Jquery源码中的Javascript基础知识(四)— jQuery.fn.init方法
$() 即调用了jQuery.fn.init方法
jQuery = function( selector, context ) { return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context, rootjQuery ); }
下面是init方法代码:
1 init: function( selector, context, rootjQuery ) { 2 var match, elem; 3 if ( !selector ) { 4 return this; 5 } 6 if ( typeof selector === "string" ) { 7 // code
8 } else if ( selector.nodeType ) { 9 this.context = this[0] = selector; 10 this.length = 1; 11 return this; 12 } else if ( jQuery.isFunction( selector ) ) { 13 return rootjQuery.ready( selector ); 14 } 15 if ( selector.selector !== undefined ) { 16 this.selector = selector.selector; 17 this.context = selector.context; 18 } 19 return jQuery.makeArray( selector, this ); 20 }
可以看到,里面对参数 selector 可能出现的值都做了判断处理。
1.是否为错误的值,如:$(""), $(null), $(undefined), $(false)。
2.是否为字符串。
3.是否为节点元素对象。如:$(this), $(document)。
4.是否为函数。如:$(function(){})。
5.是否为jQuery对象。如:$($(element))。
6.是否为数组或json。
当参数是字符串的时候
if ( typeof selector === "string" ) { if ( selector.charAt(0) === "<" && selector.charAt( selector.length - 1 ) === ">" && selector.length >= 3 ) { match = [ null, selector, null ]; } else { match = rquickExpr.exec( selector ); } // 创建元素或者选择ID
if ( match && (match[1] || !context) ) { // 创建元素
if ( match[1] ) { // code
// 选择ID
} else { // code
} // 其他选择器
} else if ( !context || context.jquery ) { return ( context || rootjQuery ).find( selector ); } else { return this.constructor( context ).find( selector ); } }
首先给变量match进行赋值
第一种情况
if ( selector.charAt(0) === "<" && selector.charAt( selector.length - 1 ) === ">" && selector.length >= 3 ) { match = [ null, selector, null ]; }
charAt方法可返回指定位置的字符。符合条件的字符串如:
"<div>", "<div></div>", "<div>111</div>"
第二种情况
match = rquickExpr.exec( selector );
rquickExpr前面已经定义过
rquickExpr = /^(?:\s*(<[\w\W]+>)[^>]*|#([\w-]*))$/,
这种语法创建了一个RegExp对象
exec方法找到匹配内容后会返回一个数组,包含表达式的完整匹配以及子表达式的匹配等,否则返回null。符合条件的字符串如:
"<div>111", "#id"
接着看后面的代码:
if ( match && (match[1] || !context) ) { if ( match[1] ) { // code 创建元素
} else { // code 选择ID
} }
由上面对match的赋值分析可以知道
这里面是针对创建元素和选择id两种情况进行处理,即我们平时这样使用的时候:
$('<div>'), $('#id')
内部又一个if-else语句则分别是对创建元素和选择ID进行处理
下面看处理创建元素部分:
if ( match[1] ) { context = context instanceof jQuery ? context[0] : context; jQuery.merge( this, jQuery.parseHTML( match[1], context && context.nodeType ? context.ownerDocument || context : document, true ) ); if ( rsingleTag.test( match[1] ) && jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) ) { for ( match in context ) { if ( jQuery.isFunction( this[ match ] ) ) { this[ match ]( context[ match ] ); } else { this.attr( match, context[ match ] ); } } } return this; }
这里简单介绍一下parseHTML方法和merge方法。
jQuery.parseHTML方法的作用是将字符串转换成节点数组,如:
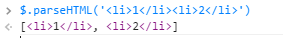
jQuery.merge方法的作用一般是合并数组

在这里也可以合并json

不过json的形式有一定特殊性,需要是类似这样的:
var obj = { 0 : 'a', 1 : 'b', length : 2 }
在我们平时使用jQuery选取或创建元素后,jQuery对象中都会为节点元素创建出一个类似数组的结构,方便后续的操作。

继续往后看还有一段代码:
if ( rsingleTag.test( match[1] ) && jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) ) { for ( match in context ) { if ( jQuery.isFunction( this[ match ] ) ) { this[ match ]( context[ match ] ); } else { this.attr( match, context[ match ] ); } } }
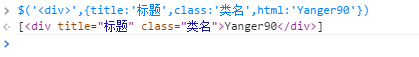
这段代码的作用是给元素标签添加属性,如:
第一个条件
rsingleTag = /^<(\w+)\s*\/?>(?:<\/\1>|)$/,
test() 方法用于检测一个字符串是否匹配某个模式,有则返回true,无返回false。
符合这个正则的字符串如:
"<div>", "<div></div>",也就是单标签。
第二个条件
jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) 判断第二个参数是否为对象字面量。
接着for...in 语句遍历对象中的属性,如果存在与属性同名的方法,就调用此方法(例如上面例子中调用了html方法),否则就调用attr方法。
创建元素就到这里。接下来就是选择id了
if ( match[1] ) { // code
} else { elem = document.getElementById( match[2] ); if ( elem && elem.parentNode ) { // Inject the element directly into the jQuery object
this.length = 1; this[0] = elem; } this.context = document; this.selector = selector; return this; }
这里就很简单了,直接用getElementById方法获取目标元素,然后就是对应进行赋值,创建之前说过的类似数组的结构。
下面看除了创建元素和选择id之外的情况
if ( match && (match[1] || !context) ) { // code
} else if ( !context || context.jquery ) { return ( context || rootjQuery ).find( selector ); } else { return this.constructor( context ).find( selector ); }
可以看到,不管走后面哪条分支,最终调用的都是find方法,所以,选择类,选择元素和更加复杂的选择器都并没有在init方法中做处理,而是调用了find,这个就到后面再说。
最后我们来看一下参数除了字符串以外其他情况:
if ( typeof selector === "string" ) { // code
} else if ( selector.nodeType ) { this.context = this[0] = selector; this.length = 1; return this; } else if ( jQuery.isFunction( selector ) ) { return rootjQuery.ready( selector ); } if ( selector.selector !== undefined ) { this.selector = selector.selector; this.context = selector.context; } return jQuery.makeArray( selector, this );
当参数为元素对象或jQuery对象时,对一些属性进行赋值。
当参数为函数时,调用了ready方法,
所以,$(function(){})这种写法算是文档加载$(document).ready(function(){})的一种简写方式。
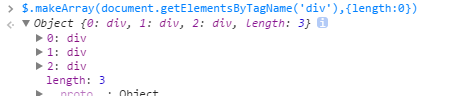
makeArray方法类似于之前提到的merge方法,一般可以用来把节点元素转换为数组

也可以转换为json,同样第二参数需要是类数组的形式
好了,总结一下, jQuery.fn.init方法对不同类型的参数进行处理,并且参数为字符串时,内部主要对创建元素和选择id作了处理,其他情况则交给find方法,最终构造出一个关于节点元素的类数组结构以及对一些属性的初始化。