Spark MLBase分布式机器学习系统入门:以MLlib实现Kmeans聚类算法
1.什么是MLBase
MLBase是Spark生态圈的一部分,专注于机器学习,包含三个组件:MLlib、MLI、ML Optimizer。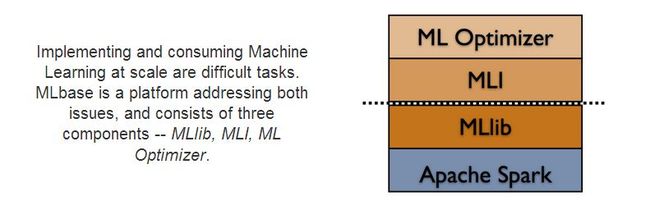
- ML Optimizer: This layer aims to automating the task of ML pipeline construction. The optimizer solves a search problem over feature extractors and ML algorithms included inMLI and MLlib. The ML Optimizer is currently under active development.
- MLI: An experimental API for feature extraction and algorithm development that introduces high-level ML programming abstractions. A prototype of MLI has been implemented against Spark, and serves as a testbed for MLlib.
- MLlib: Apache Spark's distributed ML library. MLlib was initially developed as part of the MLbase project, and the library is currently supported by the Spark community. Many features in MLlib have been borrowed from ML Optimizer and MLI, e.g., the model and algorithm APIs, multimodel training, sparse data support, design of local / distributed matrices, etc.
2.MLbase机器学习算法的流程
用户可以容易地使用MLbase这个工具来处理自己的数据。大部分的机器学习算法都包含训练以及预测两个部分,训练出模型,然后对未知样本进行预测。Spark中的机器学习包也是如此。
Spark将机器学习算法都分成了两个模块:
- 训练模块:通过训练样本输出模型参数
- 预测模块:利用模型参数初始化,预测测试样本,输出与测值。
MLbase提供了函数式编程语言Scala,利用MLlib可以很方便的实现机器学习的常用算法。
比如说,我们要做分类,只需要写如下scala代码:
1 var X = load("some_data", 2 to 10) 2 var y = load("some_data", 1) 3 var (fn-model, summary) = doClassify(X, y)
代码解释:X是需要分类的数据集,y是从这个数据集里取的一个分类标签,doClassify()分类。
这样的处理有两个主要好处:
- 每一步数据处理很清楚,可以很容易地可视化出来;
- 对用户来说,用ML算法处理是透明的,不用关心和考虑用什么分类方法,是SVM还是AdaBoost,SVM用的kernel是线性的还是RBF的,original和scaled的参数调成多少等等。
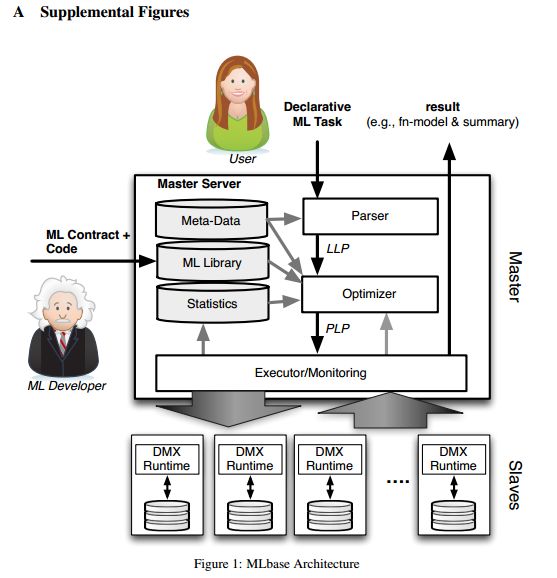
MLbase的三大组成部分之一:ML Optimizer,会选择它认为最适合的已经在内部实现好了的机器学习算法和相关参数,来处理用户输入的数据,并返回模型或别的帮助分析的结果。总体上的处理流程如下图:
- 用户输入的Task比如doClassify(X, y)或者做协同过滤doCollabFilter(X, y)、图计算findTopKDegreeNodes(G, k = 1000)之类的事情,先会传给Parser处理,然后交给LLP。LLP是logical learning plan,即是逻辑上的一个学习选择过程,在这个过程里选择该用什么算法,特征提取应该用什么做,参数应该选什么,数据集怎么拆子数据集的策略等事情。
- LLP决定之后交给Optimizer。Optimizer是MLbase的核心,它会把数据拆分成若干份,对每一份使用不同的算法和参数来运算出结果,看哪一种搭配方式得到的结果最优(注意这次最优结果是初步的),优化器做完这些事之后就交给PLP。
- PLP是physical learning plan,即物理(实际)执行的计划,让MLbase的master把任务分配给具体slave去最后执行之前选好的算法方案,把结果计算出来返回,同时返回这次计算的学习模型。
- 这个流程是Task -> Parser -> LLP -> Optimizer -> PLP -> Execute -> Result/Model,先从逻辑上,在已有的算法里选几个适合这个场景的,让优化器都去做一遍,把认为当时最优的方案给实际执行的部分去执行,返回结果。
MLbase不仅仅把结果返回给用户。在LLP、Optimizer,MLbase会存储一些中间结果和特征,然后会继续搜寻和测试结果更好的算法和相关参数,并且会通知用户。LLP内部实现的算法是可以扩充的。
总之,MLbase会自动寻找合适的算法,自动选择和优化,还可以进行扩充。
3.Scala实现KMeans算法
3.1 什么是KMeans算法
K-Means算法是一种cluster analysis的算法,其主要是来计算数据聚集的算法,主要通过不断地取离种子点最近均值的算法。
具体来说,通过输入聚类个数k,以及包含 n个数据对象的数据库,输出满足方差最小标准的k个聚类。
3.2 k-means 算法基本步骤
(1) 从 n个数据对象任意选择 k 个对象作为初始聚类中心;
(2) 根据每个聚类对象的均值(中心对象),计算每个对象与这些中心对象的距离;并根据最小距离重新对相应对象进行划分;
(3) 重新计算每个(有变化)聚类的均值(中心对象);
(4) 计算标准测度函数,当满足一定条件,如函数收敛时,则算法终止;如果条件不满足则回到步骤(2)。
算法的时间复杂度上界为O(n*k*t), 其中t是迭代次数,n个数据对象划分为 k个聚类。
3.3 MLlib实现KMeans
以MLlib实现KMeans算法,利用MLlib KMeans训练出来的模型,可以对新的数据作出分类预测,具体见代码和输出结果。
Scala代码:
1 package com.hq 2 3 import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.KMeans 4 import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors 5 import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf} 6 7 object KMeansTest { 8 def main(args: Array[String]) { 9 if (args.length < 1) { 10 System.err.println("Usage: <file>") 11 System.exit(1) 12 } 13 14 val conf = new SparkConf() 15 val sc = new SparkContext(conf) 16 val data = sc.textFile(args(0)) 17 val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.split(' ').map(_.toDouble))) 18 val numClusters = 2 19 val numIterations = 20 20 val clusters = KMeans.train(parsedData,numClusters,numIterations) 21 22 println("------Predict the existing line in the analyzed data file: "+args(0)) 23 println("Vector 1.0 2.1 3.8 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("1.0 2.1 3.8".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 24 println("Vector 5.6 7.6 8.9 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("5.6 7.6 8.9".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 25 println("Vector 3.2 3.3 6.6 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("3.2 3.3 6.6".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 26 println("Vector 8.1 9.2 9.3 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("8.1 9.2 9.3".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 27 println("Vector 6.2 6.5 7.3 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("6.2 6.5 7.3".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 28 29 println("-------Predict the non-existent line in the analyzed data file: ----------------") 30 println("Vector 1.1 2.2 3.9 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("1.1 2.2 3.9".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 31 println("Vector 5.5 7.5 8.8 belongs to clustering "+ clusters.predict(Vectors.dense("5.5 7.5 8.8".split(' ').map(_.toDouble)))) 32 33 println("-------Evaluate clustering by computing Within Set Sum of Squared Errors:-----") 34 val wssse = clusters.computeCost(parsedData) 35 println("Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = "+ wssse) 36 sc.stop() 37 } 38 }
3.4 以Spark集群standalone方式运行
①在IDEA打成jar包(如果忘记了,参见Spark:用Scala和Java实现WordCount),上传到用户目录下/home/ebupt/test/kmeans.jar
②准备训练样本数据:hdfs://eb170:8020/user/ebupt/kmeansData,内容如下
[ebupt@eb170 ~]$ hadoop fs -cat ./kmeansData
1.0 2.1 3.8
5.6 7.6 8.9
3.2 3.3 6.6
8.1 9.2 9.3
6.2 6.5 7.3
③spark-submit提交运行
[ebupt@eb174 test]$ spark-submit --master spark://eb174:7077 --name KmeansWithMLib --class com.hq.KMeansTest --executor-memory 2G --total-executor-cores 4 ~/test/kmeans.jar hdfs://eb170:8020/user/ebupt/kmeansData
输出结果摘要:
1 ------Predict the existing line in the analyzed data file: hdfs://eb170:8020/user/ebupt/kmeansData 2 Vector 1.0 2.1 3.8 belongs to clustering 0 3 Vector 5.6 7.6 8.9 belongs to clustering 1 4 Vector 3.2 3.3 6.6 belongs to clustering 0 5 Vector 8.1 9.2 9.3 belongs to clustering 1 6 Vector 6.2 6.5 7.3 belongs to clustering 1 7 -------Predict the non-existent line in the analyzed data file: ---------------- 8 Vector 1.1 2.2 3.9 belongs to clustering 0 9 Vector 5.5 7.5 8.8 belongs to clustering 1 10 -------Evaluate clustering by computing Within Set Sum of Squared Errors:----- 11 Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = 16.393333333333388
4.MLbase总结
本文主要介绍了MLbase如何实现机器学习算法,简单介绍了MLBase的设计思想。总的来说,Mlbase的核心是ML Optimizer,把声明式的任务转化成复杂的学习计划,输出最优的模型和计算结果。
与其它机器学习系统Weka、mahout不同:
- MLbase是分布式的,Weka是单机的。
- Mlbase是自动化的,Weka和mahout都需要使用者具备机器学习技能,来选择自己想要的算法和参数来做处理。
- MLbase提供了不同抽象程度的接口,可以扩充ML算法。
5.参考文献
- MLbase
- apache mlbase
- A. Talwalkar, T. Kraska, R. Griffith, J. Duchi, J. Gonzalez, D. Britz, X. Pan, V. Smith, E. Sparks, A. Wibisono, M. J. Franklin, M. I. Jordan. MLbase: A Distributed Machine Learning Wrapper. In Big Learning Workshop at NIPS, 2012.
- Spark MLlib系列——程序框架
- MLBase:Spark生态圈里的分布式机器学习系统
- Apache Spark MLlib KMeans