杭电OJ——1007 Quoit Design(最近点对问题)
Quoit Design
Problem Description
Have you ever played quoit in a playground? Quoit is a game in which flat rings are pitched at some toys, with all the toys encircled awarded.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (2 <= N <= 100,000), the total number of toys in the field. Then N lines follow, each contains a pair of (x, y) which are the coordinates of a toy. The input is terminated by N = 0.
Output
For each test case, print in one line the radius of the ring required by the Cyberground manager, accurate up to 2 decimal places.
Sample Input
2 0 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 -1.5 0 0 0 0 1.5 0
Sample Output
0.71 0.00 0.75
Author
CHEN, Yue
Source
Recommend
JGShining
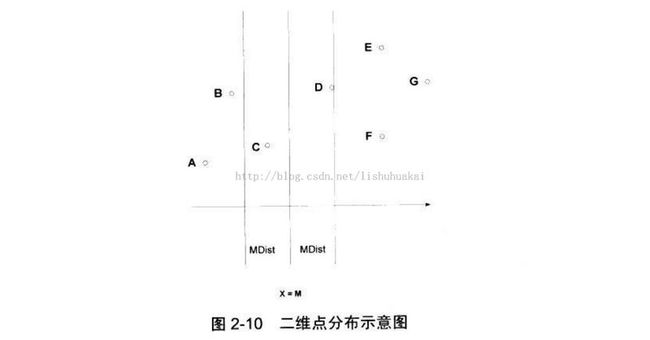
说实话,这篇文章什么意思,我看了半天都没有看懂!不过这不影响做题,这道题实际上就是要求一堆坐标里最短的坐标之间的距离的1/2.
具体算法在《编程之美》中讲得很详细!
代码如下:
/*
*最近点对的问题
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 100005;
const int L = -1;
const int R = 1;
typedef struct
{
int index;
double x;
double y; /*用于记录坐标点*/
}coord;
coord num[SIZE], c[SIZE]/*用作辅助数组*/;
double getDistance(coord &bi1, coord &bi2) /*求得两点之间的距离*/
{
return sqrt(pow(bi1.x - bi2.x, 2.0) + pow(bi1.y - bi2.y, 2.0));
}
bool cmpx(coord &bi1, coord &bi2)
{
if (bi1.x == bi1.x)
return bi1.y < bi2.y;
else
return bi1.x < bi2.x;
}
bool cmpy(coord &bi1, coord &bi2)
{
if (bi1.y == bi2.y)
return bi1.x < bi2.x;
else
return bi1.y < bi2.y;
}
inline double min(double &bi1, double &bi2, double &bi3)
{
double minLength;
minLength = bi1 > bi2 ? bi2 : bi1;
minLength = minLength > bi3 ? bi3 : minLength;
return minLength;
}
inline double minDist(double &bi1, double &bi2)
{
if (bi1 > bi2)
return bi2;
return bi1;
}
double divide_conquer(int low, int high) /*分治法求最小距离*/
{
double dis;
int count = high - low;
if (count == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (count == 1) /*两个数*/
{
dis = getDistance(num[low], num[high]);
}
else if (count == 2) /*三个数*/
{
double temp1, temp2, temp3;
temp1 = getDistance(num[low], num[low + 1]);
temp2 = getDistance(num[low + 1], num[high]);
temp3 = getDistance(num[low], num[high]);
dis = min(temp1, temp2, temp3);
}
else /*大于三个数的情况*/
{
double leftmin, rightmin, min;
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
int p = 0;
int i, j;
leftmin = divide_conquer(low, mid); /*求得左边部分的最小值*/
rightmin = divide_conquer(mid + 1, high); /*求得右边部分的最小值*/
dis = minDist(leftmin, rightmin);
/*下面从所有坐标点中找出所有x在leftCoord到rightCoord之间的点*/
for (i = low; i <= mid; i++)
{
double leftCoord = num[mid].x - dis;
if (num[i].x >= leftCoord)
{
c[p].index = L; /*标识属于左边部分*/
c[p].x = num[i].x;
c[p].y = num[i].y;
p++;
}
}
for ( ; i <= high; i++)
{
double rightCoord = num[mid].x + dis;
if (num[i].x <= rightCoord)
{
c[p].index = R; /*标识属于右边部分*/
c[p].x = num[i].x;
c[p].y = num[i].y;
p++;
}
}
sort(c, c + p, cmpy); /*找到的点再从小到大按照y排序一次*/
for (i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
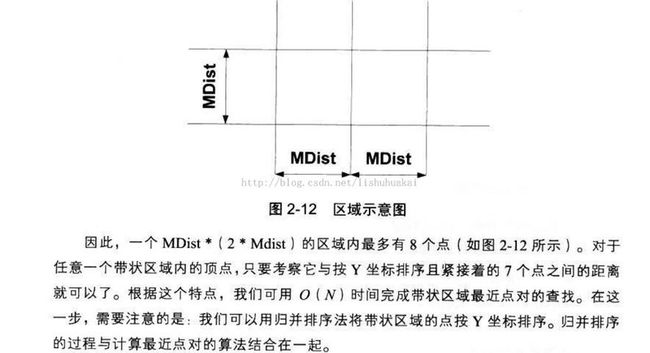
if (c[i].index == L) /*左边的点一个一个地搜索,按照规律,我们只要搜索之后的7个点就可以了*/
{
for (j = 1; (j <= 7) && (i + j < p); j++)
{
if (c[i + j].index == R) /*这个点还必须属于右边*/
{
min = getDistance(c[i], c[i + j]);
if(min < dis)
{
dis = min;
}
}
}
}
}
}
return dis;
}
int main ()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n && n != 0)
{
double result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
num[i].index = 0;
cin >> num[i].x >> num[i].y;
}
sort (num, num + n, cmpx);
result = divide_conquer(0, n - 1);
printf("%.2lf\n", result / 2);
}
//system ("pause");
return 0;
}
上面的那段代码,说实话,还有很大的问题,不过在杭电上居然也通过了,可见杭电数据之弱!现在发一段修改了bug的代码!这一段代码没有错误!
/*
*最近点对的问题
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 100005;
const int L = -1;
const int R = 1;
typedef struct
{
int index;
double x;
double y; /*用于记录坐标点*/
}coord;
coord num[SIZE], c[SIZE]/*用作辅助数组*/;
double getDistance(coord &bi1, coord &bi2) /*求得两点之间的距离*/
{
return sqrt(pow(bi1.x - bi2.x, 2.0) + pow(bi1.y - bi2.y, 2.0));
}
bool cmpx(coord &bi1, coord &bi2)
{
if (bi1.x == bi1.x)
return bi1.y < bi2.y;
else
return bi1.x < bi2.x;
}
bool cmpy(coord &bi1, coord &bi2)
{
if (bi1.y == bi2.y)
return bi1.x < bi2.x;
else
return bi1.y < bi2.y;
}
inline double min(double &bi1, double &bi2, double &bi3)
{
double minLength;
minLength = bi1 > bi2 ? bi2 : bi1;
minLength = minLength > bi3 ? bi3 : minLength;
return minLength;
}
inline double minDist(double &bi1, double &bi2)
{
if (bi1 > bi2)
return bi2;
return bi1;
}
double divide_conquer(int low, int high) /*分治法求最小距离*/
{
double dis;
int count = high - low;
if (count == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else if (count == 1) /*两个数*/
{
dis = getDistance(num[low], num[high]);
}
else if (count == 2) /*三个数*/
{
double temp1, temp2, temp3;
temp1 = getDistance(num[low], num[low + 1]);
temp2 = getDistance(num[low + 1], num[high]);
temp3 = getDistance(num[low], num[high]);
dis = min(temp1, temp2, temp3);
}
else /*大于三个数的情况*/
{
double leftmin, rightmin, min;
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
int p = 0;
int i, j;
leftmin = divide_conquer(low, mid); /*求得左边部分的最小值*/
rightmin = divide_conquer(mid + 1, high); /*求得右边部分的最小值*/
dis = minDist(leftmin, rightmin);
/*下面从所有坐标点中找出所有x在leftCoord到rightCoord之间的点*/
for (i = low; i <= mid; i++)
{
double leftCoord = num[mid].x - dis;
if (num[i].x >= leftCoord)
{
c[p].index = L; /*标识属于左边部分*/
c[p].x = num[i].x;
c[p].y = num[i].y;
p++;
}
}
for ( ; i <= high; i++)
{
double rightCoord = num[mid].x + dis;
if (num[i].x <= rightCoord)
{
c[p].index = R; /*标识属于右边部分*/
c[p].x = num[i].x;
c[p].y = num[i].y;
p++;
}
}
sort(c, c + p, cmpy); /*找到的点再从小到大按照y排序一次*/
for (i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
/*错误出现在这里,上面我是只搜索了左边,并且只计算了7个y值比c[i].y大的点到c[i]的距离,
可是实际上y值比c[i].y小的点也有可能与c[i]取得最小值,所以说上面的程序有错误。真正正确
的解答如下,那就是要搜索所有的点,并计算7个y值比c[i].y大的点到c[i]的距离,由于距离是两个
点之间产生的,一个点的y值比另一个点小,那么必然有另一个点的y值比一个点的大,由于这种关系,
从而保证了搜索出来的是最小的距离!
*/
for (j = 1; (j <= 7) && (i + j < p); j++)
{
if (c[i].index != c[i + j].index) /*最小值只可能出现在两个分别属于不同的边的点上*/
{
min = getDistance(c[i], c[i + j]);
if(min < dis)
dis = min;
}
}
}
}
return dis;
}
int main ()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n && n != 0)
{
double result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
num[i].index = 0;
cin >> num[i].x >> num[i].y;
}
sort (num, num + n, cmpx);
result = divide_conquer(0, n - 1);
printf("%.2lf\n", result / 2);
}
//system ("pause");
return 0;
}