文件参数Python--读取wav格式文件
本文纯属个人见解,是对前面学习的总结,如有描述不正确的地方还请高手指正~
1、import wave 用于读写wav文件
它提供了一个方便的WAV格式接口。
但是不支持压缩/解压缩,支持单声道/立体声。
读取格式:
open(file[, mode])
如果file是一个字符串,那么就打开文件,不然就把它当做一个类文件对象。
mode是可以缺省的,如果输入的参数是一个类文件对象,那么file.mode将会作为mode的值。
mode可选参数如下:
'r', 'rb'
Read only mode.
'w', 'wb'
Write only mode.
注意不能同时实现读/写操纵
2、wav文件读操纵
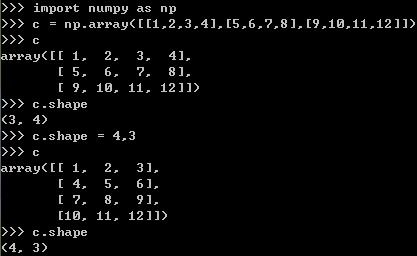
3、numpy:shape转变数组形状
当某数轴的参数为-1时,根据元素个数,主动盘算此轴的最大长度,入将c数组改成2行
4、实例代码
#!usr/bin/env python
#coding=utf-8
from Tkinter import *
import wave
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def read_wave_data(file_path):
#open a wave file, and return a Wave_read object
f = wave.open(file_path,"rb")
#read the wave's format infomation,and return a tuple
params = f.getparams()
#get the info
nchannels, sampwidth, framerate, nframes = params[:4]
#Reads and returns nframes of audio, as a string of bytes.
str_data = f.readframes(nframes)
#close the stream
f.close()
#turn the wave's data to array
wave_data = np.fromstring(str_data, dtype = np.short)
#for the data is stereo,and format is LRLRLR...
#shape the array to n*2(-1 means fit the y coordinate)
wave_data.shape = -1, 2
#transpose the data
wave_data = wave_data.T
#calculate the time bar
time = np.arange(0, nframes) * (1.0/framerate)
return wave_data, time
def main():
wave_data, time = read_wave_data("C:\Users\CJP\Desktop\miss_you.wav")
#draw the wave
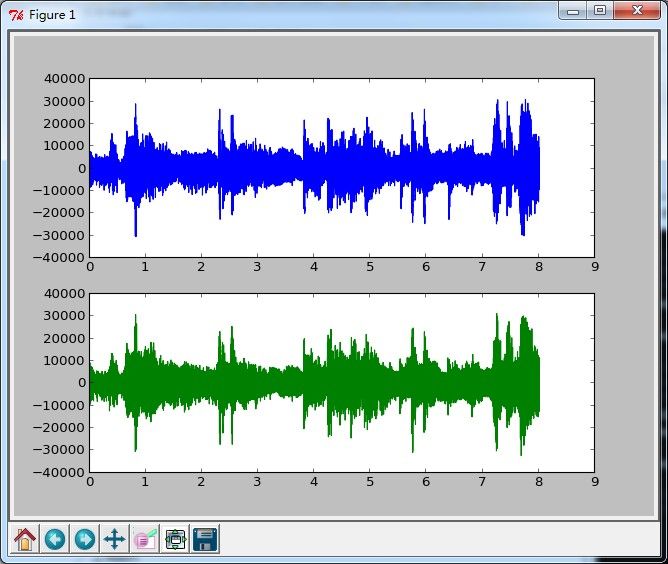
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[0])
plt.subplot(212)
plt.plot(time, wave_data[1], c = "g")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
5、效果
文章结束给大家分享下程序员的一些笑话语录: 问路
有一个驾驶热气球的人发现他迷路了。他降低了飞行的高度,并认出了地面 上的一个人。他继续下降高度并对着那个人大叫,“打扰一下,你能告诉我我 在哪吗?”
下面那个人说:“是的。你在热气球里啊,盘旋在 30 英尺的空中”。
热气球上的人说:“你一定是在 IT 部门做技术工作”。
“没错”,地面上的人说到,“你是怎么知道的?”
“呵呵”,热气球上的人说,“你告诉我的每件事在技术上都是对的,但对都没 有用”。
地面上的人说,“你一定是管理层的人”。
“没错”,热气球上的人说,“可是你是怎么知道的?”
“呵呵”,地面上的那人说到,“你不知道你在哪里,你也不知道你要去哪,你 总希望我能帮你。你现在和我们刚见面时还在原来那个地方,但现在却是我 错了”。