);
mnt->mnt_root = root;
mnt->mnt_sb = root->d_sb;
return 0;
}
----> fill_super,填充超级块
static int yaffs2_read_super(struct file_system_type *fs,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
struct vfsmount *mnt)
{
return get_sb_bdev(fs, flags, dev_name, data,
yaffs2_internal_read_super_mtd, mnt); //-->
}
---->
static int yaffs2_internal_read_super_mtd(struct super_block *sb, void *data,
int silent)
{
return yaffs_internal_read_super(2, sb, data, silent) ? 0 : -EINVAL;
}
----> 获取super block:kmalloc出空间,而后填充,返回。
static struct super_block *yaffs_internal_read_super(int yaffs_version,
struct super_block *sb,
void *data, int silent)
{
int n_blocks;
struct inode *inode = NULL;
struct dentry *root;
struct yaffs_dev *dev = 0;
char devname_buf[BDEVNAME_SIZE + 1];
struct mtd_info *mtd;
int err;
char *data_str = (char *)data;
struct yaffs_linux_context *context = NULL;
struct yaffs_param *param;
int read_only = 0;
struct yaffs_options options;
unsigned mount_id;
int found;
struct yaffs_linux_context *context_iterator;
struct list_head *l;
if (!sb) {
printk(KERN_INFO "yaffs: sb is NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
sb->s_magic = YAFFS_MAGIC;
sb->s_op = &yaffs_super_ops; //super_block层的操作函数
sb->s_flags |= MS_NOATIME;
read_only = ((sb->s_flags & MS_RDONLY) != 0);
#ifdef YAFFS_COMPILE_EXPORTFS
sb->s_export_op = &yaffs_export_ops;
#endif
... ...
sb->s_blocksize = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
sb->s_blocksize_bits = PAGE_CACHE_SHIFT;
... ...
/* Check it's an mtd device..... */
if (MAJOR(sb->s_dev) != MTD_BLOCK_MAJOR)
return NULL; /* This isn't an mtd device */
/* --判断是mtd,开始mtd相关操作-- */
/* Get the device */
mtd = get_mtd_device(NULL, MINOR(sb->s_dev)); //MTD_BLOCK_MAJOR
if (!mtd) {
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_ALWAYS,
"yaffs: MTD device #%u doesn't appear to exist",
MINOR(sb->s_dev));
return NULL;
}
/* Check it's NAND */
if (mtd->type != MTD_NANDFLASH) {
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_ALWAYS,
"yaffs: MTD device is not NAND it's type %d",
mtd->type);
return NULL;
}
/* 获得mtd之后,检查mtd各项及操作函数 */
/* OK, so if we got here, we have an MTD that's NAND and looks
* like it has the right capabilities
* Set the struct yaffs_dev up for mtd
*/
if (!read_only && !(mtd->flags & MTD_WRITEABLE)) {
read_only = 1;
printk(KERN_INFO
"yaffs: mtd is read only, setting superblock read only\n"
);
sb->s_flags |= MS_RDONLY;
}
/* struct yaffs_dev */
dev = kmalloc(sizeof(struct yaffs_dev), GFP_KERNEL);
context = kmalloc(sizeof(struct yaffs_linux_context), GFP_KERNEL);
... ...
dev->os_context = context;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(context->context_list));
context->dev = dev;
context->super = sb;
dev->read_only = read_only;
#if (LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(2, 5, 0))
sb->s_fs_info = dev;
#else
sb->u.generic_sbp = dev;
#endif
dev->driver_context = mtd;
/* struct yaffs_param */
param->name = mtd->name;
/* Set up the memory size parameters.... */
n_blocks =
YCALCBLOCKS(mtd->size,
(YAFFS_CHUNKS_PER_BLOCK * YAFFS_BYTES_PER_CHUNK));
/****************************************************************
#define YAFFS_BYTES_PER_SPARE 16
#define YAFFS_BYTES_PER_CHUNK 512
#define YAFFS_CHUNK_SIZE_SHIFT 9
#define YAFFS_CHUNKS_PER_BLOCK 32
#define YAFFS_BYTES_PER_BLOCK (YAFFS_CHUNKS_PER_BLOCK*YAFFS_BYTES_PER_CHUNK)
****************************************************************/
param->start_block = 0;
param->end_block = n_blocks - 1;
param->chunks_per_block = YAFFS_CHUNKS_PER_BLOCK; //32
param->total_bytes_per_chunk = YAFFS_BYTES_PER_CHUNK; //512
param->n_reserved_blocks = 5;
param->n_caches = (options.no_cache) ? 0 : 10;
param->inband_tags = options.inband_tags;
#ifdef CONFIG_YAFFS_DISABLE_LAZY_LOAD
param->disable_lazy_load = 1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_YAFFS_XATTR
param->enable_xattr = 1;
#endif
/**
* struct yaffs_param 的填充
* 包括yaffs所有信息,操作函数等。
*/
/* ... and the functions. */
if (yaffs_version == 2) {
param->write_chunk_tags_fn = nandmtd2_write_chunk_tags;
param->read_chunk_tags_fn = nandmtd2_read_chunk_tags;
param->bad_block_fn = nandmtd2_mark_block_bad;
param->query_block_fn = nandmtd2_query_block;
yaffs_dev_to_lc(dev)->spare_buffer
= kmalloc(mtd->oobsize, GFP_NOFS);
param->is_yaffs2 = 1;
#if (LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(2, 6, 17))
param->total_bytes_per_chunk = mtd->writesize;
param->chunks_per_block = mtd->erasesize / mtd->writesize;
#else
param->total_bytes_per_chunk = mtd->oobblock;
param->chunks_per_block = mtd->erasesize / mtd->oobblock;
#endif
n_blocks = YCALCBLOCKS(mtd->size, mtd->erasesize);
param->start_block = 0;
param->end_block = n_blocks - 1;
} else {
... ...
}
... ...
err = yaffs_guts_initialise(dev); //对dev赋值并检验。yaffs_gut.c -->
... ...
if (!inode)
return NULL;
/*索引节点操作的接口函数*/
inode->i_op = &yaffs_dir_inode_operations;
inode->i_fop = &yaffs_dir_operations;
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_OS, "yaffs_read_super: got root inode");
root = d_alloc_root(inode);
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_OS, "yaffs_read_super: d_alloc_root done");
if (!root) {
iput(inode);
return NULL;
}
sb->s_root = root;
sb->s_dirt = !dev->is_checkpointed;
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_ALWAYS,
"yaffs_read_super: is_checkpointed %d",
dev->is_checkpointed);
yaffs_trace(YAFFS_TRACE_OS, "yaffs_read_super: done");
return sb;
}
----> 完成对dev赋值并检验
int yaffs_guts_initialise(struct yaffs_dev *dev)
{
... ...
if (!init_failed && !yaffs_init_blocks(dev))
yaffs_init_tnodes_and_objs(dev);
if (!init_failed && !yaffs_create_initial_dir(dev))
init_failed = 1;
... ...
}
--mtd层--
mtd->read( ) 正式进入mtd层的地界,又是在何时挂上具体的操作函数?
nand_scan,nand驱动中相当面熟的函数。即使看不到它,十有八九也会看到它封装的nand_scan_ident和nand_scan_tail。
打开nand_scan_tail瞧一瞧:
int nand_scan_tail(struct mtd_info *mtd)
{
... ...
case NAND_ECC_HW:
/* Use standard hwecc read page function ? */
if (!chip->ecc.read_page)
chip->ecc.read_page = nand_read_page_hwecc;
if (!chip->ecc.write_page)
chip->ecc.write_page = nand_write_page_hwecc;
if (!chip->ecc.read_page_raw)
chip->ecc.read_page_raw = nand_read_page_raw;
if (!chip->ecc.write_page_raw)
chip->ecc.write_page_raw = nand_write_page_raw;
if (!chip->ecc.read_oob)
chip->ecc.read_oob = nand_read_oob_std;
if (!chip->ecc.write_oob)
chip->ecc.write_oob = nand_write_oob_std;
... ...
/* Fill in remaining MTD driver data */
mtd->type = MTD_NANDFLASH;
mtd->flags = (chip->options & NAND_ROM) ? MTD_CAP_ROM : MTD_CAP_NANDFLASH;
mtd->erase = nand_erase;
mtd->point = NULL;
mtd->unpoint = NULL;
mtd->read = nand_read; //-->
mtd->write = nand_write;
mtd->panic_write = panic_nand_write;
mtd->read_oob = nand_read_oob;
mtd->write_oob = nand_write_oob;
mtd->sync = nand_sync;
mtd->lock = NULL;
mtd->unlock = NULL;
mtd->suspend = nand_suspend;
mtd->resume = nand_resume;
mtd->block_isbad = nand_block_isbad;
mtd->block_markbad = nand_block_markbad;
mtd->writebufsize = mtd->writesize;
/* propagate ecc.layout to mtd_info */
mtd->ecclayout = chip->ecc.layout;
/* Check, if we should skip the bad block table scan */
if (chip->options & NAND_SKIP_BBTSCAN)
return 0;
/* Build bad block table */
return chip->scan_bbt(mtd);
}
也正如注释所言:
/**
* nand_scan_tail - [NAND Interface] Scan for the NAND device
* @mtd: MTD device structure
*
* This is the second phase of the normal nand_scan() function. It
* fills out all the uninitialized function pointers with the defaults
* and scans for a bad block table if appropriate.
*/
nand驱动中调用nand_scan,便为该nandFlash设备的mtd层提供了上层接口。
--drivers/mtd/nand/nand_base.c --
static int nand_read(struct mtd_info *mtd, loff_t from, size_t len,
size_t *retlen, uint8_t *buf)
{
struct nand_chip *chip = mtd->priv;
int ret;
/* Do not allow reads past end of device */
if ((from + len) > mtd->size)
return -EINVAL;
if (!len)
return 0;
nand_get_device(chip, mtd, FL_READING);
chip->ops.len = len;
chip->ops.datbuf = buf;
chip->ops.oobbuf = NULL;
ret = nand_do_read_ops(mtd, from, &chip->ops); //Read data with ECC-->
*retlen = chip->ops.retlen;
nand_release_device(mtd);
return ret;
}
---->
static int nand_do_read_ops(struct mtd_info *mtd, loff_t from,
struct mtd_oob_ops *ops)
{
while(1) {
... ...
/* Now read the page into the buffer */
if (unlikely(ops->mode == MTD_OOB_RAW))
ret = chip->ecc.read_page_raw(mtd, chip,
bufpoi, page);
else if (!aligned && NAND_SUBPAGE_READ(chip) && !oob)
ret = chip->ecc.read_subpage(mtd, chip,
col, bytes, bufpoi);
else
ret = chip->ecc.read_page(mtd, chip, bufpoi, page); //-->
if (ret < 0)
break;
... ...
}
我X,又见回调!不过在之前的nand_scan_tail中已挂上了nand_read_page_hwecc。
--drivers/mtd/nand/nand_base.c --
static int nand_read_page_hwecc(struct mtd_info *mtd, struct nand_chip *chip,
uint8_t *buf, int page)
{
int i, eccsize = chip->ecc.size;
int eccbytes = chip->ecc.bytes;
int eccsteps = chip->ecc.steps;
uint8_t *p = buf;
uint8_t *ecc_calc = chip->buffers->ecccalc;
uint8_t *ecc_code = chip->buffers->ecccode;
uint32_t *eccpos = chip->ecc.layout->eccpos;
/* 最终导向具体nand驱动中的xxx_read*/
for (i = 0; eccsteps; eccsteps--, i += eccbytes, p += eccsize) {
chip->ecc.hwctl(mtd, NAND_ECC_READ);
chip->read_buf(mtd, p, eccsize);
chip->ecc.calculate(mtd, p, &ecc_calc[i]);
}
chip->read_buf(mtd, chip->oob_poi, mtd->oobsize);
for (i = 0; i < chip->ecc.total; i++)
ecc_code[i] = chip->oob_poi[eccpos[i]];
eccsteps = chip->ecc.steps;
p = buf;
for (i = 0 ; eccsteps; eccsteps--, i += eccbytes, p += eccsize) {
int stat;
stat = chip->ecc.correct(mtd, p, &ecc_code[i], &ecc_calc[i]);
if (stat < 0)
mtd->ecc_stats.failed++;
else
mtd->ecc_stats.corrected += stat;
}
return 0;
}
--硬件驱动层--
这里以davinci_nand.c为例,TI的一款构架。
部分代码:
^^^^^^^^^^^
info->dev = &pdev->dev;
info->base = base;
info->vaddr = vaddr;
^^^^^^^^^^^
info->mtd.priv = &info->chip;
info->mtd.name = dev_name(&pdev->dev);
info->mtd.owner = THIS_MODULE;
info->mtd.dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
^^^^^^^^^^^
info->chip.IO_ADDR_R = vaddr;
info->chip.IO_ADDR_W = vaddr;
info->chip.chip_delay = 0;
info->chip.select_chip = nand_davinci_select_chip;
/* options such as NAND_USE_FLASH_BBT or 16-bit widths */
info->chip.options = pdata->options;
info->chip.bbt_td = pdata->bbt_td;
info->chip.bbt_md = pdata->bbt_md;
/* Set address of hardware control function */
info->chip.cmd_ctrl = nand_davinci_hwcontrol;
info->chip.dev_ready = nand_davinci_dev_ready;
/* Speed up buffer I/O */
info->chip.read_buf = nand_davinci_read_buf; //读 -->
info->chip.write_buf = nand_davinci_write_buf;
^^^^^^^^^^^
info->ioaddr = (uint32_t __force) vaddr;
info->current_cs = info->ioaddr;
info->core_chipsel = pdev->id;
info->mask_chipsel = pdata->mask_chipsel;
/* use nandboot-capable ALE/CLE masks by default */
info->mask_ale = pdata->mask_ale ? : MASK_ALE;
info->mask_cle = pdata->mask_cle ? : MASK_CLE;
这部分的思路很清晰,就是填充info指向的代表nand设备的结构体,其中包含了对函数指针chip.read_buf 的赋值。
其中包含了两个结构体:mtd_info 和 nand_chip。
驱动代码中出现了nand_scan_ident和nand_scan_tail,也就是mtd层挂钩子的过程。
/* Scan to find existence of the device(s) */
ret = nand_scan_ident(&info->mtd, pdata->mask_chipsel ? 2 : 1);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_dbg(&pdev->dev, "no NAND chip(s) found\n");
goto err_scan;
}
... ...
ret = nand_scan_tail(&info->mtd);
if (ret < 0)
goto err_scan;
驱动的结尾向内核注册mtd设备,两种注册方式:
1)直接注册整个flash设备(MTD Device)到MTD。
ret = add_mtd_device(mtd);
2)分partion添加到mtd_table,并将每个partion当成一个mtd设备注册到MTD。
if (!(partitions && num_part > 0) )
ret = add_mtd_partitions(mtd, parts, num_part);
-->
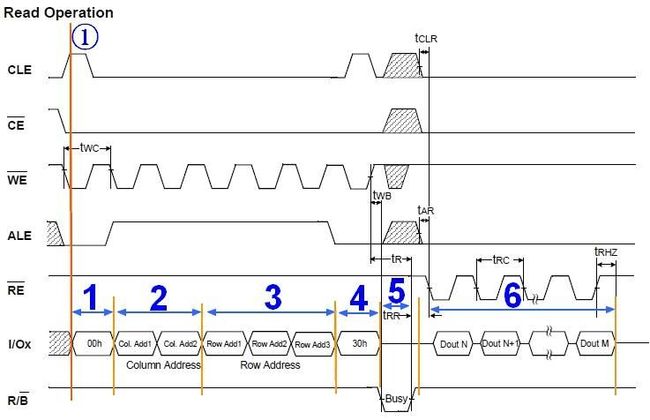
nand_davinci_read_buf是要我们自己去实现,参考使用nand的时序图,比如:
具体的说就是gpio的控制。
小小的看下该回调的函数:
static void nand_davinci_read_buf(struct mtd_info *mtd, uint8_t *buf, int len)
{
struct nand_chip *chip = mtd->priv;
if ((0x03 & ((unsigned)buf)) == 0 && (0x03 & len) == 0)
ioread32_rep(chip->IO_ADDR_R, buf, len >> 2);
else if ((0x01 & ((unsigned)buf)) == 0 && (0x01 & len) == 0)
ioread16_rep(chip->IO_ADDR_R, buf, len >> 1);
else
ioread8_rep(chip->IO_ADDR_R, buf, len);
}
从寄存器读出相应位宽的数据,最后调到io口的“原子”操作_raw_read,_raw_write。
#define ioread32_rep(p,d,c) __raw_readsl(p,d,c)
/*
* Generic IO read/write. These perform native-endian accesses. Note
* that some architectures will want to re-define __raw_{read,write}w.
*/
extern void __raw_readsb(const void __iomem *addr, void *data, int bytelen);
extern void __raw_readsw(const void __iomem *addr, void *data, int wordlen);
extern void __raw_readsl(const void __iomem *addr, void *data, int longlen);
raw_readsl这种基础的原子函数,汇编化是必须的。
1 /*
2 * linux/arch/arm/lib/io-readsb.S
3 *
4 * Copyright (C) 1995-2000 Russell King
5 *
6 * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
7 * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
8 * published by the Free Software Foundation.
9 */
10 #include <linux/linkage.h>
11 #include <asm/assembler.h>
12
13 .Linsb_align: rsb ip, ip, #4
14 cmp ip, r2
15 movgt ip, r2
16 cmp ip, #2
17 ldrb r3, [r0]
18 strb r3, [r1], #1
19 ldrgeb r3, [r0]
20 strgeb r3, [r1], #1
21 ldrgtb r3, [r0]
22 strgtb r3, [r1], #1
23 subs r2, r2, ip
24 bne .Linsb_aligned
25
26 ENTRY(__raw_readsb)
27 teq r2, #0 @ do we have to check for the zero len?
28 moveq pc, lr
29 ands ip, r1, #3
30 bne .Linsb_align
31
32 .Linsb_aligned: stmfd sp!, {r4 - r6, lr}
33
34 subs r2, r2, #16
35 bmi .Linsb_no_16
36
37 .Linsb_16_lp: ldrb r3, [r0]
38 ldrb r4, [r0]
39 ldrb r5, [r0]
40 mov r3, r3, put_byte_0
41 ldrb r6, [r0]
42 orr r3, r3, r4, put_byte_1
43 ldrb r4, [r0]
44 orr r3, r3, r5, put_byte_2
45 ldrb r5, [r0]
46 orr r3, r3, r6, put_byte_3
47 ldrb r6, [r0]
48 mov r4, r4, put_byte_0
49 ldrb ip, [r0]
50 orr r4, r4, r5, put_byte_1
51 ldrb r5, [r0]
52 orr r4, r4, r6, put_byte_2
53 ldrb r6, [r0]
54 orr r4, r4, ip, put_byte_3
55 ldrb ip, [r0]
56 mov r5, r5, put_byte_0
57 ldrb lr, [r0]
58 orr r5, r5, r6, put_byte_1
59 ldrb r6, [r0]
60 orr r5, r5, ip, put_byte_2
61 ldrb ip, [r0]
62 orr r5, r5, lr, put_byte_3
63 ldrb lr, [r0]
64 mov r6, r6, put_byte_0
65 orr r6, r6, ip, put_byte_1
66 ldrb ip, [r0]
67 orr r6, r6, lr, put_byte_2
68 orr r6, r6, ip, put_byte_3
69 stmia r1!, {r3 - r6}
70
71 subs r2, r2, #16
72 bpl .Linsb_16_lp
73
74 tst r2, #15
75 ldmeqfd sp!, {r4 - r6, pc}
76
77 .Linsb_no_16: tst r2, #8
78 beq .Linsb_no_8
79
80 ldrb r3, [r0]
81 ldrb r4, [r0]
82 ldrb r5, [r0]
83 mov r3, r3, put_byte_0
84 ldrb r6, [r0]
85 orr r3, r3, r4, put_byte_1
86 ldrb r4, [r0]
87 orr r3, r3, r5, put_byte_2
88 ldrb r5, [r0]
89 orr r3, r3, r6, put_byte_3
90 ldrb r6, [r0]
91 mov r4, r4, put_byte_0
92 ldrb ip, [r0]
93 orr r4, r4, r5, put_byte_1
94 orr r4, r4, r6, put_byte_2
95 orr r4, r4, ip, put_byte_3
96 stmia r1!, {r3, r4}
97
98 .Linsb_no_8: tst r2, #4
99 beq .Linsb_no_4
100
101 ldrb r3, [r0]
102 ldrb r4, [r0]
103 ldrb r5, [r0]
104 ldrb r6, [r0]
105 mov r3, r3, put_byte_0
106 orr r3, r3, r4, put_byte_1
107 orr r3, r3, r5, put_byte_2
108 orr r3, r3, r6, put_byte_3
109 str r3, [r1], #4
110
111 .Linsb_no_4: ands r2, r2, #3
112 ldmeqfd sp!, {r4 - r6, pc}
113
114 cmp r2, #2
115 ldrb r3, [r0]
116 strb r3, [r1], #1
117 ldrgeb r3, [r0]
118 strgeb r3, [r1], #1
119 ldrgtb r3, [r0]
120 strgtb r3, [r1]
121
122 ldmfd sp!, {r4 - r6, pc}
123 ENDPROC(__raw_readsb)
OK,流水账完毕,粗略的浏览,过程中的每一部分都是一门学问,展开来去那就是一篇篇的论文。借一校友的的社区签名:“好的论文就像一个美女,研读论文的过程就是脱衣服的过程。”