程序员面试笔试宝典学习记录(二)(程序设计相关知识)
- C++中,临时对象都是const类型的,由下面的程序测试可知。
另外const string &与string &两个参数类型可以进行函数重载,其实这就是类const与非const成员函数重载的机制,传入的是const引用(指针)于非const引用(指针)。
编译可通过,执行结果hello world
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#include<iostream>
#incldue<string>
using
namespace
std;
void
bar(
const
string &str) {
cout<<s<<endl;
}
int
main() {
bar(
"hello word"
);
}
|
编译错误~
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
#include<iostream>
#incldue<string>
using
namespace
std;
void
bar(string &str) {
cout<<s<<endl;
}
int
main() {
bar(
"hello word"
);
}
|
- volatile,被volatile类型定义的变量,系统每次使用它的时候都是直接从对应的内存当中提取。 使用场景:被不同线程访问和修改的变量。 防止编译器优化,直接取得寄存器中的值。
- 枚举变量的值默认为前一个变量的值加1,而如果第一个枚举变量没有被赋值,则其默认值为0 。枚举变量值是可以重复的。
- 一个C语言程序总是从main()函数开始执行的,对于C++程序而言,静态变量,全局变量,全局对象的分配早在mian()函数之前已经完成,所以并不是所有的动作都是由main()函数引起的,在main()函数中的显示代码执行之前,会调用一个编译器生成的_main()函数,而_main()函数会进行所有全局对象的构造以及初始化工作。main()函数退出之后会执行全局对象的析构函数~。
- *p++ 与 (*p)++区别
|
1
2
3
|
int
a[] = {1,2,3};
int
*p = a;
cout<<
"*p++:"
<<*p++<<
" "
<<
"(*p)++:"
<<(*p)++<<endl;
|
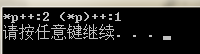
- 对于迭代器和其他模板对象一般使用前缀形式的(++i)的自增,自减运算符,效率更高!
- new/delete与malloc/free的主要区别:
(a) new能够自动计算需要分配的内存空间,而malloc需要手工计算字节数。
(b) new与delete直接带具体类型的指针,malloc与free返回void类型的指针。
(c)new是类型安全的,而malloc不是。
(d)new一般由两步构成,分别是new操作和构造。new操作对应于malloc,但new操作可以重载,可以自定义内存分配策略,不做内存分配,甚至分配到非内存设备上,而malloc不行。
(e)new将调用构造函数,而malloc不能;delete将调用析构函数,而free不能。
(f)malloc/free需要库文件stdlib.h支持,new/malloc则不需要库文件支持。
- C++中异常处理部分,finally不管代码是否有异常执行,try中如果有return,仍然需要执行finally语句,此种情况的执行过程如下:
(a)执行return返回语句,计算返回值,暂存在一个临时变量中。
(b)执行finally语句块。
(c)return原来已经计算得到的结果值。
如果finally区段中又调用一次return语句,则try区块返回值将被遮掩,返回的为finally区块中的返回值。
- 内存分配的形式:由符号起始的区块(BSS)段(未初始化的全局数据和静态数据),数据段(初始化的全局变量和静态数据),代码段,栈,堆;
堆,malloc,new分配,free,delete释放。若程序员不释放,程序结束时由系统释放。
栈,编译器自动分配和释放。
全局(静态)存储区:包括DATA段(全局初始化区)与BSS段(全局未初始化区)。BSS段特点,程序执行之前自动清0。所以未初始化的全局变量和静态变量程序执行之前为0。
文字常量区
程序代码区
- 栈的速度快,空间小,不灵活(因为栈是向低地址扩展的数据结构)。堆是向高地址扩展的数据结构,是不连续的内存区域,堆获得的空间比较灵活,速度相对慢一些(相对栈)。
- struct的sizeof是所有成员对齐长度相加,而union的sizeof是取最大的成员长度。
- 防止溢出求取两个数平均数的方法int x,int y,int mid = (x&y) + ((x^y)>>1);
- 求解整型数的二进制表示的1的个数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int
func(
int
x)
{
int
countx = 0;
while
(x)
{
countx++;
x = x&(x-1);
}
return
countx;
}
//函数功能统计x的二进制表示的1的个数
|
- 不用除法操作符如何实现两个整数的除法~
常用的等式:
(a)-n = ~(n-1)=~n+1。
(b)获取整数n的二进制的最后一个1:n&(-n)或者n&~(n-1)。
(c)去掉整数n的二进制的最后一个1:n&(n-1)。
方法一:一个一个减,效率较低。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int
div
(
int
a,
int
b) {
int
result = 0;
if
( b == 0) {
return
result;
}
while
( a>=b ) {
result++;
a-=b;
}
return
result;
}
|
方法二:递归法求解,每次将比较数翻倍。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
int
div
(
int
a,
int
b) {
int
curres = 0;
int
c = b;
int
res = 0;
if
( b == 0) {
return
res;
}
if
(a < b) {
return
res;
}
for
(;a >= c;c <<= 1,k++) {
if
(a-c < b) {
return
1<<k;
}
}
return
div
(a - (c>>1),b) + (1<<(k-1));
}
|
方法三:采用移位的方法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int
div
(
int
a,
int
b) {
int
left_num = a;
int
res = 0;
while
(left_num >= b) {
int
multi = 1;
while
(b*multi <= (left_num >> 1)) {
multi = multi << 1;
}
res += multi;
left_num -= y*multi;
}
return
res;
}
|
- 位运算实现加法。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
int
add(
int
num1,
int
num2) {
if
( 0 == num2 )
return
num1;
int
sumT = num1^num2;
int
carry = (num1&num2)<<1;
return
add(sumT,carry);
}
|
- 位运算实现乘法。1011*1010,拆解为1011*0010与1011*1000的和,对于二进制运算,左移一位相当于乘以0010,左移3位相当于乘以1000。乘法可以通过一系列移位与加法实现。
- 函数指针/指针函数,数组指针(pointer to array,int(*p)[4])/指针数组,函数模板/模板函数(具化),类模板/模板类(具化),常量指针(int const *p or const int *p)/指针常量(this is similar to refer,must initialization when defined and can't change)
- 只有编译器行为调用的构造函数才会执行初始化表达式。只有在声称对象时,初始化表达式才会随相应的构造函数一起调用,用户行为调用的构造函数不会执行相应的初始化表达式(例如默认构造函数内调用带参数的构造函数就属于用户行为)。
- 理解非常复杂的声明:
int a; int *a; int **a; int a[10]; int *a[10]; int (*a)[10]; int (*a)(int); int (*a[10])(int); int (*a[])(int);(数组a为一个函数指针数组,函数带一个整型变量,并且返回一个整型) int (*p())[10];(函数p返回类型为一个指向一位数组的指针) (*void(*)())0)();(调用地址为0的子程序,函数类型参数和返回值均为void)
复杂的声明解释起来比较有难度,一般出现在笔试题目中。
- C语言全局变量放在内存的全局数据区,由编译器建立,如果在定义的时候不做初始化,则系统将自动为其初始化,数值型为0,字符型为NULL,指针变量为NULL。静态变量情况与全局变量类似。而非静态局部变量如果不显示初始化,那么其内容是不可预料的,将是随机数。
- C++的全局对象,变量的构造函数调用顺序跟声明有一定的关系,同一个文件中先声明先调用,不同文件的全局对象,变量的构造函数调用顺序未定义。
- C++中的多态种类包含参数多态,引用多态,过载多态以及强制多态等。这种概念总觉无意义,了解多态的意义即可。
- 已知随机数函数rand7(),如何构造rand10()函数?
- 要保证rand10()产生的随机数是整数1~10的均匀分布,可以构造一个1~10*n的均匀分布的随机整数区间(n为任意正整数)。假设x是这个1~10*n区间上的一个随机数,那么x%10+1就是均匀分布在1~10区间上的整数。