项目日记 -云备份 -服务端工具类
博客主页:【夜泉_ly】
本文专栏:【项目日记-云备份】
欢迎点赞收藏⭐关注❤️
![]()
代码已上传 gitee
目录
- FileUtils -文件实用工具类
-
- 1. 获取文件属性
-
- GetSize
- GetMTime
- GetATime
- GetFileName
- 2. 获取/设置文件内容
-
- GetContentFromPos
- GetContent
- SetContent
- 3. 压缩/解压缩文件
-
- Compress
- Decompress
- 4. 目录相关
-
- Exists
- CreateDirectory
- ScanDirectory
- JsonUtils -Json实用工具类
- 测试
如题,今天来实现服务端工具类。
本项目名为云备份,
涉及了大量的文件操作,
因此,
可以先把这些文件操作简单封装一下。
这就是接下来实现的第一个工具类,
FileUtils。
FileUtils -文件实用工具类
先建立文件 CloudBackup/src/Utils.hpp,
然后来看看需要实现的接口:
namespace Cloud {
class FileUtils {
public:
FileUtils(const std::string& filePath) : _filePath(filePath) {}
int64_t GetSize() const;
time_t GetMTime() const;
time_t GetATime() const;
std::string GetFileName() const;
bool GetContentFromPos(std::string* pContent, size_t pos, size_t len) const;
bool GetContent(std::string* pContent) const;
bool SetContent(const std::string& content);
bool Compress(const std::string& dst) const;
bool DeCompress(const std::string& dst) const;
bool Exists() const;
bool CreateDirectory();
void ScanDirectory(std::vector<std::string>* pArr);
private:
std::string _filePath;
};
} // namespace Cloud
共分四类,一类一类的实现。
1. 获取文件属性
第一类,获取文件属性的:
GetSize 获取大小
GetMTime 获取最后修改时间(modify)
GetATime 获取最后访问时间(access)
GetFileName 获取文件名
这里可以使用 stat 结构体,
兼容性问题不用考虑,
毕竟这是服务器工具类。
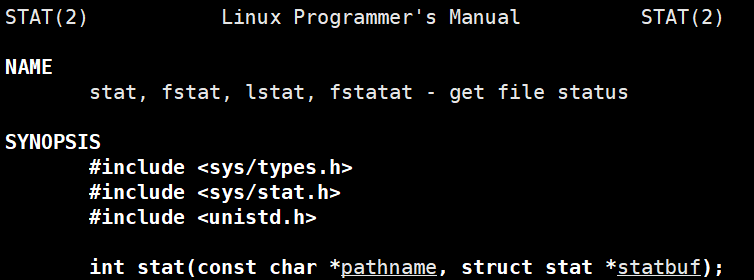
获取 stat 结构体很简单,
传个文件路径和结构体进去就行,
失败返回 -1。
获取了 stat 结构体,剩下的就好办了。
GetSize
int64_t GetSize() const
{
struct stat file_info;
if (stat(_filePath.c_str(), &file_info) == -1)
{
perror("FileUtils::GetSize::stat");
return -1;
}
return file_info.st_size;
}
有一个点需要注意,
st_size 的类型是 long,
long 可4可8,
这个返回值的长度最好还是固定一下,
所以用 int64_t。
GetMTime
time_t GetMTime() const
{
struct stat file_info;
if (stat(_filePath.c_str(), &file_info) == -1)
{
perror("FileUtils::GetMTime::stat");
return -1;
}
return file_info.st_mtim.tv_sec;
}
GetATime
time_t GetATime() const
{
struct stat file_info;
if (stat(_filePath.c_str(), &file_info) == -1)
{
perror("FileUtils::GetATime::stat");
return -1;
}
return file_info.st_atim.tv_sec;
}
这个获取最后访问时间,
是
这也是上面的函数使用 stat 的原因。
GetFileName
std::string GetFileName() const
{
size_t pos = _filePath.find_last_of('/');
if (pos == std::string::npos)
return _filePath;
return _filePath.substr(pos + 1);
}
找最后一个 '/' 就行,毕竟服务器是Linux的。
找不到说明 _filePath 本身就是文件名。
不过这个对一些非法的路径名无法处理,
暂时不管了。。。
2. 获取/设置文件内容
因为后面要支持断点续传,
所以需要提供一个从指定位置开始读的接口,
那么目前设计的接口如下:
GetContentFromPos 从指定位置读指定长度
GetContent 获取文件内容
SetContent 设置文件内容
GetContentFromPos
bool GetContentFromPos(std::string* pContent, size_t pos, size_t len) const
{
if (!pContent)
return false;
size_t size = GetSize();
if (size == -1)
return false;
if (size > pos && len > size - pos)
{
std::cerr << "GetContentFromPos: pos + len > size\n";
return false;
}
判断(size > pos && len > size - pos),
写的有点挫,
主要是为了防止越界(pos + len > size)和溢出(size_t无负数),
很明显意义不大。
std::ifstream ifs(_filePath, std::ios::binary);
if (!ifs) {
std::cerr << "GetContentFromPos: open file error\n";
return false;
}
std::ios::binary,
打开时必须用二进制,
因为文件格式我们并不清楚。
ifs.seekg(pos, std::ios_base::beg);
pContent->resize(len);
ifs.read(&((*pContent)[0]), len);
if (!ifs) {
std::cerr << "GetContentFromPos: read file error\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
seekg 移动文件指针,
resize 预留大小,
最后,ifs 在这里不用手动 close(),
因为 ifstream 出作用域会自动 close() (它也属于RAII)。
GetContent
bool GetContent(std::string *pContent) const
{
return GetContentFromPos(pContent, 0, GetSize());
}
我 GetContentFromPos 得了 mvp!
你 GetContent 就是躺赢狗
SetContent
bool SetContent(const std::string &content)
{
std::ofstream ofs(_filePath, std::ios::binary);
if (!ofs)
{
std::cerr << "SetContent: open file error\n";
return false;
}
ofs.write(&content[0], content.size());
if (!ofs)
{
std::cerr << "SetContent: write file error\n";
return false;
}
return true;
}
write 处,
用 &content[0]、content.c_str()、 content.data()都行。
3. 压缩/解压缩文件
Compress 压缩
Decompress 解压缩
这里需要用到之前下的第三方库,
把bundle.h和bundle.cpp挪到CloudBackup/src/就行
然后记得 #include "bundle.h"。
Compress
bool Compress(const std::string &dst) const
{
std::string org;
if (!GetContent(&org))
return false;
std::string packed_text = bundle::pack(bundle::LZIP, org);
if (packed_text.empty() && !org.empty())
{
std::cerr << "DeCompress: pack error\n";
return false;
}
return FileUtils(dst).SetContent(packed_text);
}
Decompress
bool DeCompress(const std::string &dst) const
{
std::string org;
if (!GetContent(&org))
return false;
std::string unpacked_text = bundle::unpack(org);
if (unpacked_text.empty() && !org.empty())
{
std::cerr << "DeCompress: unpack error\n";
return false;
}
return FileUtils(dst).SetContent(unpacked_text);
}
4. 目录相关
Exists 判断文件是否存在
CreateDirectory 创建目录
ScanDirectory 扫描目录
这一部分,
如果继续用 POSIX API 的话还是太吃操作了,
所以我们用 filesystem。
先加头文件:
#include 再简化命名空间:
namespace fs = std::experimental::filesystem;
另外,编译时最好加上链接选项 -lstdc++fs。
函数实现:
Exists
bool Exists() const
{
return fs::exists(_filePath);
}
CreateDirectory
bool CreateDirectory()
{
if (Exists())
return true;
return fs::create_directories(_filePath);
}
ScanDirectory
void ScanDirectory(std::vector<std::string> *pArr)
{
if (!pArr)
return;
for (auto &p : fs::directory_iterator(_filePath))
{
if (fs::is_directory(p))
FileUtils(p.path().string()).ScanDirectory(pArr); // 递归目录
else
pArr->push_back(p.path().string());
}
}
如果目录太深。。
也不至于栈溢出吧,
那就用递归了。
JsonUtils -Json实用工具类
第二个类 JsonUtils
是对Json序列化和反序列化操作的简单封装,
只有两个静态成员函数 Serialize 和 DeSerialize
class JsonUtils
{
public:
static bool Serialize(const Json::Value &root, std::string *pStr)
{
if (!pStr)
return false;
std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> pWriter(Json::StreamWriterBuilder().newStreamWriter());
std::stringstream sout;
if (pWriter->write(root, &sout) || !sout)
return false;
*pStr = sout.str();
return true;
}
static bool DeSerialize(const std::string &str, Json::Value *pRoot)
{
if (!pRoot)
return false;
std::unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> pReader(Json::CharReaderBuilder().newCharReader());
std::string errs;
if (!pReader->parse(&str[0], &str[0] + str.size(), pRoot, &errs))
{
std::cerr << "DeSerialize::parse error: " << errs << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
噢对了,
关于Json::StreamWriter::write的返回,
zero on success (For now, we always return zero, so check the stream instead.),
提示是这么说的,
所以我返回值和 stream 都检查了。
测试
注意,最好每写几个函数就测一下,
不然 make 后就会看见一片红。
我就这里直接给测试文件了,
感兴趣的可以去试试:
#include "Utils.hpp"
void Test1(const std::string &filePath)
{
Cloud::FileUtils fu(filePath);
std::cout << fu.GetSize() << std::endl;
std::cout << fu.GetATime() << std::endl;
std::cout << fu.GetMTime() << std::endl;
std::cout << fu.GetFileName() << std::endl;
}
void Test2(const std::string &filePath)
{
Cloud::FileUtils(filePath).Compress(filePath + ".lz");
Cloud::FileUtils(filePath).DeCompress(filePath + "2");
}
void Test3(const std::string &filePath)
{
Cloud::FileUtils f(filePath);
std::cout << f.Exists() << std::endl;
f.CreateDirectory();
std::cout << f.Exists() << std::endl;
std::vector<std::string> Path;
f.ScanDirectory(&Path);
for (auto &e : Path)
std::cout << e << std::endl;
}
void TestJson()
{
// 数据初始化
double a = 1.11;
std::string b("Hello World");
int arr[]{1, 2, 3};
Json::Value va;
va["double"] = a;
va["string"] = b;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
va["arr"].append(arr[i]);
std::string str;
Cloud::JsonUtils::Serialize(va, &str);
std::cout << "Serialized JSON: ";
std::cout << str << std::endl;
Json::Value v;
Cloud::JsonUtils::DeSerialize(str, &v);
double a2 = v["double"].asDouble();
std::string b2 = v["string"].asString();
int arr2[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
arr2[i] = v["arr"][i].asInt();
std::cout << "\nDeserialized Data:\n";
std::cout << "a2: " << a2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "b2: " << b2 << std::endl;
std::cout << "arr2: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
std::cout << arr2[i] << " \n"[i == 2];
exit(0);
}
void Usage(const std::string &str)
{
std::cout << "Usage:\n\t";
std::cout << str << " [number] [filepath]\n";
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc == 1)
TestJson();
if (argc == 3)
{
if (argv[1][0] == '1')
Test1(argv[2]);
if (argv[1][0] == '2')
Test2(argv[2]);
if (argv[1][0] == '3')
Test3(argv[2]);
}
else
{
Usage(argv[0]);
}
return 0;
}
![]()
希望本篇文章对你有所帮助!并激发你进一步探索编程的兴趣!
本人仅是个C语言初学者,如果你有任何疑问或建议,欢迎随时留言讨论!让我们一起学习,共同进步!