MyBatis框架常见面试题
1、#{}和${}区别
- ${}是Properties文件中的变量占位符,可以用于标签属性值和sql内部,属于静态文本替换,比如 :
${driver} 会被静态替换为com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#{}是 sql 的参数占位符,MyBatis 会将 sql 中的#{}替换为? 号,在sql执行前会使用PrepareStatement的参数设置方法,按序给sql的?号占位符设置参数值 。#{item.name}的取值方式为从参数对象中调用getItem()方法获取Item对象,然后调用item对象的getName方法,获取name属性值。.name不是获取属性而是调用方法
2、Dao接口的工作原理是什么
Dao接口里的方法,参数不同时,方法能重载吗?
工作原理
通常一个xml映射文件都会写一个Dao接口与之对应,也就是常说的Mapper接口。接口的全限名,就是映射文件中的namespace的值,接口的方法名,就是映射文件中MappedStatement的id值,接口方法内的参数就是传递给sql的参数。Mapper接口是没有实现类的,当调用接口方法时,接口全限名+方法名拼接字符串作为key值,可唯一定位一个MappedStatement 。在MyBatis中,每一个< select > 、< insert >、< update > 、< delete >标签,都会被解析为一个MappedStatement对象
举例,根据id查询用户的业务
dao接口
//根据ID查询用户
user getUserById(int id);
xml
<mapper namespace="com.qian.dao.UserMapper">
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.qian.pojo.user">
select * from mybatis.user where id=#{id}
select>
业务层调用
public void getUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
user user = mapper.getUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
Dao接口中的方法可以重载,但是xml文件中的id不能相同
即xml文件中的id是唯一的
/**
* Mapper接口里面方法重载
*/
public interface StuMapper {
List<Student> getAllStu();
List<Student> getAllStu(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
xml
<select id="getAllStu" resultType="com.pojo.Student">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="id != null">
id = #{id}
if>
where>
select>
Mapper接⼝开发规范
Mapper接⼝开发需要遵循以下规范:
- Mapper.xml⽂件中的namespace与mapper接⼝的类路径相同。
- Mapper接⼝⽅法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个Mappedstatement的id相同
- Mapper接⼝⽅法的输⼊参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同
- Mapper接⼝⽅法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
3、MyBatis是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理
如何分页:
- 使用Limit分页(sql实现分页),在sql内直接写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能
xml
<select id="getUserByLimit" parameterType="map" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex},#{pageSize}
</select>
limit 从哪条数据开始 一页有多少条数据
使用
@Test
public void getUserByLimit(){
SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
HashMap<String,Integer>map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("startIndex",0);
map.put("pageSize",2);
List<User>userList = mapper.getUserByLimit(map);
for (User user:userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
用一个map存储 从哪条数据开始和一页多少条数据
- 使用RowBounds对象进行分页。它是针对ResultSet 结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页;
xml
<select id="getUserByRowBounds" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user
select>
java实现分页
@Test
public void getUserByRowBounds(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//RowBounds实现
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1, 2);
//通过java代码层面实现分页
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("com.qian.dao.UserMapper.getUserByRowBounds",null,rowBounds);
for (User user:userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1, 2);
- 使用分页插件来完成物理分页
分页插件的原理
分页插件的基本原理是使用MyBatis提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的sql,然后重写sql,根据dialect方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数
举例:**select _ from student ** ,拦截 sql 后重写为:select t._ from (select * from student)t limit 0,10
4、简述MyBatis的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件
MyBatis在四大组件处提供了简单易用的插件扩展机制。Mybatis对持久层的操作就是借助于四大核心对象。Mybatis支持用插件对四大核心进行拦截,对mybatis来说,插件就是拦截器,用来增强核心对象的功能 。增强功能本质上是借助于底层的动态代理实现的。MyBatis使用JDK的动态代理,为需要拦截的接口生成代理对象以实现接口方法拦截功能,每当执行这4种接口对象的方法时,就会进入拦截方法。
1、四大核心对象
- ParamterHandler:处理SQL的参数对象
- ResultSetHandler:处理SQL的返回结果集
- StatementHandler:数据库的处理对象,用于执行SQL语句
- Executor:Mybatis的执行器,用于执行增删改查操作
2、MyBatis插件原理
- Mybatis的插件借助于JDK动态代理和责任链设计模式 进行对拦截的处理
- 使用动态代理对目标对象进行包装,达到拦截的目的
- 作用于Mybatis的作用域对象之上
3、自定义插件
- 自定义插件需要实现MyBatis的Interceptor接口,复写intercept()方法
- 增加@Intercepts注解 (声明是哪个核心组件的插件,以及对哪些方法进行扩展)
- 在xml文件中配置插件
自定义插件类
/** 插件签名,告诉mybatis插件用来拦截那个对象的哪个方法 **/
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class,method
="handleResultSets",args = Statement.class)})
public class MyFirstInterceptor implements Interceptor {
/** @Description 拦截目标对象的目标方法 **/
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("拦截的目标对象:"+invocation.getTarget());
Object object = invocation.proceed();
return object;
}
}
配置文件中配置插件
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="mybatis.interceptor.MyFirstInterceptor">
<property name="name" value="Bob"/>
plugin>
plugins>
5、MyBatis如何将sql执行结果封装为目标对象并返回?都有哪些映射形式
首先将列名与属性名映射
- 用< resultMap >标签。逐一定义列名和对象属性名之间的映射关系。
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="user">
<result column="pwd" property="password">result>
resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="UserMap">
select * from mybatis.user where id=#{id}
select>
- 使用sql的别名功能。将列名书写为对象属性名 ,如 T_NAME AS NAME。MyBatis会忽略列名大小写
有了列名与属性名映射关系后,MyBatis通过反射创建对象,同时使用反射给对象的属性逐一赋值并返回
6、MyBatis执行多对一查询和一对多查询
多个学生对应一个老师
对于老师:一对多,查询学生,查询的是一个集合,collection
对于学生:多对一,查询老师,association
联表查询:
多对一查询
查询多个学生对应的老师
<select id="getStudent2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname from mybatis.student s,mybatis.teacher t where s.tid=t.id;
select>
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="com.qian.pojo.Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.qian.pojo.Teacher">
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
association>
resultMap>
一对多查询
查询一个老师对应的多个学生
<mapper namespace="com.qian.dao.TeacherMapper">
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tid from mybatis.student s,mybatis.teacher t where s.id=t.id and t.id=#{tid}
select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="com.qian.pojo.Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="com.qian.pojo.Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
collection>
resultMap>
7、MyBatis的xml映射文件中,不同的xml映射文件,id否可以重复?
- 不同的xml映射文件中,如果配置了namespace,id可以重复(相当于指定了确定的类中的方法名),可以重复
- 但是如果没有配置namespace,那么即便在不同的xml映射文件,id也不能重复
- 因为当调用接口方法时,接口全限名+方法名拼接字符串作为key 值,可唯一定位一个MappedStatement,如果没有接口全限名,id重复的话不能唯一定位MappedStatement对象
8、MyBatis都有哪些Executor执行器?
- SimpleExecutor :每执行一次update或select ,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象
- ReuseExecutor:执行update或select,以sql作为key查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭Statemnt对象,而是放置于Map< String ,Statement >内,供下一次使用。重复使用Statement对象
- BatchExecutor:执行update,将所有sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch())。它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addbatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理,与JDBC批处理相同
9、简述MyBatis的xml映射文件和MyBatis内部数据结构之间的映射关系
- MyBatis将所有的xml配置信息都封装到ALL-IN-ONE 重量级对象 Configuration 内部
- 在xml映射文件中,< parameterMap > 标签会被解析为 ParameterMap对象,其每个子元素都会被解析为ParameterMapping对象。
- < resultMap>标签会被解析为ResultMap对象。其每个子元素会被解析为ResultMapping对象
- 每一个< select > 、< insert >、< update > 、< delete >标签,都会被解析为一个MappedStatement对象
- 标签内的sql会被解析为BoundSql对象
10、为什么说MyBatis是半自动ORM映射工具?
- Hibernate 属于全自动 ORM映射工具 ,使用 Hibernate 查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取,所以它是全自动的
- 而MyBatis在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写sql来完成,所以称之为半自动ORM映射工具
- 针对简单逻辑,二者都有相应的代码生成工具,可以生成简单基本的DAO层方法。但是针对高级查询,MyBatis需要手动编写SQL语句以及resultMap,而Hibernate有良好的映射机制,开发者无需关心SQL的生成与结果映射,可以更关注于业务流程
- MyBatis没有自己的日志统计,要借助log4j来记录日志,Hibernate具有自己的日志统计
- MyBatis由于所有SQL都是依赖数据库书写,扩展性差,迁移性差;Hibernate与数据库的具体的关联都在XML中,所以对具体是用什么数据库并不是很关心
总结:
mybatis:小巧、方便、高效、简单、直接、半自动
hibernate:强大、方便、高效、复杂、绕弯子、全自动
Hibernate与MyBatis都可以是通过SessionFactoryBuider由XML配置文件生成SessionFactory,然后
由SessionFactory 生成Session,最后由Session来开启执行事务和SQL语句。
而MyBatis的优势是MyBatis可以进行更为细致的SQL优化,可以减少查询字段,并且容易掌握。
Hibernate的优势是DAO层开发比MyBatis简单,Mybatis需要维护SQL和结果映射。数据库移植性很
好,MyBatis的数据库移植性不好,不同的数据库需要写不同SQL。有更好的二级缓存机制,可以使用
第三方缓存。MyBatis本身提供的缓存机制不佳。
11、MyBatis的一级缓存和二级缓存
1、一级缓存
- 一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存,在操作数据库时需要构造SqlSession对象。在对象中有一个数据结果用于存储缓存数据
- 不同的SqlSession之间的缓存数据区域是互相不影响的。也就是说他只能作用在同一个SqlSession中,不同的SqlSession中的缓存是互相不能读取的
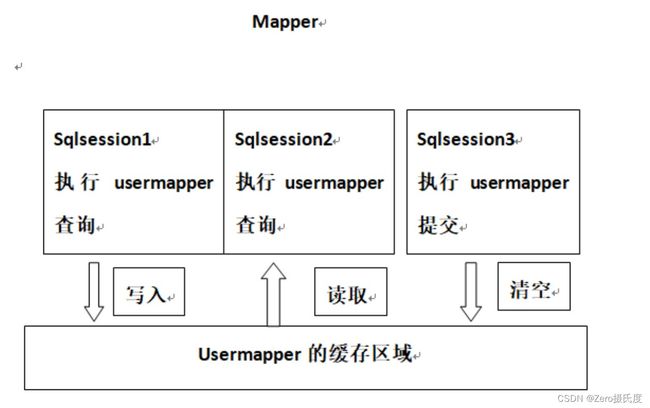
工作原理:
用户第一次查询时,从数据库中查询到数据后,写入一级缓存区域,第二次查询相同数据时,会先从一级缓存区域中读取 。用户对该数据执行修改、添加、删除操作后,会将一级缓存中对应的缓存数据清空,以防止出现缓存和数据库中数据不一致的问题
用户发起查询请求,查找某条数据,sqlSession 先去缓存中查找,是否有该数据,如果有,读取;如果没有,从数据库中查询,并将查询到的数据放入一级缓存区域,供下次查找使用。
2、二级缓存
- 为什么有了一级缓存还要提供二级缓存?
二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,多个SqlSession去操作同一个mapper的sql语句,这多个SqlSession可以共用这个mapper的二级缓存。二级缓存是跨SqlSession的,作用范围更大
实际开发中,Spring与mybatis进行整合开发,每次查询之后,Spring都会关闭SqlSession,关闭之后缓存数据就会清空,所以spring整合后,如果没有事务,一级缓存是没有意义的。而二级缓存是基于mapper的,仍然存在。
- 工作原理
修改时会对缓存区域对应缓存数据清空。
每个Mapper有自己的二级缓存区域,根据namespace区分。
- 开启
在MyBatis全局配置文件中
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
在需要开启二级缓存的mapper.xml中,加入cache标签
<cache/>
让使用二级缓存的POJO类实现Serializable接口
public class User implements Serializable {
}
3、总结
- 对于查询多、commit少且用户对查询结果实时性要求不高,此时采用mybatis二级缓存技术降低数据库访问量,提高访问速度
- 不能滥用。有很明显的弊端。二级缓存是建立在namespace下的,如果对表的操作设计多个namespace,得到的缓存数据就会有错:
例如,订单 和 订单详情 分别是 orderMapper、orderDetailMapper。
在查询订单详情(orderDetailMapper)时,我们需要把订单信息(orderMapper)也查询出来,那么
这个订单详情(orderDetailMapper)的信息被二级缓存在 orderDetailMapper 的 namespace中 (里面包含orderMapper的数据),这个时候有人要修改订单的基本信息(orderMapper),那就是在 orderMapper 的 namespace 下修改,他是不会影响到 orderDetailMapper 的缓存 的,那么你再次查找订单详情时,拿到的是缓存的数据,这个数据其实已经是过时的。不同namespace的二级缓存不会互相影响
- 所以二级缓存需要注意:
只能在一个基于命名空间下的查询使用二级缓存 。在表单上使用二级缓存时也要注意,因为如果一个表与其他表有关联关系,那么就非常有可能存在多个namespace对同一数据操作。造成数据不一致
- 查询多于修改时可以使用二级缓存,提高查询速度。
12、MyBatis动态sql
1、动态SQL的应用
动态SQL是MyBatis的强大特性之一。当根据不同条件拼接SQL语句时,利用动态SQL可以不用那么痛苦的拼接
2、有哪些动态sql
- if
<select id="findActiveBlogWithTitleLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<if test="title != null">
AND title = #{title}
if>
select>
提高了可选的查找文本功能。如果不传入title,则直接返回符合state=’ACTIVE‘的BLOG数据,如果传入title,则执行if语句,对’title‘一列也进行匹配查找并返回对应的BLOG结果
- choose,when,otherwise
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’
<choose>
<when test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
when>
<when test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
when>
<otherwise>
AND featured = 1
otherwise>
choose>
select>
类似Java中的switch 。我们只是想从多个条件中选择符合一个条件的使用,对于这种情况,使用choose元素。
当传入的是title就按title查找,传入的是author就按author查找
- trim,where,set
在上面的例子中,如果没有匹配的条件,最终SQL会变成
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
如果匹配的只是第二个条件,会变成
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE
AND title LIKE 'someTitle'
MyBatis通过where元素,可以解决这个场景问题
<select id="findActiveBlogLike"
resultType="Blog">
SELECT * FROM BLOG
<where>
<if test="state != null">
state = #{state}
if>
<if test="title != null">
AND title like #{title}
if>
<if test="author != null and author.name != null">
AND author_name like #{author.name}
if>
where>
select>
where元素只会在子元素返回任何内容的情况下才会插入“where”子句。
- foreach
对集合进行遍历
<select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
WHERE ID in
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
foreach>
select>
foreach元素的功能非常强大,它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。
3、动态SQL执行原理
从设计上看,动态 sql实现主要涉及三个模式:
- 解释器模式:初始化过程中构建出抽象语法树,请求处理时根据参数对象解释语法树,生成sql语句
- 工厂模式:为动态标签的处理方式创建工厂类(sqlTagHandlerFactory),根据该标签名称获取对应的处理方式
- 策略模式:将动态标签处理方式抽象为接口,针对不同标签有相应的实现类。
sql配置—生成语法树,sql语句—解释语法树。
13、MyBatis的延迟加载
1、延迟加载
MyBatis中的延迟加载,也叫作懒加载。是指在进行表的关联查询时,按照设置延迟规则推迟对关联对象的select查询 。
例如,在进行一对多查询时,先只查询出1的一方,当程序中需要多方的数据时,mybatis再发出sql语句进行查询。
延迟加载可以减少数据库压力。MyBatis的延迟加载只是对关联对象的查询有迟延设置,对于主加载对象都是直接执行查询语句的
延迟加载的应用要求:关联对象的查询与主加载对象的查询必须是分别进行的select语句,不能是使用多表连接所进行的select查询
不是用联表查询,而是用子查询的方式,按照查询嵌套处理
2、加载时机
mybatis对于延迟加载的时机支持三种形式:
- 直接加载:执行完对主加载对象的 select 语句,马上执行对关联对象的 select 查询。
- 侵入式延迟: 执行对主加载对象的查询时,不会执行对关联对象的查询。但当要访问主加载对象的详情属性时,就会马上执行关联对象的select查询。
- 深度延迟: 执行对主加载对象的查询时,不会执行对关联对象的查询。访问主加载对象的详情时也不会
执行关联对象的select查询。只有当真正访问关联对象的详情时,才会执行对关联对象的 select 查询。
3、延迟加载使用场景
在一对多中,我们有一个用户,他有100个账户,
在查询用户时,用户下的账户信息应该是我们什么时候使用,什么时候再去查询–延迟加载
在查询账户时,账户所属的用户信息应该是随着账户查询时一起查询出来
一对多、多对多通常采用延迟加载;一对一、多对一通常采用直接加载
4、开启
在MyBatis 的配置文件中通过设置settings的lazyLoadingEnabled属性为true 进行开启全局的延迟加载,通过
aggressiveLazyLoading属性开启立即加载。
14、MyBatis执行过程的初始化如何执行?
1、MyBatis的执行过程分为:
- MyBatis的初始化
- SQL执行过程
2、MyBatis的初始化
在MyBatis的初始化过程中,会加载mybatis-config.xml 配置文件、Mapper.xml映射配置文件以及Mapper接口中的注解信息 ,解析后的配置信息会形成相应的对象保存到Configuration对象中 。
2.1、解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件
初始化流程入口是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment,
Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment,
properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
- XMLConfigBuilder.parse()解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件
- 先解析标签configuration内的数据封装成XNode
- 根据XNode解析mybatis-config.xml 配置文件的各个标签转变为各个对象
- 再基于Configuration使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder :: build()生成DefaultSqlSeesionFactory供给后续执行使用。
2.2、解析Mapper.xml映射文件
-
首先使用 XMLMapperBuilder.parse()解析Mapper.xml
-
通过XPathParser::evalNode将mapper标签中内容解析到XNode
-
再由configurationElement()方法去解析XNode中的各个标签
- namespace
- parameterMap
- resultMap
- select…
-
生成MappedStatement对象
2.3、解析Mapper接口中的注解
- 调用XMLMapperBuilder::bindMapperForNamespace() ,会转换成对接口上注解进行扫描,具体通过
MapperRegistry::addMapper() 调用 **MapperAnnotationBuilder ** 实现
- MapperAnnotationBuilder::parse() 是注解构造器,负责解析 Mapper 接口上的注解,解析时需要注
意避免和 XMLMapperBuilder::parse() 方法冲突,重复解析,最终使用 parseStatement 解析。
总结
在MyBatis初始化过程中,会加载mybatis-config.xml配置文件、Mapper.xml映射配置文件以及Mapper接口中的注解信息,解析后的配置信息会形成相应的对象并全部保存到Configuration对象中,并创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory供SQL执行过程创建出顶层接口SqlSession供给用户操作。