大厂必备的加解密算法分析与应用场景
加解密算法分析与应用场景
在日常开发中,无论是使用何种编程语言,我们都会遇到加解密的需求。例如,为了保护接口数据安全,我们需要对数据进行加密传输;在HTTPS协议中,通过非对称加密传输客户端私钥,然后双方使用该私钥进行对称加密通信;使用MD5算法进行文件一致性校验等。然而,面对众多的加解密方案,我们往往不清楚何时使用哪种方法。本文将为您梳理当前主流的加解密技术,并对算法进行科普性说明,但不涉及具体算法分析。根据日常应用场景,加解密技术大致可分为以下四类:
散列函数(信息摘要)算法
- 应用场景:密码存储、文件完整性校验等。
- 示例:MD5、SHA-1、SHA-256。
对称加密算法
- 应用场景:数据加密传输、数据库加密存储等。
- 示例:AES、DES、3DES、RC4。
非对称加密算法
- 应用场景:安全证书、数字签名、密钥交换等。
- 示例:RSA、ECC(椭圆曲线加密)、ElGamal。
组合加密技术
- 应用场景:综合使用多种加密技术,提高安全性。
- 示例:SSL/TLS协议(结合了对称加密、非对称加密和散列函数)。
散列函数(信息摘要)算法
散列函数特点
散列函数(又称信息摘要算法)是一种将任意长度的输入数据映射到固定长度输出的算法。
- 输入敏感:输入数据的任何微小变化都会导致输出结果的巨大变化。
- 唯一性:对于不同的输入数据,散列函数的输出结果几乎不会相同。
- 不可逆性:从输出结果无法直接推导出输入数据。
- 耗时性:计算散列值需要一定的计算时间。
散列函数应用
- 密码存储:将用户密码通过散列函数计算得到散列值,然后将散列值存储在数据库中。当用户登录时,再次计算输入密码的散列值并与数据库中的散列值进行比较,以验证密码是否正确。
- 文件完整性校验:通过散列函数计算文件的散列值,并将其与文件发送方提供的散列值进行比较。如果散列值相同,说明文件在传输过程中未被篡改。
- 数字签名:在数据传输过程中,发送方使用散列函数计算数据的散列值,然后使用自己的私钥对散列值进行加密。接收方使用发送方的公钥解密散列值,并与数据的散列值进行比较。如果相同,说明数据未被篡改。
散列常见的函数
- MD5:是一种广泛使用的散列函数,生成128位散列值。然而,由于其安全性较低,现已被更安全的散列函数所取代。
- SHA-1:SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm)家族中的一种散列函数,生成160位散列值。相对于MD5,SHA-1安全性更高,但仍然存在被碰撞攻击的风险。
- SHA-256:SHA-2家族中的一种散列函数,生成256位散列值。相较于SHA-1,SHA-256安全性更高,目前被广泛应用。
MD5
MD5(Message-Digest Algorithm 5)是一种广泛使用的散列函数,它生成一个128位(16字节)的散列值。MD5的主要特点是输入敏感、唯一性高、不可逆性和耗时性。然而,由于其安全性较低,现已被更安全的散列函数(如SHA-1、SHA-256)所取代。
用途
- 密码存储:将用户密码通过MD5计算得到散列值,然后将散列值存储在数据库中。当用户登录时,再次计算输入密码的散列值并与数据库中的散列值进行比较,以验证密码是否正确。
- 文件完整性校验:通过MD5计算文件的散列值,并将其与文件发送方提供的散列值进行比较。如果散列值相同,说明文件在传输过程中未被篡改。
Java示例
我们使用Java的MessageDigest类计算输入字符串的MD5散列值。需要注意的是,由于MD5的安全性较低,现已被更安全的散列函数(如SHA-256)所取代。在实际应用中,建议使用更安全的散列函数。
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class MD5Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "Hello, world!";
String md5Hash = getMD5Hash(input);
System.out.println("MD5 Hash: " + md5Hash);
}
public static String getMD5Hash(String input) {
try {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] messageDigest = md.digest(input.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
BigInteger number = new BigInteger(1, messageDigest);
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder(number.toString(16));
// 补齐16位
while (hexString.length() < 32) {
hexString.insert(0, '0');
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
SHA 系列算法
SHA系列算法是一组常用的密码学哈希函数,包括SHA-1、SHA-2和SHA-3三个变种。这些哈希算法可以将任意长度的输入数据转换为固定长度的哈希值,通常用于密码学应用,如数据完整性验证、数字签名等。
SHA-1算法的设计原理是基于MD4、MD5等哈希算法的经验,它采用了类似于MD4的思路,将输入数据划分为512位的消息块,并使用一个160位的中间状态来计算输出。然而,由于SHA-1存在一些安全弱点,如哈希碰撞攻击,因此,SHA-2被广泛使用。SHA-2算法家族包括SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384、SHA-512、SHA-512/224和SHA-512/256六种变体。SHA-2算法采用了新的压缩函数,使得其更加安全和高效。SHA-2算法的底层原理是基于Merkle–Damgrd结构,它将输入数据划分为512位的消息块,并使用一个中间状态来计算输出。SHA-2的哈希值长度可以是224、256、384或512比特,越长的哈希值通常意味着更高的安全性。
SHA-3算法是一种新的密码学哈希函数,它不同于SHA-1和SHA-2,它采用了Keccak算法作为其内部压缩函数。SHA-3算法家族包括多个变体,其中SHA-3-256是其其中之一,它产生一个256位的哈希值。与SHA-2类似,SHA-3也采用了Merkle–Damgrd结构来计算哈希值,但是采用了新的压缩函数。
下面是一个表格,展示了SHA系列算法的主要特性对比:
| 算法名称 | 输出长度(位) | 消息块长度(位) | 安全性 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHA-1 | 160 | 512 | 中等 | 已不推荐使用,存在安全漏洞 |
| SHA-224 | 224 | 512 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,更安全的变种 |
| SHA-256 | 256 | 512 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,广泛使用的变种 |
| SHA-384 | 384 | 1024 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,使用1024位块处理更大的消息 |
| SHA-512 | 512 | 1024 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,提供最大的输出长度 |
| SHA-512/224 | 224 | 1024 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,是SHA-512的一个裁剪版本 |
| SHA-512/256 | 256 | 1024 | 高 | 属于SHA-2系列,是SHA-512的一个裁剪版本 |
| SHA3-224 | 224 | 不定长 | 高 | 属于SHA-3系列,使用Keccak算法 |
| SHA3-256 | 256 | 不定长 | 高 | 属于SHA-3系列,使用Keccak算法,推荐使用 |
| SHA3-384 | 384 | 不定长 | 高 | 属于SHA-3系列,使用Keccak算法 |
| SHA3-512 | 512 | 不定长 | 高 | 属于SHA-3系列,使用Keccak算法 |
请注意,"不定长"的消息块长度意味着SHA-3算法可以处理不同大小的消息块,而无需像SHA-1和SHA-2那样固定为512位或1024位。此外,随着密码学的发展,SHA-1已被认为不再安全,因此不建议在新的应用中使用。SHA-2和SHA-3是目前推荐的哈希算法,其中SHA-256和SHA-3-256是最常用的变种。
SHA-256 经典示例
我们使用Java的MessageDigest类来创建SHA-256摘要算法实例。然后,我们将原始字符串转换为字节数组,并调用digest方法来计算SHA-256摘要。最后,我们将得到的字节数组转换为十六进制字符串表示,作为SHA-256摘要的结果。
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public class SHAExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String originalString = "Hello, world!";
String sha256Hash = getSHA256(originalString);
System.out.println("SHA-256 Hash of '" + originalString + "': " + sha256Hash);
}
public static String getSHA256(String input) {
try {
// 创建SHA-256摘要算法实例
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
// 将输入字符串转换为字节数组,并计算SHA-256摘要
byte[] messageDigest = md.digest(input.getBytes());
// 将字节数组转换为十六进制字符串表示
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : messageDigest) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// 如果指定的SHA-256算法不存在,处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
对称加密算法
对称加密算法是一种加密和解密使用相同密钥的加密算法。在对称加密算法中,加密和解密过程都使用相同的密钥,因此它们通常被称为“对称”的。对称加密算法的主要优点是加密和解密速度快,适用于大量数据的加密和传输。然而,对称加密算法的主要缺点是密钥管理和分发,因为在通信双方之间共享密钥可能会导致密钥泄露。
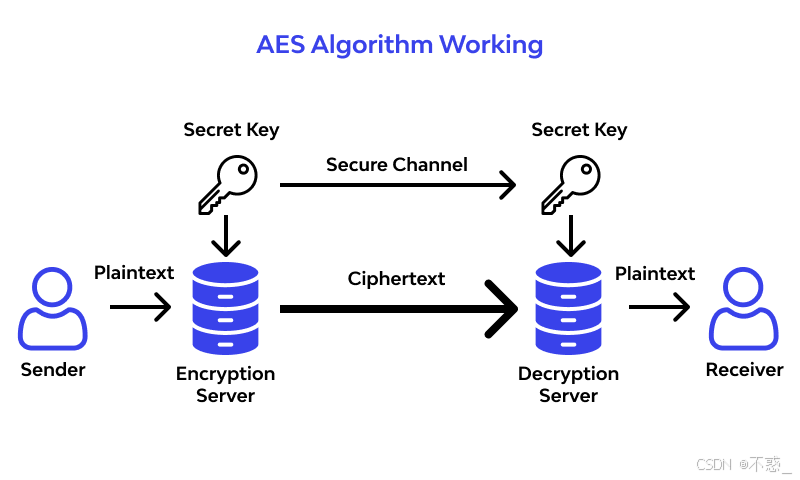
常见对称加密算法
- DES(Data Encryption Standard):DES是一种较早的对称加密算法,它使用56位密钥和64位数据块。DES已经被认为不再安全,因为它的密钥长度太短,容易受到暴力破解攻击。
- 3DES(Triple DES):3DES是DES的一个变种,它使用三次DES加密操作来提高安全性。3DES使用112位或168位密钥,分别对应于双长密钥(2TDEA)和三长密钥(3TDEA)。虽然3DES比DES更安全,但它的加密速度较慢,且仍然容易受到攻击。
- AES(Advanced Encryption Standard):AES是一种广泛使用的对称加密算法,它使用128位、192位或256位密钥,并支持128位数据块。AES已经成为密码学领域的标准,因为它具有较高的安全性和性能。AES的加密和解密过程都使用相同的密钥,因此它是一种对称加密算法。
- RC4(Rivest Cipher 4):RC4是一种流密码算法,它使用一个密钥流来加密和解密数据。RC4使用一个简单的密钥调度算法来生成密钥流,然后将其与明文或密文进行异或操作。RC4的主要优点是速度快,但它的安全性较低,容易受到攻击。
- Blowfish:Blowfish是一种对称加密算法,它使用一个可变长度的密钥(最小为32位,最大为448位)和64位数据块。Blowfish使用一种名为“Feistel网络”的结构来实现加密和解密操作。虽然Blowfish的安全性较高,但它的性能较低,且已经被更现代的加密算法(如AES)所取代。
DES(Data Encryption Standard)
DES是一种较早的对称加密算法,它使用56位密钥和64位数据块。DES已经被认为不再安全,因为它的密钥长度太短,容易受到暴力破解攻击。
ִ໋͙֒ 作用
DES主要用于加密和解密数据,它使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密操作。
ִ໋͙֒ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Base64;
public class DESExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
String key = "12345678"; // DES密钥长度为8字节
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "DES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
// 加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String encryptedText = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedText);
// 解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedText));
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
3DES(Triple DES)
3DES是DES的一个变种,它使用三次DES加密操作来提高安全性。3DES使用112位或168位密钥,分别对应于双长密钥(2TDEA)和三长密钥(3TDEA)。虽然3DES比DES更安全,但它的加密速度较慢,且仍然容易受到攻击。
ִ໋͙֒ 作用
3DES主要用于加密和解密数据,它使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密操作。
ִ໋͙֒ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Base64;
public class TripleDESExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
String key = "1234567812345678"; // 3DES密钥长度为16字节
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "DESede");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede");
// 加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String encryptedText = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedText);
// 解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedText));
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
AES(Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES是一种广泛使用的对称加密算法,它使用128位、192位或256位密钥,并支持128位数据块。AES已经成为密码学领域的标准,因为它具有较高的安全性和性能。AES的加密和解密过程都使用相同的密钥,因此它是一种对称加密算法。
ִ໋͙֒ 作用
AES主要用于加密和解密数据,它使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密操作。
ִ໋͙֒ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Base64;
public class AESExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
String key = "123456789012345"; // AES密钥长度为16字节
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
// 加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String encryptedText = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedText);
// 解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedText));
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
RC4(Rivest Cipher 4)
RC4是一种流密码算法,它使用一个密钥流来加密和解密数据。RC4使用一个简单的密钥调度算法来生成密钥流,然后将其与明文或密文进行异或操作。RC4的主要优点是速度快,但它的安全性较低,容易受到攻击。
ִ໋͙֒ 作用
RC4主要用于加密和解密数据,它使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密操作。
ִ໋͙֒ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Base64;
public class RC4Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
String key = "123456789012345"; // RC4密钥长度为16字节
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "RC4");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RC4");
// 加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String encryptedText = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedBytes);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedText);
// 解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey);
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedText));
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
Blowfish
Blowfish是一种对称加密算法,它使用一个可变长度的密钥(最小为32位,最大为448位)和64位数据块。Blowfish使用一种名为“Feistel网络”的结构来实现加密和解密操作。虽然Blowfish的安全性较高,但它的性能较低,且已经被更现代的加密算法(如AES)所取代。
ִ໋͙֒ 作用
Blowfish主要用于加密和解密数据,它使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密操作。
ִ໋͙֒ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
public class BlowfishExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String originalText = "Hello, world!"; // 原始文本
String keyString = "myblowfishkey1234"; // 密钥字符串(16字节)
// 将密钥字符串转换为 SecretKey 对象
byte[] keyData = keyString.getBytes();
SecretKey key = new SecretKeySpec(keyData, "Blowfish");
// 创建 Cipher 实例并初始化为加密模式
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("Blowfish/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
// 加密数据
byte[] encryptedData = cipher.doFinal(originalText.getBytes());
// 将加密后的数据转换为 Base64 字符串,用于存储或传输
String encryptedBase64 = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedData);
System.out.println("Encrypted: " + encryptedBase64);
}
}
非对称加密
非对称加密,也称为公钥密码学,是一种加密和解密使用不同密钥的加密技术。在这种系统中,有两个不同的密钥:一个公钥和一个私钥。公钥是公开的,任何人都可以使用它来加密数据,但只有私钥的持有者才能解密这些数据。这种加密技术的关键优势在于不需要安全地交换密钥就可以实现加密通信。
非对称加密算法的工作原理通常涉及到复杂的数学问题,如大数因子分解(如RSA算法)或椭圆曲线上的离散对数问题(如ECC算法)。这些问题被设计得非常困难,以至于在当前的计算能力下,即使知道加密算法和加密后的数据,也无法在没有相应私钥的情况下解密数据。
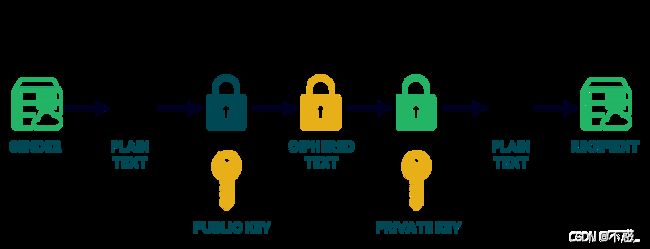
常见非对称加密算法
- RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman):RSA是最早和最广泛使用的非对称加密算法之一。它基于大数因子分解的困难性。RSA算法可以用于加密数据,也常用于数字签名和密钥交换。
- ECC(Elliptic Curve Cryptography):ECC利用椭圆曲线上的离散对数问题来提供加密服务。与RSA相比,ECC通常使用较小的密钥长度就能提供相同级别的安全性,因此在特定情况下更加高效。
- ElGamal:ElGamal是一种基于离散对数问题的非对称加密算法。它可以用于加密和数字签名,其安全性依赖于密钥的长度。
- DSA(Digital Signature Algorithm):DSA专门用于数字签名,而不是加密。它也基于离散对数问题,并且通常与RSA或ECC一起使用,以提供完整的加密和认证解决方案。
非对称与对称加密算法对比
非对称加密算法与对称加密算法是两种不同的加密技术,它们在加密和解密方法、密钥管理、安全性和速度等方面存在显著差异。
加密和解密方法
- 对称加密:使用单一密钥进行加密和解密。发送方和接收方共享相同的密钥,这使得加密和解密过程相对简单,但同时也带来了密钥管理的挑战。
- 非对称加密:使用一对密钥,即公钥和私钥。公钥用于加密数据,私钥用于解密数据。由于公钥和私钥是分开的,这增加了数据的安全性,但加密和解密过程相对复杂。
密钥管理
- 对称加密:密钥需要在通信双方之间进行安全地共享,这可能导致安全风险,因为密钥的泄露或未经授权的访问可能导致数据泄露。
- 非对称加密:公钥可以公开分发,而私钥必须保密。这消除了最终用户交换密钥的需要,降低了密钥泄露的风险。
安全性
- 对称加密:安全性依赖于密钥的保密性。由于使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密,如果密钥被泄露,那么数据的安全性将受到威胁。
- 非对称加密:提供了更高级别的安全性。由于私钥是保密的,只有接收方知道,所以即使攻击者获得了公钥,也无法解密数据。
速度
- 对称加密:由于使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密,速度较快,适用于大规模数据的传输和处理。
- 非对称加密:由于密钥生成和数学计算的复杂性,速度较慢。
非对称加密工作原理
非对称加密是一种加密技术,它使用一对密钥,即公钥和私钥,来实现信息的加密和解密。这两个密钥是通过数学算法生成的,具有特定的数学关系,但它们是独立且不同的。
在非对称加密的工作原理中,公钥用于加密信息,而私钥用于解密信息。这意味着,只要拥有公钥的人都可以对信息进行加密,但只有拥有对应私钥的人才能解密这些加密后的信息。
以电子邮件通信为例,假设Alice想要向Bob发送一条加密信息。首先,Bob会生成一对公钥和私钥,并将公钥发送给Alice。然后,Alice使用Bob的公钥对信息进行加密,并将加密后的信息发送回Bob。最后,Bob使用自己的私钥对加密信息进行解密,以获取原始信息。
非对称加密的一个重要特点是,公钥可以被公开分发,而私钥必须保密。这是因为,即使公钥被截获,由于没有对应的私钥,攻击者也无法解密信息。这种安全性使得非对称加密在许多安全通信场景中得到了广泛应用,如HTTPS、SSL/TLS等。
常见的非对称加密算法包括RSA、Diffie-Hellman和ECC(椭圆曲线密码学)。这些算法都利用了数学上的困难问题,如大数分解、离散对数和椭圆曲线上的离散对数问题,来确保加密和解密过程的安全性。
在Java中,非对称加密算法通常使用
java.security包中的类和接口来实现
RSA
RSA是一种基于大数因子分解的非对称加密算法。它使用一对密钥,即公钥和私钥。公钥用于加密数据,私钥用于解密数据。RSA算法广泛应用于安全通信和数字签名。
作用
RSA主要用于加密和解密数据,以及生成和验证数字签名。
Java示例
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
public class RSAExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成RSA密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); // 设置密钥长度为2048位
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 使用公钥加密数据
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
byte[] encryptedData = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes());
// 使用私钥解密数据
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedData = cipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedData);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedData);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
ECC
ECC(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是一种基于椭圆曲线上的离散对数问题的非对称加密算法。与RSA相比,ECC通常使用较小的密钥长度就能提供相同级别的安全性,因此在特定情况下更加高效。
作用
ECC主要用于加密和解密数据,以及生成和验证数字签名。
Java示例
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
public class ECCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成ECC密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("EC");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(256); // 设置密钥长度为256位
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 使用公钥加密数据
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("ECIES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
byte[] encryptedData = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes());
// 使用私钥解密数据
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedData = cipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedData);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedData);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
ElGamal
ElGamal是一种基于离散对数问题的非对称加密算法。它使用一对密钥,即公钥和私钥。公钥用于加密数据,私钥用于解密数据。ElGamal算法广泛应用于安全通信和数字签名。
作用
ElGamal主要用于加密和解密数据,以及生成和验证数字签名。
Java示例
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
public class ElGamalExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成ElGamal密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("ElGamal");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); // 设置密钥长度为2048位
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 使用公钥加密数据
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("ElGamal");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
byte[] encryptedData = cipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes());
// 使用私钥解密数据
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedData = cipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedData);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedData);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
DSA
DSA(Digital Signature Algorithm)是一种基于离散对数问题的非对称加密算法。它主要用于数字签名,而不是加密。DSA算法广泛应用于安全通信和数字签名。
作用
DSA主要用于生成和验证数字签名。
Java示例
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.Signature;
public class DSAExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成DSA密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); // 设置密钥长度为2048位
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 使用私钥签名数据
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withDSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
signature.update(plaintext.getBytes());
byte[] signatureBytes = signature.sign();
// 使用公钥验证签名
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(plaintext.getBytes());
boolean isVerified = signature.verify(signatureBytes);
System.out.println("Signature: " + signatureBytes);
System.out.println("Is signature verified: " + isVerified);
}
}
组合加密技术
组合加密是一种结合了多种加密技术的加密策略,旨在提高数据传输和存储的安全性。这种方法通常涉及使用对称加密和非对称加密算法的组合,以及其他可能的增强措施,如密钥交换协议、数字签名和消息认证码(MACs)。
组合加密的常见做法
- 密钥交换:使用非对称加密算法(如Diffie-Hellman或RSA)安全地交换对称加密算法的密钥。这样,即使在不安全的通道上,也可以建立一个只有通信双方知道的共享秘密密钥。
- 数字签名:使用非对称加密算法(如RSA或ECDSA)对消息进行签名,以确保消息的完整性和来源的真实性。签名通常与消息一起发送,并由接收方使用发送方的公钥进行验证。
- 消息认证码(MAC):使用对称加密算法或专门的MAC算法(如HMAC)来验证消息的完整性。MAC通常与消息一起发送,并由接收方使用相同的密钥和算法进行验证。
- 混合加密系统:在这种系统中,非对称加密用于密钥交换和/或数字签名,而对称加密用于加密大量的数据。这种方法结合了非对称加密的安全性和对称加密的高效性。
示例流程
- 密钥交换:Alice和Bob使用非对称加密算法(如Diffie-Hellman)生成并交换公共参数,从而建立一个共享的秘密密钥。
- 数据加密:Alice使用这个共享的秘密密钥和对称加密算法(如AES)来加密她的消息。
- 数字签名:Alice使用她的私钥和非对称加密算法(如RSA)对加密后的消息进行签名。
- 消息传输:Alice将加密的消息和数字签名一起发送给Bob。
- 验证和解密:Bob使用Alice的公钥验证数字签名,确认消息的完整性和来源。然后,他使用之前交换的共享秘密密钥和对称加密算法来解密消息。
在Java中,组合加密算法通常使用**
javax.crypto**包中的类和接口来实现
RSA-AES
RSA-AES是一种常见的组合加密算法,它结合了RSA和AES加密算法。RSA用于密钥交换和数字签名,而AES用于加密和解密数据。
️ 作用
RSA-AES主要用于加密和解密数据,以及生成和验证数字签名。
️ Java示例
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.Signature;
import java.util.Base64;
public class RSA_AESExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成RSA密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(2048); // 设置密钥长度为2048位
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 生成AES密钥
KeyGenerator aesKeyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
aesKeyGenerator.init(256); // 设置密钥长度为256位
SecretKey aesKey = aesKeyGenerator.generateKey();
// 使用AES密钥加密数据
Cipher aesCipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
aesCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, aesKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
byte[] encryptedData = aesCipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes());
// 使用RSA公钥加密AES密钥
Cipher rsaCipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
rsaCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] encryptedAESKey = rsaCipher.doFinal(aesKey.getEncoded());
// 使用RSA私钥解密AES密钥
rsaCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedAESKey = rsaCipher.doFinal(encryptedAESKey);
SecretKeySpec decryptedAESKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(decryptedAESKey, "AES");
// 使用解密后的AES密钥解密数据
aesCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, decryptedAESKeySpec);
byte[] decryptedData = aesCipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedData);
// 使用RSA私钥签名数据
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(plaintext.getBytes());
byte[] signatureBytes = signature.sign();
// 使用RSA公钥验证签名
signature.initVerify(publicKey);
signature.update(plaintext.getBytes());
boolean isVerified = signature.verify(signatureBytes);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedData);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
System.out.println("Signature: " + Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(signatureBytes));
System.out.println("Is signature verified: " + isVerified);
}
}
ECDH-AES
ECDH-AES是一种基于椭圆曲线密码学的组合加密算法,它结合了ECDH(椭圆曲线Diffie-Hellman)和AES加密算法。ECDH用于密钥交换,而AES用于加密和解密数据。
️ 作用
ECDH-AES主要用于加密和解密数据。
️ Java示例
使用Java中的javax.crypto包实现RSA-AES和ECDH-AES组合加密算法。在实际应用中,这些算法通常会结合使用,以实现既安全又高效的通信和数据保护解决方案。
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.spec.ECGenParameterSpec;
public class ECDH_AESExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 生成ECDH密钥对
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("EC");
keyPairGenerator.initialize(new ECGenParameterSpec("secp256r1")); // 设置椭圆曲线为secp256r1
KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// 生成AES密钥
KeyGenerator aesKeyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
aesKeyGenerator.init(256); // 设置密钥长度为256位
SecretKey aesKey = aesKeyGenerator.generateKey();
// 使用AES密钥加密数据
Cipher aesCipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES");
aesCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, aesKey);
String plaintext = "Hello, world!";
byte[] encryptedData = aesCipher.doFinal(plaintext.getBytes());
// 使用ECDH公钥加密AES密钥
Cipher ecdhCipher = Cipher.getInstance("ECIES");
ecdhCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] encryptedAESKey = ecdhCipher.doFinal(aesKey.getEncoded());
// 使用ECDH私钥解密AES密钥
ecdhCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] decryptedAESKey = ecdhCipher.doFinal(encryptedAESKey);
SecretKeySpec decryptedAESKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(decryptedAESKey, "AES");
// 使用解密后的AES密钥解密数据
aesCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, decryptedAESKeySpec);
byte[] decryptedData = aesCipher.doFinal(encryptedData);
String decryptedText = new String(decryptedData);
System.out.println("Encrypted text: " + encryptedData);
System.out.println("Decrypted text: " + decryptedText);
}
}
消息认证码(MAC)算法简介
消息认证码(MAC)是一种加密算法,用于验证消息的完整性和来源。MAC算法通常基于对称加密算法(如AES、DES或3DES)或哈希函数(如SHA-256、SHA-3或HMAC)生成。
️ 作用
MAC主要用于验证消息的完整性和来源。它可以确保消息在传输过程中没有被篡改,并且确保消息的接收者是预期的接收者。
️ Java示例
以下示例展示了如何使用Java中的javax.crypto包和java.security包生成和验证HMAC(基于哈希的消息认证码)。我们首先生成一个密钥(secretKeySpec),然后使用Mac类生成HMAC。接着,我们将生成的MAC与原始消息一起发送。接收方可以使用相同的密钥和算法重新计算MAC,并将其与接收到的MAC进行比较,以验证消息的完整性和来源。
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Base64;
public class MACExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
// 生成密钥
String secret = "mySecretKey";
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "HmacSHA256");
// 创建MAC实例
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
// 生成MAC
String message = "Hello, world!";
byte[] messageBytes = message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] macBytes = mac.doFinal(messageBytes);
String macString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(macBytes);
System.out.println("MAC: " + macString);
// 验证MAC
Mac verificationMac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
verificationMac.init(secretKeySpec);
byte[] verificationMacBytes = verificationMac.doFinal(messageBytes);
boolean isValid = MessageDigest.isEqual(macBytes, verificationMacBytes);
System.out.println("Is MAC valid: " + isValid);
}
}
这个示例展示了如何使用Java中的javax.crypto和java.security包生成和验证HMAC。在实际应用中,MAC算法通常与其他加密技术(如对称加密和非对称加密)结合使用,以提供更强的安全性。
写在最后
在现代软件开发中,加密算法扮演着至关重要的角色。作为一名开发者,我深知加密算法的重要性,并在我的工作中积极采用这些技术来确保数据安全。
首先,我理解加密算法的核心目的是确保信息的机密性、完整性和可用性。这些算法通过复杂的数学运算,将明文数据转换成只有拥有密钥的人才能解读的密文。这种转换确保了未经授权的用户无法访问数据内容,从而保护了数据的隐私。
在使用加密算法时,我会仔细考虑几个关键因素。首先是算法的选择,不同的加密算法有不同的优缺点。例如,对称加密算法如AES因其高性能而被广泛用于大数据量的加密,而非对称加密算法如RSA则因其密钥管理方便而被用于安全通信和数字签名。我会根据项目的具体需求,如数据量大小、通信频率和安全级别,来选择最合适的算法。
其次,密钥管理是加密算法能否发挥效用的关键。我会确保密钥的生成是随机的、安全的,并且在存储和传输过程中受到保护。此外,我还会定期更新密钥,以减少被破解的风险。
合规性也是我使用加密算法时考虑的一个重要方面。随着数据保护法规的日益严格,如欧盟的通用数据保护条例(GDPR),我必须确保我的加密实践符合所有适用的法律和行业标准。
在实际开发中,我会将加密算法集成到软件的架构中,并在不同的环境和条件下进行彻底测试,以确保加密功能的可靠性和安全性。我还会监控最新的安全漏洞和攻击手段,以便及时更新我的加密策略和实践。
加密算法的意义不仅仅在于技术层面。它们为用户提供了信心,让用户相信他们的数据是受到保护的。这对于建立和维护用户信任至关重要。同时,加密算法也是企业保护自己免受数据泄露和其他安全事件影响的有力工具。这不仅有助于维护企业的声誉,还可以避免潜在的法律和财务风险。
总之,作为一名开发者,我认识到加密算法不仅是数据安全的技术基础,也是维护用户信任和业务连续性的关键。我会持续学习和适应最新的加密技术和最佳实践,以确保我的软件产品能够在不断变化的威胁环境中保持安全。