BFS中的双向广搜和A-star
双向广搜
双向广搜一般用于最小步数模型
双向搜索,就是在起点搜索的过程,终点也在往回搜,从而达到优化的效果。
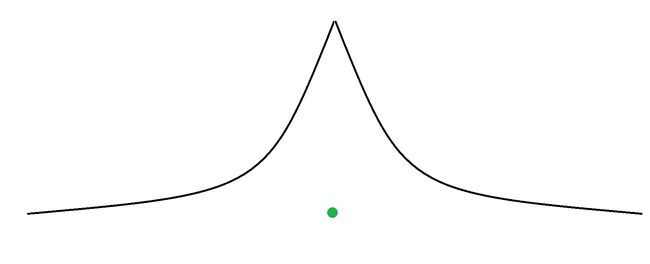
普通搜索:(绿色点为终点)
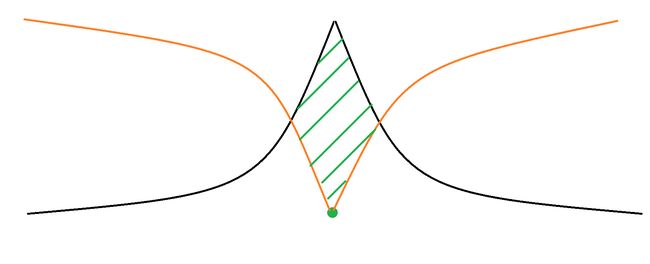
双向搜索:
大家可以发现,双向搜索的大小非常小,所以已知起点和终点状态的搜索尽量用双向搜索。
190. 字串变换
已知有两个字串 A A A, B B B 及一组字串变换的规则(至多 6 6 6 个规则):
A 1 → B 1 A_1→B_1 A1→B1
A 2 → B 2 A_2→B_2 A2→B2
…
规则的含义为:在 A A A 中的子串 A 1 A_1 A1 可以变换为 B 1 B_1 B1、 A 2 A_2 A2 可以变换为 B 2 B_2 B2…。
例如: A A A=abcd B B B=xyz
变换规则为:
abc → xu ud → y y → yz
则此时, A A A 可以经过一系列的变换变为 B B B,其变换的过程为:
abcd → xud → xy → xyz
共进行了三次变换,使得 A A A 变换为 B B B。
注意,一次变换只能变换一个子串,例如 A A A=aa B B B=bb
变换规则为:
a → b
此时,不能将两个 a 在一步中全部转换为 b,而应当分两步完成。
输入格式
输入格式如下:
A A A B B B
A 1 A_1 A1 B 1 B_1 B1
A 2 A_2 A2 B 2 B_2 B2
… …
第一行是两个给定的字符串 A A A 和 B B B。
接下来若干行,每行描述一组字串变换的规则。
所有字符串长度的上限为 20 20 20。
输出格式
若在 10 10 10 步(包含 10 10 10 步)以内能将 A A A 变换为 B B B ,则输出最少的变换步数;否则输出 NO ANSWER!。
输入样例:
abcd xyz
abc xu
ud y
y yz
输出样例:
3
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int N = 6;
int n;
string A, B, a[N], b[N];
int extend(queue &qa, unordered_map &da, unordered_map &db, string a[], string b[]){
int d=da[qa.front()];
while (qa.size()&&da[qa.front()]==d){ //保持遍历同一层
string t = qa.front();
qa.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(t.substr(i, a[j].size()) == a[j]){
string tt = t.substr(0, i) + b[j] + t.substr(i + a[j].size());
if(db.count(tt)) return 1 + da[t] + db[tt];
if(da.count(tt)) continue;
qa.push(tt);
da[tt] = da[t] + 1;
}
}
}
}
return 11;
}
int bfs(){
queue qa, qb;
unordered_map da, db;
qa.push(A), qb.push(B);
da[A] = 0, db[B] = 0;
int step = 0;
while(qa.size() && qb.size()){
int t;
if(qa.size() <= qb.size()) t = extend(qa, da, db, a, b);
else t = extend(qb, db, da, b, a);
if(t <= 10) return t;
if(++step == 10) return 11; // 如果遍历了10层还没找到直接返回
}
return 11;
}
int main(){
cin >> A >> B;
while(cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) n++;
if(A == B){
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
int step = bfs();
if(step > 10) puts("NO ANSWER!");
else cout << step << endl;
return 0;
}
此题数据加强了,添加遍历层数进行优化,每次取出相同层的所有点进行扩展,如果到达 10 10 10 层后还未找到就直接返回
A*
做法:
- 引入一个估值函数,用来估计某个点到达终点的距离。
- 记 f f f 是估值函数, g g g 是真实值,那么 f ( s t a t e ) < = g ( s t a t e ) f(state) <= g(state) f(state)<=g(state),越接近越好(当估值是 0 0 0 时,类似于
Dijkstra算法) - 记 d i s t dist dist 是从起点到 s t a t e state state 状态的步数;
- 利用的是优先队列,排序依据是 d i s t [ s t a t e ] + f ( s t a t e ) dist[state] + f(state) dist[state]+f(state)
证明:(反证法)
- 假设终点第一次出堆时不是最小值,那么意味着 $dist[end] > dist $优
- 那么说明堆中存在一个最优路径中的某个点(起码起点在路径上),记该点为 u u u,
- d i s t 优 dist优 dist优 = d i s t [ u ] + g ( u ) > = d i s t [ u ] + f ( u ) = dist[u] + g(u) >= dist[u] + f(u) =dist[u]+g(u)>=dist[u]+f(u)
- − > d i s t [ e n d ] > d i s t 优 > = d i s t [ u ] + f ( u ) -> dist[end] > dist优 >= dist[u] + f(u) −>dist[end]>dist优>=dist[u]+f(u),说明优先队列中存在一个比出堆元素更小的值,这就矛盾了。
- 所以说终点第一次出堆时就是最优的。
应用的环境:
- 有解(无解时,仍然会把所有空间搜索,会比一般的
bfs慢,因为优先队列的操作是 l o g n logn logn 的) - 边权非负,如果是负数,那么终点的估值有可能是负无穷,终点可能会直接出堆
性质:除了终点以外的其他点无法在出堆或者入堆的时候确定距离,只能保证终点出堆时是最优的可以。
179. 八数码
在一个 3 × 3 3×3 3×3 的网格中, 1 ∼ 8 1∼8 1∼8 这 8 8 8 个数字和一个 x 恰好不重不漏地分布在这 3 × 3 3×3 3×3 的网格中。
例如:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
在游戏过程中,可以把 x 与其上、下、左、右四个方向之一的数字交换(如果存在)。
我们的目的是通过交换,使得网格变为如下排列(称为正确排列):
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 x
例如,示例中图形就可以通过让 x 先后与右、下、右三个方向的数字交换成功得到正确排列。
交换过程如下:
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
x 4 6 4 x 6 4 5 6 4 5 6
7 5 8 7 5 8 7 x 8 7 8 x
把 x 与上下左右方向数字交换的行动记录为 u、d、l、r。
现在,给你一个初始网格,请你通过最少的移动次数,得到正确排列。
输入格式
输入占一行,将 3 × 3 3×3 3×3 的初始网格描绘出来。
例如,如果初始网格如下所示:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
则输入为:1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
输出格式
输出占一行,包含一个字符串,表示得到正确排列的完整行动记录。
如果答案不唯一,输出任意一种合法方案即可。
如果不存在解决方案,则输出 unsolvable。
输入样例:
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
输出样例
ullddrurdllurdruldr
思路:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pair PIS;
int f(string state){
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < state.size(); i++){
if(state[i] != 'x'){
int t = state[i] - '1';
res += abs(i / 3 - t / 3) + abs(i % 3 - t % 3);
}
}
return res;
}
string bfs(string start){
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char c[] = "urdl";
string end = "12345678x";
unordered_map dist;
unordered_map> pre;
priority_queue, greater> heap;
dist[start] = 0;
heap.push({f(start), start});
while(heap.size()){
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
string state = t.second;
if(state == end) break;
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
if(state[i] == 'x'){
x = i / 3, y = i % 3;
break;
}
}
string source = state;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int tx = x + dx[i], ty = y + dy[i];
if(tx < 0 || tx >= 3 || ty < 0 || ty >= 3) continue;
state = source;
swap(state[x * 3 + y], state[tx * 3 + ty]);
if(!dist.count(state) || dist[state] > dist[source] + 1){
dist[state] = dist[source] + 1;
pre[state] = {c[i], source};
heap.push({dist[state] + f(state), state});
}
}
}
string res = "";
while(end != start){
res += pre[end].first;
end = pre[end].second;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
int main(){
string start, seq, c;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
cin >> c;
start += c;
if(c != "x") seq += c;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
for (int j = i + 1; j < 8; j++){
if(seq[i] > seq[j]) cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt & 1) puts("unsolvable");
else cout << bfs(start) << endl;
return 0;
}
178. 第K短路
给定一张 N N N 个点(编号 1 , 2 … N 1,2…N 1,2…N), M M M 条边的有向图,求从起点 S S S 到终点 T T T 的第 K K K 短路的长度,路径允许重复经过点或边。
注意: 每条最短路中至少要包含一条边。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N N N 和 M M M。
接下来 M M M 行,每行包含三个整数 A , B A,B A,B 和 L L L,表示点 A A A 与点 B B B 之间存在有向边,且边长为 L L L。
最后一行包含三个整数 S , T S,T S,T 和 K K K,分别表示起点 S S S,终点 T T T 和第 K K K 短路。
输出格式
输出占一行,包含一个整数,表示第 K K K 短路的长度,如果第 K K K 短路不存在,则输出 − 1 −1 −1。
数据范围
1 ≤ S , T ≤ N ≤ 1000 1≤S,T≤N≤1000 1≤S,T≤N≤1000,
0 ≤ M ≤ 1 0 4 0≤M≤10^4 0≤M≤104,
1 ≤ K ≤ 1000 1≤K≤1000 1≤K≤1000,
1 ≤ L ≤ 100 1≤L≤100 1≤L≤100
输入样例:
2 2
1 2 5
2 1 4
1 2 2
输出样例:
14
思路:
- 第 K K K 短路,就是终点出队 K K K 次的距离。注意:当起点和终点一样时, K + + K++ K++
- 只要从 S S S 能到达 T T T,就一定存在第 K K K 短路,故不存在则一定不能从 S S S 到达 T T T
- 估价函数:从该点到终点的最短距离,即求一遍
Dijkstra,大于等于 0 0 0,小于等于真实值 - 取出堆顶,记录出队次数,把该点能枚举到的所有点都放入小根堆
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PIII;
const int N = 1010, M = 2e4 + 10;
int n, m, S, T, K;
int h[N], rh[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx, dist[N], cnt[N]; // cnt为每个点出队的次数
bool st[N];
void add(int h[], int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void dijkstra(){
priority_queue, greater> q;
q.push({0, T});
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[T] = 0;
while(q.size()){
auto t = q.top();
q.pop();
int ver = t.second;
if(st[ver]) continue;
st[ver] = true;
int dis = t.first;
for (int i = rh[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dis + w[i]){
dist[j] = dis + w[i];
q.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
}
int astar(){
priority_queue, greater> q;
q.push({dist[S], {0, S}});
while(q.size()){
auto t = q.top();
q.pop();
int ver = t.second.second, dis = t.second.first;
cnt[ver]++;
if(cnt[T] == K) return dis;
for (int i = h[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(cnt[j] < K) q.push({dis + w[i] + dist[j], {dis + w[i], j}});
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(rh, -1, sizeof rh);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(h, a, b, c);
add(rh, b, a, c);
}
cin >> S >> T >> K;
if(S == T) K++;
dijkstra();
cout << astar() << endl;
return 0;
}