UVa 11524:In-Circle(解析几何)
Problem E
In-Circle
Input: Standard Input
Output: Standard Output
In-circle of a triangle is the circle that touches all the three sides of the triangle internally. The center of the in-circle of a triangle happens to be the common intersection point of the three bisectors of the internal angles. In this problem you will not be asked to find the in-circle of a triangle, but will be asked to do the opposite!!
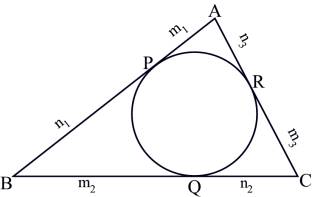
You can see in the figure above that the in-circle of triangle ABC touches the sides AB, BC and CA at point P, Q and R respectively and P, Q and R divides AB, BC and CA in ratio m1:n1, m2:n2 and m3:n3 respectively. Given these ratios and the value of the radius of in-circle, you have to find the area of triangle ABC.
Input
First line of the input file contains an integer N (0<N<50001), which denotes how many input sets are to follow. The description of each set is given below.
Each set consists of four lines. The first line contains a floating-point number r (1<r<5000), which denotes the radius of the in-circle. Each of the next three lines contains two floating-point numbers, which denote the values of m1, n1, m2, n2, m3 and n3 (1<m1, n1, m2, n2, m3, n3<50000) respectively.
Output
For each set of input produce one line of output. This line contains a floating-point number that denotes the area of the triangle ABC. This floating-point number should contain four digits after the decimal point. Errors less than 5*10-3 will be ignored. Use double-precision floating-point number for calculation.
Sample Input Output for Sample Input
| 2 140.9500536497 15.3010457320 550.3704847907 464.9681681852 65.9737378230 55.0132446384 10.7791711946 208.2835101182 145.7725891419 8.8264176452 7.6610997600 436.1911036207 483.6031801012 140.2797089713 |
400156.4075 908824.1322 |
Problemsetter: Shahriar Manzoor
Special Thanks: Mohammad Mahmudur Rahman
解析几何。
思路是先设AP=AC=x,则根据比例关系可以知道:
三边 a = (n1+m1)/m1*x; b = (n3+m3)/n3*x; c = m3/n3*(n2+m2)/n2*x;
将系数提出,设 k1 = (n1+m1)/m1; k2 = (n3+m3)/n3; k3 = m3/n3*(n2+m2)/n2;
由海伦公式可知 S = sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)); (p = (a+b+c)/2) //公式一
由边和半径的也能求出三角形的面积 S = (a*r+b*r+c*r)/2 = p*r; //公式二
联立公式一和公式二可得:
x = 2*sqrt(r*r*(k1+k2+k3)/((k2+k3-k1)*(k1+k3-k2)*(k1+k2-k3)));
带入公式一得:
S = (k1+k2+k3)*x*r/2;
PS:代码很短,主要是分析过程。
代码:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cmath>
3 #include <iomanip>
4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 int n; 8 cin>>n; 9 while(n--){ 10 double r; 11 double m1, n1, m2, n2, m3, n3; 12 cin>>r; //输入半径
13 cin>>m1>>n1>>m2>>n2>>m3>>n3; //输入比例
14 double k1,k2,k3; 15 k1 = (n1+m1)/m1; 16 k2 = m3*(n2+m2)/(n3*n2); 17 k3 = (n3+m3)/n3; 18 double x = 2*sqrt(r*r*(k1+k2+k3)/((k2+k3-k1)*(k1+k3-k2)*(k1+k2-k3))); //设AP=AR=x
19 double s = (k1+k2+k3)*x*r/2; 20 cout<<setiosflags(ios::fixed)<<setprecision(4); 21 cout<<s<<endl; 22 } 23 return 0; 24 }
Freecode : www.cnblogs.com/yym2013