Python学习5
Python标准库
Python标准库是随Python附带安装的。这些模块可以解决大部分的问题。
1.sys模块:包含系统对应的功能。
使用sys.args即命令行参数
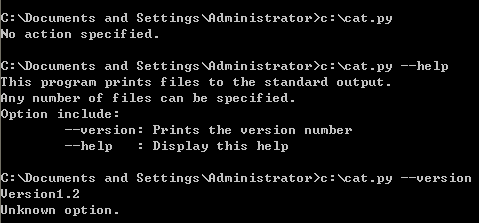
一下代码类似cat功能,命令参数为“--version”或“-help”时,打印相关说明;为文件时,打印其内容。
1 # Filename: cat.py
2 import sys
3 def readfile(filename):
4 '''Print a file to the standard output.'''
5 f = file(filename)
6 while True:
7 line = f.readline()
8 if len(line) == 0:
9 break
10 print line,
11 f.close()
12
13 # scripts start from here
14 if len(sys.argv) < 2:
15 print 'No action specified.'
16 sys.exit()
17 if sys.argv[1].startswith('--'):
18 option = sys.argv[1][2:]
19 #fetch sys.argv[1] but without the first two characters
20 if option == 'version':
21 print 'Version1.2'
22 if option == 'help':
23 print '''\
24 This program prints files to the standard output.
25 Any number of files can be specified.
26 Option include:
27 --version: Prints the version number
28 --help : Display this help'''
29 else:
30 print 'Unknown option.'
31 sys.exit()
32 else:
33 for filename in sys.argv[1]:
34 readfile(filename)
此外,值得关注的还有:sys.version, sys.version_info, sys.stdin, sys.stdout, sys.stderr
2.os模块:包含普遍的操作系统的功能。“普遍”即这个模块与平台无关。
os.seq代表系统路径分隔符
os.name代表使用的系统名称
os.getcwd()得到当前工作目录
os.getnv() os.setnv()读取和设置环境变量
os.listdir()返回指定目录下的所有文件盒目录名
os.remove()删除一个文件
os.system()运行shell命令
os.linesep字符串给出当前平台使用的行终止符。windows使用'\r\n', linux使用'\n',mac使用'\r'
os.path.split()返回一个路径的目录名和文件名。(元组)
os.path.isfile() os.path.isdir() 检验路径是否文件 目录
os.path.existe()检验路径是否真实存在
特殊的方法
前已提及,__init__ 和__del__是两个特殊方法
一般来说,特殊方法用来模仿某个行为(这听起来像是接口)
__init__(self,...) 这个方法在新建对象时,返回之前被调用
__del__(self)对象删除之前被调用
__str__(self)对象使用print语句或使用str()时调用
__lt__(self, other)小于运算符时调用。类似地,还有> +等等
__getitem__(self, key) 使用x[key]索引操作符时调用
__len__(self)对象使用内建的len()时调用
列表综合
列表之间的映射。已有列表经过运算得到新列表。
1 # Filename: list_comprehension.py
2 listone = [2, 3, 4]
3 listtwo = [2*i for i in listone if i > 2]
4 print listtwo
测试结果:
>>>
[6, 8]
函数接收多余的参数
参数加上*前缀,多余的参数形成元组。
参数加上**前缀,多余的参数形成键值对。
lambda形式
lambda语句创建新的函数对象,并且在运行时返回他们。
lambda 需要一个参数,后面跟一个表达式,表达式的值被这个新建的函数返回。
1 # Filename: lambda.py
2 def make_repeater(n):
3 return lambda s: s*n
4 twice = make_repeater(2)
5 print twice('word')
6 print twice(5)
测试结果:
>>>
wordword
10
exec语句和eval语句
exec语句用来执行存储在字符串或文件中的Python语句。
>>> exec 'print "Hello world"'
Hello world
>>>
>>> eval('2*3')
6
assert语句
用来声明某个条件是真的。当assert语句失败时,会引发一个AssertionError。
>>> mylist = ['item']
>>> assert len(mylist) >= 1
>>> mylist.pop()
'item'
>>> assert len(mylist) >= 1
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module>
assert len(mylist) >= 1
AssertionError
>>>
repr函数
repr函数用来取得对象的规范字符串表示(``可以完成相同功能),linux中shell也有类似用法。