【原】Fatfs 移植的那些事
FatFs 移植
Fatfs 是一個平台无关,兼容 Windows FAT 的轻型文件系统。据官网介绍,目前 Fatfs 已经在AVR, 8051, PIC, ARM, Z80, 68k 等平台上移植成功(并不需要改变源码的任何接口),并且运行良好,事实确实是这样的。笔者目前在某通信公司做 II 型集中器的项目,项目选用的芯片是日产瑞萨(后面简称RX)半导体作为主控芯片,完成处理任务。而在移植本文所讲述之文件系统的时候,需要做的就是完成底层存储的访问接口。
Fatfs 的接口介绍
Fatfs 的接口如图所示:
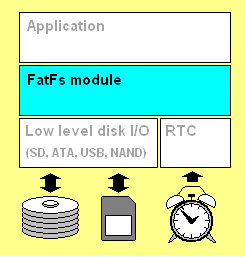
我在移植 Fatfs 的时候,底层存储媒体是SPI+FLASH,时钟采用片内时钟或者外部Rx8025T时钟。
应用程序接口
该接口提供给在操作系统(因为Fatfs 已经明确指出对 RTOS 的支持)上运行的应用程序。该接口表明 Fatfs 可以如何去访问 FAT 卷,如下:
 Application Interface
Application Interface
1 f_mount - Register/Unregister a work area 2 3 f_open - Open/Create a file 4 5 f_close - Close a file 6 7 f_read - Read file 8 9 f_write - Write file 10 11 f_lseek - Move read/write pointer, Expand file size 12 13 f_truncate - Truncate file size 14 15 f_sync - Flush cached data 16 17 f_opendir - Open a directory 18 19 f_readdir - Read a directory item 20 21 f_getfree - Get free clusters 22 23 f_stat - Get file status 24 25 f_mkdir - Create a directory 26 27 f_unlink - Remove a file or directory 28 29 f_chmod - Change attribute 30 31 f_utime - Change timestamp 32 33 f_rename - Rename/Move a file or directory 34 35 f_chdir - Change current directory 36 37 f_chdrive - Change current drive 38 39 f_getcwd - Retrieve the current directory 40 41 f_forward - Forward file data to the stream directly 42 43 f_mkfs - Create a file system on the drive 44 45 f_fdisk - Divide a physical drive 46 47 f_gets - Read a string 48 49 f_putc - Write a character 50 51 f_puts - Write a string 52 53 f_printf - Write a formatted string 54 55 f_tell - Get the current read/write pointer 56 57 f_eof - Test for end-of-file on a file 58 59 f_size - Get size of a file 60 61 f_error - Test for an error on a file
磁盘访问接口
文件系统需要访问物理介质,也就是我们常说的存储。Fatfs 将存储接口做了封层,移植者只需要将存储访问实现就行。包括磁盘初始化、磁盘状态、读磁盘、写磁盘、磁盘控制以及提供FAT时间。
 Disk IO Interface
Disk IO Interface
1 disk_initialize - Initialize disk drive 2 3 disk_status - Get disk status 4 5 disk_read - Read sector(s) 6 7 disk_write - Write sector(s) 8 9 disk_ioctl - Control device dependent features 10 11 get_fattime - Get current time
值得一说的是,Fatfs 是按照扇区的概念来访问介质的,每个扇区的大小(占用的字节数),对于不同的存储媒体来说是不一样的。同时对于不同的存储介质,“扇区“的概念也有不同。当使用 I/O 接口进行磁盘访问的时候,每次最少读写 SSIZE 个字节(SSIZE就是扇区大小)。
移植过程
在移植之前,需要注意以下几点:
FLASH的存取是线性的,没有扇区的概念,而只有PAGE和BLOCK
提到这一点,Fatfs中要求扇区大小不能小于512 bytes,但是FLASH中的PAGE时常会小于这个值(因为我现在用的FLASH的PAGE是256bytes)。于是需要人为抽象扇区,也就是说需要在磁盘读写函数中实现分步多次读写。
FLASH的写特点所决定的一些特性
例如:FLASH在写之前需要进行擦除操作,那么如果擦除不成功的话,对于写接口来说是没有任何意义的。
FLASH上移植Fatfs文件系统,不同于其他存储媒体的特点
如sdcard,sdcard在Windows下能够自动被格式化(在你将sd卡通过读卡器插入Windows的时候),但是FLASH不能,这需要调用Fatfs中的f_mkfs 接口,先对FLASH进行格式化,待格式化完成之后,后面的文件操作才能顺利进行。笔者所使用的FLASH具有写保护机制,所以在进行写操作之前需要进行保护关闭操作。
下载源码
源码的下载可通过官网地址下载:http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html
文件系统的基本代码
diskio.c diskio.h ff.c ff.h ffconf.h integer.h cc9xx.c。这几个文件对于移植已经够用了。
diskio.c的改写
diskio.c 中实现了底层存储介质的读写操作和状态访问,具体请参见源码解释。移植需要做的就是将自己对存储的访问接口用diskio中相对应的接口来实现。
初始化
1 DSTATUS disk_initialize ( 2 BYTE drv /* Physical drive number (0) */ 3 ) 4 { 5 if (drv) return STA_NOINIT; /* Supports only drive 0 */ 6 if(!init_flag) 7 if(R_SPIFLASH_Initialise()) 8 { 9 Stat &= ~STA_NOINIT; /* Clear STA_NOINIT flag */ 10 init_flag = 1; 11 printf("disk_initialized OKAY !\n"); 12 } 13 R_SPIFLASH_MemoryProtection(false); 14 return Stat; 15 }
读数据
1 DRESULT disk_read ( 2 BYTE drv, /* Physical drive number (0) */ 3 BYTE *buff, /* Pointer to the data buffer to store read data */ 4 DWORD sector, /* Start sector number (LBA) */ 5 BYTE count /* Number of sectors to read (1..128) */ 6 ) 7 { 8 UINT address = 0; 9 UINT i = 0; 10 UINT bycount = count; 11 12 if(drv || (!count)) return RES_PARERR; 13 if (Stat & STA_NOINIT) return RES_NOTRDY; /* Check if drive is ready */ 14 15 /* Bytes addressing conversion, address is the start of sector */ 16 address = (sector * SSIZE); 17 printf("Read sector:%04d, address range in: ", sector); 18 /* One sector - eight pages, one page - 256bytes */ 19 if(count == 1){ /* READ_SINGLE_BLOCK */ 20 if(R_SPIFLASH_Read(buff, address, SSIZE)){ 21 printf("0x%08x-0x%08x ", address, (address + SSIZE - 1)); 22 count = 0; 23 } 24 }else{ /* READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK */ 25 do { 26 if(!R_SPIFLASH_Read(&buff[0], address, SSIZE)) 27 break; 28 else{ 29 printf("0x%08x-0x%08x ", address, (address + SSIZE - 1)); 30 } 31 /* Data pointer moved */ 32 buff += SSIZE; 33 /* Address pointer moved */ 34 address += SSIZE; 35 } while (--count); 36 } 37 if((bycount == 1) || ((bycount > 1) && (count == 0))) printf("success\n"); 38 return count ? RES_ERROR : RES_OK; /* Return result */ 39 }
该例中,实现单个扇区或者多个扇区的访问。
写数据
1 DRESULT disk_write ( 2 BYTE drv, /* Physical drive number (0) */ 3 const BYTE *buff, /* Ponter to the data to write */ 4 DWORD sector, /* Start sector number (LBA) */ 5 BYTE count /* Number of sectors to write (1..128) */ 6 ) 7 { 8 DWORD address; 9 DWORD i=1000000; 10 UINT bycount = count; 11 12 if(drv || !count) return RES_PARERR; 13 if (Stat & STA_NOINIT) return RES_NOTRDY; /* Check if drive is ready */ 14 if (Stat & STA_PROTECT) return RES_WRPRT; /* Check write protect */ 15 16 /* Bytes addressing conversion, address is the start of sector */ 17 address = (sector * SSIZE); 18 printf("Write sector:%04d, address range in: ", sector); 19 if(count == 1){ /* Single sector write */ 20 if(erase_4k_sst25v_spiflash(address)) 21 if(R_SPIFLASH_Write(&buff[0], address, SSIZE)) 22 { 23 printf("0x%08x-0x%08x ", address, (address + SSIZE - 1)); 24 while(i--); 25 count = 0; 26 } 27 else printf("error !\n"); 28 }else{ /* Multiple sector write */ 29 do { 30 if(!R_SPIFLASH_Write(&buff[0], address, SSIZE)) 31 break; 32 /* Data pointer moved */ 33 buff += SSIZE; 34 /* Address pointer moved */ 35 address += SSIZE; 36 } while (--count); 37 } 38 if((bycount == 1) || ((bycount > 1) && (count == 0))) printf("success\n"); 39 return count ? RES_ERROR : RES_OK; /* Return result */ 40 }
磁盘状态
1 DSTATUS disk_status ( 2 BYTE drv /* Physical drive number (0) */ 3 ) 4 { 5 if (drv) return STA_NOINIT; /* Supports only drive 0 */ 6 return Stat; /* Return disk status */ 7 }
磁盘控制
1 DRESULT disk_ioctl ( 2 BYTE drv, /* Physical drive number (0) */ 3 BYTE ctrl, /* Control command code */ 4 void *buff /* Pointer to the conrtol data */ 5 ) 6 { 7 int a; 8 DRESULT res = 0; 9 BYTE *ptr = buff; 10 11 if (drv) return RES_PARERR; /* Check parameter */ 12 if (Stat & STA_NOINIT) return RES_NOTRDY; /* Check if drive is ready */ 13 res = RES_ERROR; 14 switch (ctrl) { 15 case CTRL_SYNC : /* Wait for end of internal write process of the drive */ 16 for(a=0;a<100000;a++); 17 res = RES_OK; 18 break; 19 20 case GET_SECTOR_COUNT : /* Get drive capacity in unit of sector (DWORD) */ 21 *(DWORD*)buff = ( STORAGE_SST25V/SSIZE); /* 16K sectors in one spi flash */ 22 res = RES_OK; 23 break; 24 25 case GET_SECTOR_SIZE : /* Get sector size in unit of byte (WORD) */ 26 *(DWORD*)buff = SSIZE; 27 res = RES_OK; 28 break; 29 30 case GET_BLOCK_SIZE : /* Get erase block size in unit of sector (DWORD) */ 31 *(DWORD*)buff = 1; /* 4K bytes */ 32 res = RES_OK; 33 break; 34 /* Following command are not used by FatFs module */ 35 36 default: 37 res = RES_PARERR; 38 } 39 40 return res; 41 }
Fatfs时间
1 DWORD get_fattime (void) 2 { 3 INT8U rx8025t_buff[MAX_8025T_COUNTORS + 1]; 4 5 i2c_read(RX8025T_DEV_ADDRESS, 0, &rx8025t_buff[0], MAX_8025T_COUNTORS); 6 7 return ((DWORD)(2000 + bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_YR_REG_ADDR]) - 1980) << 25) /* Y */ 8 | ((DWORD)(bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_MON_REG_ADDR])) << 21) /* M */ 9 | ((DWORD)(bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_DAY_REG_ADDR])) << 16) /* D */ 10 | ((DWORD)(bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_HR_REG_ADDR])) << 11) /* H */ 11 | ((DWORD)(bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_MIN_REG_ADDR])) << 5) /* M */ 12 | ((DWORD)(bcd2dec(rx8025t_buff[RTC_SEC_REG_ADDR])) >> 1); /* S */ 13 } 14 /* 时间格式参见官网给出的文档。*/
最后,读写接口对存储的操作单位都是扇区,所以当传进扇区的时候,笔者在内部进行了地址转换,从而能够寻址FLASH。
测试例程
测试例程如下
1 int fs_test() 2 { 3 /* Disk init */ 4 ret = disk_initialize(0); 5 if(ret & STA_NOINIT){ 6 printf("Disk init error !\n"); 7 return; 8 } 9 10 /* Mount Fs */ 11 f_mount(0, &Fs); 12 printf("Erase disk: "); 13 //需要的话请进行全片擦除 14 printf("success !\n"); 15 16 /* Format Disk*/ 17 printf("Format disk: "); 18 f_ret = f_mkfs(0, 0, 4096); 19 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 20 printf("MKFS disk err : "); 21 put_rc(f_ret); 22 return; 23 } 24 printf("success !\n"); 25 put_rc(f_ret); 26 27 /* Create one file */ 28 f_ret = f_open(&fdst,"dstfile.dat", FA_OPEN_ALWAYS|FA_WRITE|FA_READ); 29 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 30 printf("Open file err : "); 31 put_rc(f_ret); 32 return; 33 }else printf("Open file success!\n"); 34 35 /* Write 512 bytes to fdst */ 36 f_ret = f_write(&fdst, &buffer[0], 512, &tt); 37 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 38 printf("Write file err : "); 39 put_rc(f_ret); 40 return; 41 }else{ printf("Write file success!\n"); } 42 43 /* Close file */ 44 f_ret = f_close(&fdst); 45 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 46 printf("Close file err : "); 47 put_rc(f_ret); 48 return; 49 }else{ printf("Close file success!\n");} 50 51 /* Open an EXIT file with writtenable mode */ 52 f_ret = f_open(&fdst, "dstfile.dat", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ | FA_WRITE); 53 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 54 printf("Open file err : "); 55 put_rc(f_ret); 56 return; 57 }else printf("FA_OPEN_EXISTING success!\n"); 58 59 /* Read 512 bytes from fdst to buffer */ 60 f_ret = f_read(&fdst, &buffer[0], 512, &tt); 61 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 62 printf("Read file err : "); 63 put_rc(f_ret); 64 return; 65 }else printf("FA_OPEN_EXISTING read success!\n"); 66 67 b=512; 68 while(b--) printf("%2x",buffer[b]); putchar('\n'); 69 70 f_ret = f_close(&fdst); 71 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 72 printf("Close file err : "); 73 put_rc(f_ret); 74 return; 75 }elseprintf("Close file success!\n"); 76 77 /* Unmount FS */ 78 f_ret = f_mount(0, NULL); 79 if(f_ret != RES_OK){ 80 printf("Umount filesystem err : "); 81 put_rc(f_ret); 82 return; 83 } 84 printf("\r\n\t********************** END ********************\t\n"); 85 return 0; 86 }
