听说你还不懂设计模式,来这里让你轻松掌握
这篇文章我们会详细介绍设计模式的背景、使用场景、以及使用的优缺点、以及我们最关心的如何使用
一、设计模式相关概念介绍
1、背景:设计模式的出现是为了解决面向对象设计中反复出现的问题,提供了一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的解决方案,这些方案被分类编目,旨在实现代码的可重用性、可读性和可靠性。设计模式不仅提高了代码的质量,还使得代码更易于他人理解。它们是一组相互紧密作用的类与对象的描述,用于指导开发者如何设计和实现软件,从而避免重复造轮子,提高开发效率和软件质量;
2、使用场景:涵盖了多个方面,包括但不限于资源管理、对象创建、事件处理、消息通知、算法选择、文件解析等等;
3、优点:提高代码可重用性、增加代码的可读性和维护性、减少开发工作量、适应需求变化的能力
缺点:增加了代码复杂性以及学习成本、可能导致请求的处理链过长,难于定位错误等等,不过好像我们现实生活中存在的事物,都有两面性,看你出发的点权衡利弊,做出选择
二、我们先来看一下常用的设计模式分类
设计模式可以分为三大类别:创建型模式、结构型模式、行为型模式,
1、创建型模式:抽象工厂模式、工厂方法模式、建造者模式、原型模式、单例模式,总计5种
2、结构型模式:适配器模式、组合模式、外观模式、桥接模式、装饰器模式,总计5种
3、行为型模式:责任链模式、命令模式、解释器模式、迭代器模式、中介者模式、备忘录模式、观察者模式、状态模式、策略模式、模版方法模式、访问者模式,总计11种
4、J2EE模式:MVC模式、业务代表模式,23种设计模式全在这了,小伙伴们注意查收
三、设计模式的使用
1、抽象工厂模式:它提供了一种创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定其具体类。
流程图如下
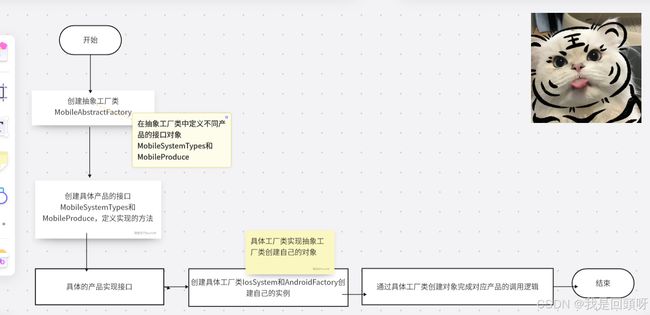
以下是流程图的关键步骤:
- 开始:流程的起点。
- 创建抽象工厂接口MobileAbstractFactory:定义抽象工厂的接口,用于创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象。
- 创建具体工厂IosFactory接口和具体工厂AndroidFactory接口:定义具体工厂的接口,它们将实现抽象工厂接口。
- 创建抽象产品MobileSystemTypes接口和抽象产品接口MobileProduce:定义抽象产品的接口,具体产品将实现这些接口。
- 具体工厂IosFactory实现抽象工厂接口MobileAbstractFactory:具体工厂实现抽象工厂接口,并负责创建具体产品IosSystemProduce、IosSystem。
- 具体工厂AndroidFactory实现抽象工厂接口MobileAbstractFactory:具体工厂实现抽象工厂接口,并负责创建具体产品AndroidSystem、AndroidSystemProduce。
- 客户端代码使用抽象工厂:客户端代码通过抽象工厂接口创建具体工厂,并通过具体工厂创建具体产品。
- 结束:流程的终点。
注意,这只是一个抽象的流程图描述,每个人的想法不一样,实际的流程图可能需要根据具体的实现细节进行调整。
代码实现如下:
a 创建抽象工厂类:MobileAbstractFactory
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
//手机抽象工厂类
public interface MobileAbstractFactory {
//系统分类
MobileSystemTypes mobileSystemType();
//系统产品分类
MobileProduce mobileProduce();
}
b 创建具体工厂IosFactory接口和具体工厂AndroidFactory接口实现抽象工厂接口MobileAbstractFactory
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 苹果具体工厂
*/
public class IosFactory implements MobileAbstractFactory{
@Override
public MobileSystemTypes mobileSystemType() {
return new IosSystem();
}
@Override
public MobileProduce mobileProduce() {
return new IosSystemProduce();
}
}
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
public class AndroidFactory implements MobileAbstractFactory {
@Override
public MobileSystemTypes mobileSystemType() {
return new AndroidSystem();
}
@Override
public MobileProduce mobileProduce() {
return new AndroidSystemProduce();
}
}
c 创建抽象产品MobileSystemTypes接口和抽象产品接口MobileProduce
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 手机系统种类接口
*/
public interface MobileSystemTypes{
/**
* 获取系统种类
*/
void getSystem();
}
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 手机产品具体工厂
*/
public interface MobileProduce {
/**
* 手机系统分类产品
*/
void getProduce();
}
d 定义抽象产品MobileSystemTypes接口和抽象产品接口MobileProduce具体实现接口
抽象产品MobileSystemTypes接口具体实现类
安卓系统
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 具体实现安卓系统
*
*/
public class AndroidSystem implements MobileSystemTypes{
@Override
public void getSystem() {
System.out.println("我是安卓系统!!!");
}
}
ios系统
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* ios系统
*/
public class IosSystem implements MobileSystemTypes{
@Override
public void getSystem() {
System.out.println("我是IOS系统!!!!");
}
}
抽象产品接口MobileProduce具体类
安卓类产品
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 我是安卓类产品
*/
public class AndroidSystemProduce implements MobileProduce {
@Override
public void getProduce() {
System.out.println("我是安卓款的电子产品!!!");
}
}
IOS款的电子产品
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
/**
* 我是IOS系统产品
*/
public class IosSystemProduce implements MobileProduce {
@Override
public void getProduce() {
System.out.println("我是IOS款的电子产品!!!");
}
}
e 客户端代码使用抽象工厂
package org.storemanage.regestercenter.designmode;
public class TestAbstractFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 安卓产品
*/
MobileAbstractFactory androidFactory = new AndroidFactory();
MobileSystemTypes mobileSystemTypes = androidFactory.mobileSystemType();
MobileProduce mobileProduce = androidFactory.mobileProduce();
mobileProduce.getProduce();
mobileSystemTypes.getSystem();
System.err.println("-------------分割线-------------------------------");
/**
* 苹果产品
*/
MobileAbstractFactory iosFactory = new IosFactory();
MobileProduce iosMobileProduce = iosFactory.mobileProduce();
MobileSystemTypes iosMobileSystemTypes1 = iosFactory.mobileSystemType();
iosMobileProduce.getProduce();
iosMobileSystemTypes1.getSystem();
}
}
到这里抽象工厂模式已完成啦,有不足欢迎指出,共同进步,谢谢

后面设计模式持续更新中----------------------------------