A meta-model for the analysis and design of organizations in multi-agent systems
1. Solved Problem
1) Heterogeneity of language. While heterogeneity has been considered as an important issue in multi-agent systems, there are no implemented systems, to our knowledge, that accept agents speaking different languages. Efforts to bring a standardized language such as KQML or ACL of the FIPA group, show that the problem of language heterogeneity has been considered so important that it required standardization methods to reduce language discrepancies.
2) Multiple applications and architectures. No implemented systems, to our knowledge, allow several applications with different objectives and different internal architectures to work concurrently on the same platform.
3) Security. While security is a major concern in distributed systems, no multi-agent techniques, to our knowledge, have been proposed to prevent agents from interacting with other agents. Any agent, in a system, is supposed to be able to interact with any other agent regardless of its capabilities, goals and authorizations.
2. How to Solve
(1)The concrete level
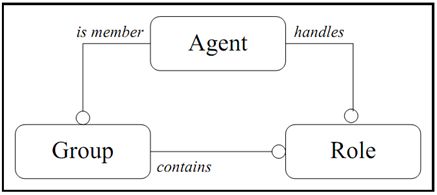
Agent: active entity that plays roles within groups.
Group: set of agents sharing common characteristics.
Role: abstract representation of the status, position, function of an agent within a group.
Note:
- Agents may have several roles and may belong to several groups.
- Two agents can’t communicate with each other if they don’t belong to the same group
Figure1 The Core Model
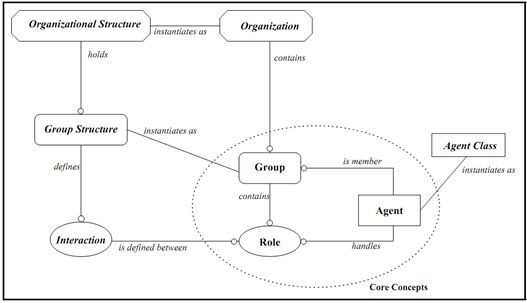
(2)The abstract, methodological level
Figure2 The Methodological Model
Group structure
Define a group structure as a tuple: ![]() .
.
is a finite set of roles identifiers. It represents the enumeration of all possible roles than can be played by agents within a group.
is the interaction graph. More precisely, it is a labelled oriented graph specifying the valid interactions between two roles.
. The edge orientation correponds to the role initiating the interaction. Each edge represents an interaction initiated by
with a role
and named
.
is the interaction language. It is the chosen formalism for the individual interaction definitions. For each relation within the graph, we associate a unique protocol definition p to any edge
within
.
,
Organizational structure
Define an organizational structure as a couple ![]() .
.
is a set a valid group structures.
is the representative graph. It is a labelled graph where each edge
is labelled where two roles
, with
and
, and where
and
are roles which are included in the set of roles defined in the group structures
and
, respectively.
Therefore, a representative structure definition between two groups A andB is an agent having simulteneously the role
in group a and role
in group b.
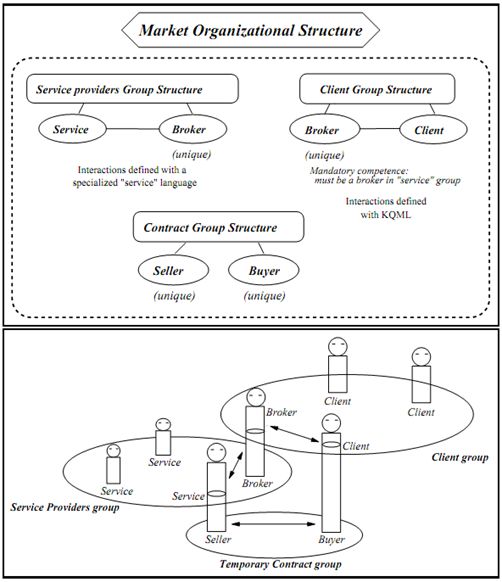
A market organization example
Figure3 (a) The organizational and group structure of a market organization, (b) An actual market organization
We define three groups. The link between the two different interaction models is held by the broker role, which acts as a representative of the service provider group by the way of its broker role within this group. The clients interact with the broker to find a suitable service agent, and the contract group structure definition is aimed at ephemeral groups containing only the two agents involved in the final phase of a negociation.
A possible state of a market organization resulting from this organizational structure is shown in figure 3b.
参考文献:
[1] Ferber J., Gutknecht O.. A meta-model for the analysis and design of organizations in multi-agent systems. Proceedings on International Conference of Multi Agent Systems, 1998.