DFS深搜——Red and Black——A Knight's Journey
深搜,从一点向各处搜找到全部能走的地方。
Problem Description
There is a rectangular room, covered with square tiles. Each tile is colored either red or black. A man is standing on a black tile. From a tile, he can move to one of four adjacent tiles. But he can't move on red tiles, he can move only on black tiles.
Write a program to count the number of black tiles which he can reach by repeating the moves described above.
Write a program to count the number of black tiles which he can reach by repeating the moves described above.
Input
The input consists of multiple data sets. A data set starts with a line containing two positive integers W and H; W and H are the numbers of tiles in the x- and y- directions, respectively. W and H are not more than 20.
There are H more lines in the data set, each of which includes W characters. Each character represents the color of a tile as follows.
'.' - a black tile
'#' - a red tile
'@' - a man on a black tile(appears exactly once in a data set)
There are H more lines in the data set, each of which includes W characters. Each character represents the color of a tile as follows.
'.' - a black tile
'#' - a red tile
'@' - a man on a black tile(appears exactly once in a data set)
Output
For each data set, your program should output a line which contains the number of tiles he can reach from the initial tile (including itself).
Sample Input
6 9 ....#. .....# ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... #@...# .#..#. 11 9 .#......... .#.#######. .#.#.....#. .#.#.###.#. .#.#..@#.#. .#.#####.#. .#.......#. .#########. ........... 11 6 ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..### ..#..#..#@. ..#..#..#.. ..#..#..#.. 7 7 ..#.#.. ..#.#.. ###.### ...@... ###.### ..#.#.. ..#.#.. 0 0
Sample Output
45 59 6 13
Source
Asia 2004, Ehime (Japan), Japan Domestic
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
char map[22][22];//定义最大数组
int sum,l,h;
int dir[4][2]={{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; //四个方位,上、下、左、右
bool border(int x,int y)//推断是否超范围
{
if(x<0||x>=h||y<0||y>=l) return 0;
return 1;
}
void search(int x,int y)
{
int i;
int xx,yy;
sum++;//记录长度
map[x][y]='#';//标记为已走
for(i=0;i<4;i++) //以当前位置向四个方向扩展
{
xx=x+dir[i][0];
yy=y+dir[i][1];
if(border(xx,yy)&&map[xx][yy]=='.') //满足条件就以当前位置继续扩展
search(xx,yy);
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
int x0,y0;
while(cin>>l>>h)
{
sum=0;
if(l==0&&h==0)break;
for(i=0;i<h;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<l;j++)
{
cin>>map[i][j];
if(map[i][j]=='@')//记录当前位置
{
x0=i;
y0=j;
}
}
}
search(x0,y0);//调用当前位置
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
A Knight's Journey
Description
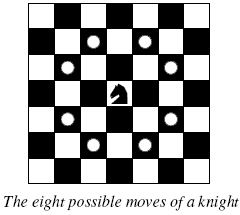 Background
Background
The knight is getting bored of seeing the same black and white squares again and again and has decided to make a journey
around the world. Whenever a knight moves, it is two squares in one direction and one square perpendicular to this. The world of a knight is the chessboard he is living on. Our knight lives on a chessboard that has a smaller area than a regular 8 * 8 board, but it is still rectangular. Can you help this adventurous knight to make travel plans?
Problem
Find a path such that the knight visits every square once. The knight can start and end on any square of the board.
Input
The input begins with a positive integer n in the first line. The following lines contain n test cases. Each test case consists of a single line with two positive integers p and q, such that 1 <= p * q <= 26. This represents a p * q chessboard, where p describes how many different square numbers 1, . . . , p exist, q describes how many different square letters exist. These are the first q letters of the Latin alphabet: A, . . .
Output
The output for every scenario begins with a line containing "Scenario #i:", where i is the number of the scenario starting at 1. Then print a single line containing the lexicographically first path that visits all squares of the chessboard with knight moves followed by an empty line. The path should be given on a single line by concatenating the names of the visited squares. Each square name consists of a capital letter followed by a number.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
If no such path exist, you should output impossible on a single line.
Sample Input
3 1 1 2 3 4 3
Sample Output
Scenario #1: A1 Scenario #2: impossible Scenario #3: A1B3C1A2B4C2A3B1C3A4B2C4
Source
TUD Programming Contest 2005, Darmstadt, Germany
八个方向的深搜回溯 把移动方向打好 (网上好多人说要按字典序走才干A 測试了一下 不按字典序也A了)
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#define M 30
int dx[8] = {-1, 1, -2, 2, -2, 2, -1, 1};
int dy[8] = {-2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 1, 2, 2};
using namespace std;
int cas,n,m,tag;
int map[M][M],t;
char ans[900][2];
void dfs(int x,int y,int k)
{
int xx,yy,i,j;
if(k==n*m)
{
tag=1;
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
xx=x+dx[i];
yy=y+dy[i];
if(map[xx][yy]==0&&xx>0&&xx<=n&&yy>0&&yy<=m)
{
ans[k][0]=ans[k-1][0]+dy[i];//注意这里x轴移动的位移并非字母轴的位移而是数字轴的位移。。坑我好久
ans[k][1]=ans[k-1][1]+dx[i];
map[xx][yy]=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
cout<<map[i][j];cout<<endl;
}cout<<endl;
dfs(xx,yy,k+1);
if(tag)
return ;
map[xx][yy]=0;
}
}
//return ;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,l=1;
cin>>cas;
while(l<=cas)
{
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
memset(ans,'0',sizeof(ans));
map[1][1]=1;
ans[0][0]='A';
ans[0][1]='1';
cin>>n>>m;
t=1;
tag=0;
cout<<"Scenario #"<<l<<":"<<endl;
dfs(1,1,1);
if(tag)
{
//cout<<ans[0][0]<<ans[0][1];
for(i=0;i<n*m;i++)
cout<<ans[i][0]<<ans[i][1];
}
else
cout<<"impossible";
cout<<endl<<endl;
l++;
}
}