按键驱动的恩恩怨怨之查询方式
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ruoyunliufeng/article/details/23950459
查询是耗费资源严重,不建议使用。那为什么还要拿出来讲啊,原因就是知道这个设计非常烂,你就会设计出比他更好的驱动。
一.驱动代码:
/*查询法,按键*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/arch/regs-gpio.h>
#include <asm/hardware.h>
static struct class *seconddrv_class;
static struct class_device *seconddrv_class_dev;
volatile unsigned long *gpgcon;
volatile unsigned long *gpgdat;
static int second_drv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
/*
* K1,K2,K3,K4相应GPG0,GPG3,GPG5,GPG6
*/
/* 配置GPG0,GPG3,GPG5,GPG6为输入引脚 */
*gpgcon &= ~((0x3<<(0*2)) | (0x3<<(3*2)) | (0x3<<(5*2)) | (0x3<<(6*2))); //00表示输入
return 0;
}
ssize_t second_drv_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
{
/* 返回4个引脚的电平 */
unsigned char key_vals[4];
int regval;
if (size != sizeof(key_vals))
return -EINVAL;
regval = *gpgdat;
key_vals[0] = (regval & (1<<0)) ? 1 : 0; //推断寄存器是否变为0假设为0则表示按下,则数组位被写入0
key_vals[1] = (regval & (1<<3)) ? 1 : 0;
key_vals[2] = (regval & (1<<5)) ? 1 : 0;
key_vals[3] = (regval & (1<<6)) ? 1 : 0;
copy_to_user(buf, key_vals, sizeof(key_vals)); //告诉应用程序
return sizeof(key_vals);
}
static struct file_operations sencod_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自己主动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = second_drv_open,
.read = second_drv_read,
};
int major;
static int second_drv_init(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "second_drv", &sencod_drv_fops); //注冊
seconddrv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "second_drv"); //创建设备
seconddrv_class_dev = class_device_create(seconddrv_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "buttons"); /* /dev/buttons */
gpgcon = (volatile unsigned long *)ioremap(0x56000060, 16); //虚拟地址
gpgdat = gpgcon + 1;
return 0;
}
static void second_drv_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(major, "second_drv");
class_device_unregister(seconddrv_class_dev);
class_destroy(seconddrv_class);
iounmap(gpgcon);
return 0;
}
module_init(second_drv_init);
module_exit(second_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); //证书
二.应用程序代码
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* seconddrvtest
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
unsigned char key_vals[4];
int cnt = 0;
fd = open("/dev/buttons", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can't open!\n");
}
while (1)
{
read(fd, key_vals, sizeof(key_vals));
if (!key_vals[0] || !key_vals[1] || !key_vals[2] || !key_vals[3]) //有随意一个按下(!0)则运行,则输出四个键的值
{
printf("%04d key pressed: %d %d %d %d\n", cnt++, key_vals[0], key_vals[1], key_vals[2], key_vals[3]);
}
}
return 0;
}
三.分析
1. 应用程序:首先打开设备,假设不能打开给出提示。然后进入一个while(1)循环(悲催的程序从此就没出来过一直检測,CPU就一直运转,这就是耗费资源的根本原因)。接下来是read()函数读取寄存器是否发生变化(是否按键)通过copy_to_user()告诉应用程序。然后进行推断有随意一个按键按下就进行打印。然后继续循环。
2.驱动程序:驱动程序的框架与我之前写的LED的框架并没有太大区别(都是字符型的框架)。在open()函数中对寄存器进行配置。然后再read()函数中推断寄存器的状态传给应用程序。
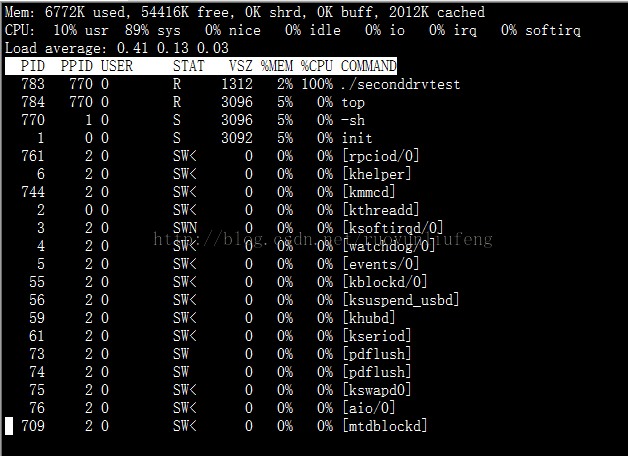
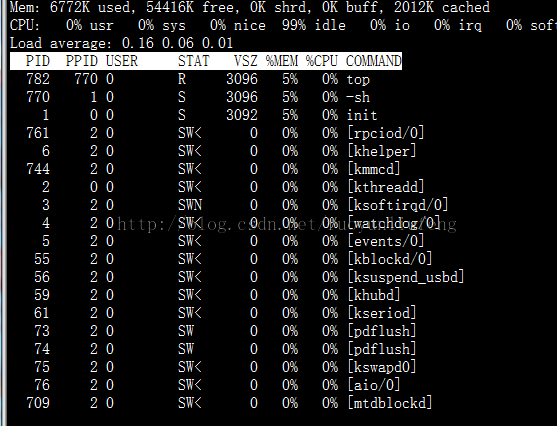
3.实际工作截图: 为了叫小伙伴们看到这种驱动有多糟糕,接两个图先。
未使用驱动状态
使用之后