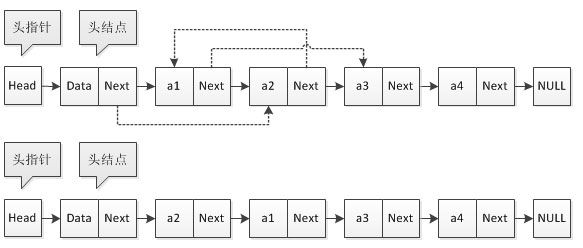
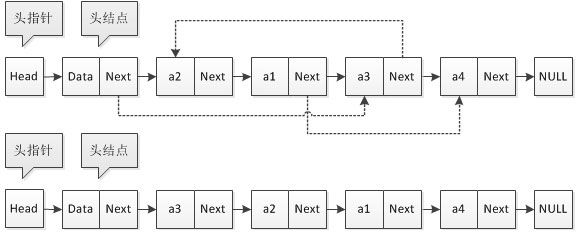
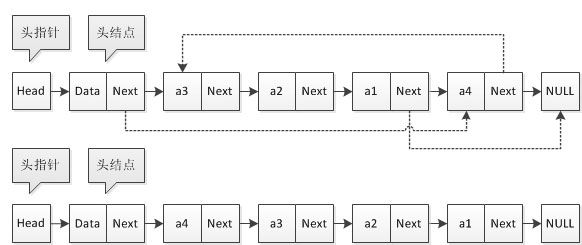
- 数组模拟单链表
Star_.
蓝桥杯java数据结构链表
实现一个单链表,链表初始为空,支持三种操作:向链表头插入一个数;删除第k个插入的数后面的数;在第k个插入的数后插入一个数。现在要对该链表进行M次操作,进行完所有操作后,从头到尾输出整个链表。注意:题目中第k个插入的数并不是指当前链表的第k个数。例如操作过程中一共插入了n个数,则按照插入的时间顺序,这n个数依次为:第1个插入的数,第2个插入的数,…第n个插入的数。输入格式第一行包含整数M,表示操作次
- 深入链表的遍历——快慢指针算法(LeetCode——876题)
欺霜
链表算法java
今天我们一起来学习一下一个快速遍历链表的方法我们先来看看一道经典的需要遍历链表的题目(题目来自LeetCode)876.链表的中间结点https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/给你单链表的头结点head,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。普通方法publicListNodemiddleNode
- 【百日算法计划】:每日一题,见证成长(013)
码上一元
数据结构与算法算法
题目回文链表给你一个单链表的头节点head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。输入:head=[1,2,2,1]输出:true思路找到中间节点反转后半部分链表前后链表顺序比对publicbooleanisPalindrome2(ListNodehead){if(head==null||head.next==null)returntrue;ListNodep=
- 代码随想录算法训练营第三天| 链表01
咕咕鹄鹄
算法
一、链表基础链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构。每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针)。最后一个节点的指针域指向null(空指针的意思)。链表的入口节点称为链表的头结点也就是head。链表类型:单链表、双链表、循环链表单链表:双链表:每一个节点有两个指针域,一个指向下一个节点,一个指向上一个节点。双链表既可以向前查询也可以向后查询。循环链表,就是链表首尾相
- 可利用空间表(Free List)
寿寿_32206
可利用空间表(单链表)1、"可利用空间表",是动态内存管理得一种方法。通过吧空闲得内存划分成固定得数据块,然后利用指针吧这些数据块链接起来,并使用指针指向首结点。2、当用户请求分配时候,系统从可利用的空间表种删除一个结点并分配,当用户释放其所占的内存时,系统既回收并将它插入到可利用的空间表中,空间表也称“存储池”。3、空间表的三种结点结构a.结点大小相同:把内存分为大小相同的若干块,将各块链接起来
- 面试题 链表相交 -剑指offer简单
努力搬砖的小王
日常杂记链表leetcode数据结构
面试题链表相交题目链接给你两个单链表的头节点headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回null。图示两个链表在节点c1开始相交:题目数据保证整个链式结构中不存在环。注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须保持其原始结构。示例1:输入:intersectVal=8,listA=[4,1,8,4,5],listB=[5,0,1,8,4,5],skipA=2,ski
- 数据结构与算法 python实现单链表实现对列
我只要一发
python数据结构与算法Python实现单链表实现对列
对列:先来的先走,后来的后走FIFO实现FIFO的实现数据结构:arroylistlinkedlistdoubllinkedlist最基本的操作,push入列pop出列单链表实现appendpopleftclassFullError(Exception):passclassEmptyError(Exception):passclassQueue(object):def__init__(self,m
- 数据结构:链表、栈、队列
小朱在敲代码
数据结构链表c语言ubuntuvscode
目录链表、栈、队列链表空间使用的区别链表类型单链表节点定义单链表示例双链表节点定义双链表使用栈(Stack)LIFO栈定义栈的使用中缀表达式转后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)队列(queue)FIFO队列的定义队列的使用链表、栈、队列计算机科学中的数据结构是算法设计的基础。本文将详细介绍链表、栈和队列这三种常见的数据结构,并重点分析链表的各种形式及其操作方法。链表链表是一种线性数据结构,与数组不同的是,
- 数据结构——单链表实现和注释浅解
迷迭所归处
数据结构数据结构
关于单链表的基础部分增删查改的实现和一点理解,写在注释里~SList.h#pragmaonce#include#include#include//定义节点的结构//数据+指向下一个节点的指针typedefintSLTDataType;typedefstructSListNode{SLTDataTypedata;//当前节点存储的数据structSListNode*next;//指向下一个节点的指针
- 【408DS算法题】023提高-判断带头结点的链表是否对称
Owlet_woodBird
算法链表数据结构
Index题目分析实现总结题目基础:给定链表的头结点,判断双循环链表是否对称。提高:给定链表的头结点,判断单链表是否对称。分析实现首先分析基础题目:双循环链表的对称判断双循环链表可以方便地访问任意结点的前驱,可直接设置分别指向链表结点的前后指针,不断判断前后指针所指元素是否相等。当两指针相遇/交错的时候,对称性判断完毕,具体实现如下:boolisSymmetric(DLNode*head){DLN
- 为什么不带头节点的非循环单链表进行插入需要使用二级指针,而带头结点的循环双链表不需要二级指针
考研势在必行
C语言模糊知识点数据结构c语言开发语言java数据结构游戏
是否需要使用二级指针的条件,看是否需要改变实参的地址那么为什么不带头节点的非循环单链表进行插入需要使用二级指针,而带头结点的循环双链表不需要二级指针呢,原因就是不带头节点的非循环单链表进行插入需要改变实参的地址,而带头结点的循环双链表不需要改变实参的地址以头插为例function_Slist.cvoidSLIitPushFront(node**pphead,DataTypex){node*newn
- C++ STL->list模拟实现
C++下等马
C++c++liststl
theme:smartbluelistlist文档list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。与其他的序
- 经典数据结构题目解析
xace007
数据结构算法
链表1.删除单链表的重复节点遍历法classSolution{public:ListNode*removeDuplicateNodes(ListNode*head){//先检查头节点是否为空,快速判断if(head==NULL){returnNULL;}ListNode*current=head;//循环遍历检查每一个元素,如果有相同元素则去掉while(current){ListNode*p=c
- #数据结构# 单链表的实现3(C语言)
Asuiiiyi
数据结构数据结构
目录6.尾删结点(SListPopBack):7.头删结点(SListPopFront):8.在pos位置之后插入数据x(SListInsertAfter):9.删除pos位置的数据(SListErase):10.销毁链表(SListDestroy):6.尾删结点(SListPopBack):思路:我们需要找到最后一个结点,并且删除并释放内存,而倒数第二个结点即成为了新的尾结点。因此,我们不仅要得
- #数据结构# 单链表的实现1(C语言)
Asuiiiyi
数据结构数据结构
目录链表的概念:单链表的实现:1.链表的基本单元:2.申请结点(BuySListNode):3.打印链表(SListPrint):链表的概念:“链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。”简单来说可以说为“一环扣一环”,每个结点的数据都有着联系下一个结点的方式。为了方便,我们把链表的名称简化为“SList”。单链表的实现:1.链表的基本单
- 数据结构——单链表多链表基本操作菜单实现(c语言)
weth
c语言作业集数据结构链表c语言
本文将单链表与双向链表的基本操作在同一个程序中实现。其中单链表头文件中的函数与双向链表头文件中的函数可以分离出来单独使用。菜单程序的实现的程序较为复杂,变量多且作用范围不同,如果修改代码需要对代码非常熟悉,没有很好的做到函数的可分离。见谅!完整头文件和代码下载链接请拉到最底端!一、菜单功能及从属关系注意:1.程序设置了两个单链表节点指针和两个双向链表节点指针,但是表现给使用者的链表数同时间内最多两
- LeetCode——反转链表&&相交链表
宁檬精
leetcode链表javascript
目录一.反转链表题目介绍:代码实现:解题思路:二.相交链表题目介绍:代码实现:分析题目:解题思路:一.反转链表题目介绍:给你单链表的头节点head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。示例1:输入:head=[1,2,3,4,5]输出:[5,4,3,2,1]示例2:输入:head=[1,2]输出:[2,1]示例3:输入:head=[]输出:[]提示:链表中节点的数目范围是[0,5000]-5000n
- 链表小总结
万事尽全力
算法题汇总链表数据结构
1.介绍:1.分类:单链表、双链表、循环链表(可以用来解决约瑟夫环问题)。2.存储方式:链表的节点在内存中是分散存储的,通过指针连在一起。3.时间复杂度:链表的增添和删除都是O(1);查找的时间复杂度是O(n)。2.链表的定义:publicclassListNode{//结点的值intval;//下一个结点ListNodenext;//节点的构造函数(无参)publicListNode(){}//
- 二叉树展开为列表(LeetCode)
好好学习Py
算法与数据结构leetcode算法python
题目给你二叉树的根结点root,请你将它展开为一个单链表:展开后的单链表应该同样使用TreeNode,其中right子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为null。展开后的单链表应该与二叉树先序遍历顺序相同。解题classTreeNode:def__init__(self,val=0,left=None,right=None):self.val=valself.left=leftself.r
- leetcode刷题记录-两数相加
每天都一万遍想吃
leetcode
leetcode小白每日做题记录习题集:hot100(c++)题目:第二题两数相加(难度中等)做题思路小白目前只能想到比较直接的方法:本题是采用不带头结点的单链表进行操作的(这里要注意!不然后续的进位计算会出错!!这是我最开始踩的坑)通过对链表中数据的观察,发现只需要维护一个进位变量,这里我采用的是bool型变量,当需要进位时置进位变量st为true,反之为false。由于链l1,l2链表的长度不
- 【LeetCode】刷题记录--单链表相关
DelTTAA
leetcode算法职场和发展
21publicListNodemergeTwoLists(ListNodelist1,ListNodelist2){if(list1==null)returnlist2;if(list2==null)returnlist1;ListNoderesult=newListNode(0);ListNodep=result;while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){if(list1
- LeeCode打卡第十六天
一只大毛吖
leetcode算法数据结构java
LeeCode打卡第十六天第一题:回文链表(LeeCode第234题):给你一个单链表的头节点head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。解法一:暴力求解法主要思想:将链表中的所有元素存到数组中,然后数组首尾进行遍历,看是否相等,相等即为回文链表,不相等则返回false/***Definitionforsingly-linkedlist.*publiccla
- 数据结构代码集训day11(适合考研、自学、期末和专升本)
摆烂的小白
数据结构考研算法链表
今日习题来自B站up:白话拆解数据结构题目如下:1、判断B链表的值是否是A链表值的连续子序列2、假定采用带头结点的单链表保存单词,当两个单词有相同的后缀时,则可共享相同的后缀存储空间,例如,“loading”和“being”的存储映像如下图所示。设str1和str2分别指向两个单词所在单链表的头结点,链表结点结构为{[data][next]},请设计一个时间上尽可能高效的算法,找出由str1和st
- 数据结构集训day12(适合考研、自学、期末和专升本)
摆烂的小白
数据结构考研算法链表
习题来自B站up:白话拆解数据结构今日题目如下:(1)判断带头结点的循环双链表是否对称(2)判断单链表是否有环,有就返回环的入口点,否则返回Null题1首先是结构体,比单链表多了一个前驱指针域。typedefstructDLnode{intdata;DLnode*next;DLnode*prior;}DLnode,*DLinklist;所以建表的过程也需要对前驱进行操作。DLinklistlist
- 力扣237题详解:删除链表中的节点的模拟面试问答
数据分析螺丝钉
LeetCode刷题与模拟面试leetcode算法面试python经验分享
在本篇文章中,我们将详细解读力扣第237题“删除链表中的节点”。通过学习本篇文章,读者将掌握如何在单链表中删除给定的节点,并了解相关的复杂度分析和模拟面试问答。每种方法都将配以详细的解释,以便于理解。问题描述力扣第237题“删除链表中的节点”描述如下:请编写一个函数,用于删除单链表中某个节点。请注意,你只能删除该节点自身,而不能删除其他节点。你将不会得到该节点的前一个节点,但是会得到那个节点本身。
- 【MAC 上学习 C++】Day 55-7. 实验11-2-8 单链表结点删除 (20 分)
RaRasa
实验11-2-8单链表结点删除(20分)1.题目摘自https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/13/problems/6092.题目内容本题要求实现两个函数,分别将读入的数据存储为单链表、将链表中所有存储了某给定值的结点删除。链表结点定义如下:structListNode{intdata;ListNode*next;};函数接口定义:structListNode*readlis
- 力扣234题详解:回文链表的多种解法与模拟面试问答
数据分析螺丝钉
LeetCode刷题与模拟面试leetcode面试算法经验分享python
在本篇文章中,我们将详细解读力扣第234题“回文链表”。通过学习本篇文章,读者将掌握如何判断一个链表是否为回文链表,并了解相关的复杂度分析和模拟面试问答。每种方法都将配以详细的解释,以便于理解。问题描述力扣第234题“回文链表”描述如下:给你一个单链表的头节点head,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回true;否则,返回false。示例:输入:head=[1,2,2,1]输出:true示
- 2020最新大厂内部 PHP 高级工程师面试题汇总(一)
it阿布
1、给你四个坐标点,判断它们能不能组成一个矩形,如判断([0,0],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0])能组成一个矩形。勾股定理,矩形是对角线相等的四边形。只要任意三点不在一条直线上,任选一点,求这一点到另外三点的长度的平方,两个短的之和如果等于最长的,那么这就是矩形。2、写一段代码判断单向链表中有没有形成环,如果形成环,请找出环的入口处,即P点/**单链表的结点类*/classLNode{//为
- 单链表(无头结点)(C/C++)
网络安全电子信息
C/C++数据结构c语言c++数据结构
带头结点与不带头结点的单链表,在进行操作时有哪些区别呢?1.当对单链表的表首元素进行删除或插入操作时,要进行区别处理,无头结点的单链表进行头指针的更新。2.带头结点的单链表,无论单链表是否为空链表,头指针都指向头结点。不带头结点的单链表,当单链表为非空链表时,头指针指向链表第一个结点(LNode),当单链表为空链表时,头指针指向空(NULL)。创建结点//创建不带头结点链表的结点typedefst
- 相交链表
windUtterance
题目描述:编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。示例:image.png输入:intersectVal=8,listA=[4,1,8,4,5],listB=[5,0,1,8,4,5],skipA=2,skipB=3输出:Referenceofthenodewithvalue=8输入解释:相交节点的值为8(注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表A为[4,1,8,4,5]
- ASM系列四 利用Method 组件动态注入方法逻辑
lijingyao8206
字节码技术jvmAOP动态代理ASM
这篇继续结合例子来深入了解下Method组件动态变更方法字节码的实现。通过前面一篇,知道ClassVisitor 的visitMethod()方法可以返回一个MethodVisitor的实例。那么我们也基本可以知道,同ClassVisitor改变类成员一样,MethodVIsistor如果需要改变方法成员,注入逻辑,也可以
- java编程思想 --内部类
百合不是茶
java内部类匿名内部类
内部类;了解外部类 并能与之通信 内部类写出来的代码更加整洁与优雅
1,内部类的创建 内部类是创建在类中的
package com.wj.InsideClass;
/*
* 内部类的创建
*/
public class CreateInsideClass {
public CreateInsideClass(
- web.xml报错
crabdave
web.xml
web.xml报错
The content of element type "web-app" must match "(icon?,display-
name?,description?,distributable?,context-param*,filter*,filter-mapping*,listener*,servlet*,s
- 泛型类的自定义
麦田的设计者
javaandroid泛型
为什么要定义泛型类,当类中要操作的引用数据类型不确定的时候。
采用泛型类,完成扩展。
例如有一个学生类
Student{
Student(){
System.out.println("I'm a student.....");
}
}
有一个老师类
- CSS清除浮动的4中方法
IT独行者
JavaScriptUIcss
清除浮动这个问题,做前端的应该再熟悉不过了,咱是个新人,所以还是记个笔记,做个积累,努力学习向大神靠近。CSS清除浮动的方法网上一搜,大概有N多种,用过几种,说下个人感受。
1、结尾处加空div标签 clear:both 1 2 3 4
.div
1
{
background
:
#000080
;
border
:
1px
s
- Cygwin使用windows的jdk 配置方法
_wy_
jdkwindowscygwin
1.[vim /etc/profile]
JAVA_HOME="/cgydrive/d/Java/jdk1.6.0_43" (windows下jdk路径为D:\Java\jdk1.6.0_43)
PATH="$JAVA_HOME/bin:${PATH}"
CLAS
- linux下安装maven
无量
mavenlinux安装
Linux下安装maven(转) 1.首先到Maven官网
下载安装文件,目前最新版本为3.0.3,下载文件为
apache-maven-3.0.3-bin.tar.gz,下载可以使用wget命令;
2.进入下载文件夹,找到下载的文件,运行如下命令解压
tar -xvf apache-maven-2.2.1-bin.tar.gz
解压后的文件夹
- tomcat的https 配置,syslog-ng配置
aichenglong
tomcathttp跳转到httpssyslong-ng配置syslog配置
1) tomcat配置https,以及http自动跳转到https的配置
1)TOMCAT_HOME目录下生成密钥(keytool是jdk中的命令)
keytool -genkey -alias tomcat -keyalg RSA -keypass changeit -storepass changeit
- 关于领号活动总结
alafqq
活动
关于某彩票活动的总结
具体需求,每个用户进活动页面,领取一个号码,1000中的一个;
活动要求
1,随机性,一定要有随机性;
2,最少中奖概率,如果注数为3200注,则最多中4注
3,效率问题,(不能每个人来都产生一个随机数,这样效率不高);
4,支持断电(仍然从下一个开始),重启服务;(存数据库有点大材小用,因此不能存放在数据库)
解决方案
1,事先产生随机数1000个,并打
- java数据结构 冒泡排序的遍历与排序
百合不是茶
java
java的冒泡排序是一种简单的排序规则
冒泡排序的原理:
比较两个相邻的数,首先将最大的排在第一个,第二次比较第二个 ,此后一样;
针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个
例题;将int array[]
- JS检查输入框输入的是否是数字的一种校验方法
bijian1013
js
如下是JS检查输入框输入的是否是数字的一种校验方法:
<form method=post target="_blank">
数字:<input type="text" name=num onkeypress="checkNum(this.form)"><br>
</form>
- Test注解的两个属性:expected和timeout
bijian1013
javaJUnitexpectedtimeout
JUnit4:Test文档中的解释:
The Test annotation supports two optional parameters.
The first, expected, declares that a test method should throw an exception.
If it doesn't throw an exception or if it
- [Gson二]继承关系的POJO的反序列化
bit1129
POJO
父类
package inheritance.test2;
import java.util.Map;
public class Model {
private String field1;
private String field2;
private Map<String, String> infoMap
- 【Spark八十四】Spark零碎知识点记录
bit1129
spark
1. ShuffleMapTask的shuffle数据在什么地方记录到MapOutputTracker中的
ShuffleMapTask的runTask方法负责写数据到shuffle map文件中。当任务执行完成成功,DAGScheduler会收到通知,在DAGScheduler的handleTaskCompletion方法中完成记录到MapOutputTracker中
- WAS各种脚本作用大全
ronin47
WAS 脚本
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/websphere/library/samples/SampleScripts.html
无意中,在WAS官网上发现的各种脚本作用,感觉很有作用,先与各位分享一下
获取下载
这些示例 jacl 和 Jython 脚本可用于在 WebSphere Application Server 的不同版本中自
- java-12.求 1+2+3+..n不能使用乘除法、 for 、 while 、 if 、 else 、 switch 、 case 等关键字以及条件判断语句
bylijinnan
switch
借鉴网上的思路,用java实现:
public class NoIfWhile {
/**
* @param args
*
* find x=1+2+3+....n
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=10;
int re=find(n);
System.o
- Netty源码学习-ObjectEncoder和ObjectDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
Netty中传递对象的思路很直观:
Netty中数据的传递是基于ChannelBuffer(也就是byte[]);
那把对象序列化为字节流,就可以在Netty中传递对象了
相应的从ChannelBuffer恢复对象,就是反序列化的过程
Netty已经封装好ObjectEncoder和ObjectDecoder
先看ObjectEncoder
ObjectEncoder是往外发送
- spring 定时任务中cronExpression表达式含义
chicony
cronExpression
一个cron表达式有6个必选的元素和一个可选的元素,各个元素之间是以空格分隔的,从左至右,这些元素的含义如下表所示:
代表含义 是否必须 允许的取值范围 &nb
- Nutz配置Jndi
ctrain
JNDI
1、使用JNDI获取指定资源:
var ioc = {
dao : {
type :"org.nutz.dao.impl.NutDao",
args : [ {jndi :"jdbc/dataSource"} ]
}
}
以上方法,仅需要在容器中配置好数据源,注入到NutDao即可.
- 解决 /bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory
daizj
shell
在Linux中执行.sh脚本,异常/bin/sh^M: bad interpreter: No such file or directory。
分析:这是不同系统编码格式引起的:在windows系统中编辑的.sh文件可能有不可见字符,所以在Linux系统下执行会报以上异常信息。
解决:
1)在windows下转换:
利用一些编辑器如UltraEdit或EditPlus等工具
- [转]for 循环为何可恨?
dcj3sjt126com
程序员读书
Java的闭包(Closure)特征最近成为了一个热门话题。 一些精英正在起草一份议案,要在Java将来的版本中加入闭包特征。 然而,提议中的闭包语法以及语言上的这种扩充受到了众多Java程序员的猛烈抨击。
不久前,出版过数十本编程书籍的大作家Elliotte Rusty Harold发表了对Java中闭包的价值的质疑。 尤其是他问道“for 循环为何可恨?”[http://ju
- Android实用小技巧
dcj3sjt126com
android
1、去掉所有Activity界面的标题栏
修改AndroidManifest.xml 在application 标签中添加android:theme="@android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar"
2、去掉所有Activity界面的TitleBar 和StatusBar
修改AndroidManifes
- Oracle 复习笔记之序列
eksliang
Oracle 序列sequenceOracle sequence
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2098859
1.序列的作用
序列是用于生成唯一、连续序号的对象
一般用序列来充当数据库表的主键值
2.创建序列语法如下:
create sequence s_emp
start with 1 --开始值
increment by 1 --増长值
maxval
- 有“品”的程序员
gongmeitao
工作
完美程序员的10种品质
完美程序员的每种品质都有一个范围,这个范围取决于具体的问题和背景。没有能解决所有问题的
完美程序员(至少在我们这个星球上),并且对于特定问题,完美程序员应该具有以下品质:
1. 才智非凡- 能够理解问题、能够用清晰可读的代码翻译并表达想法、善于分析并且逻辑思维能力强
(范围:用简单方式解决复杂问题)
- 使用KeleyiSQLHelper类进行分页查询
hvt
sql.netC#asp.nethovertree
本文适用于sql server单主键表或者视图进行分页查询,支持多字段排序。KeleyiSQLHelper类的最新代码请到http://hovertree.codeplex.com/SourceControl/latest下载整个解决方案源代码查看。或者直接在线查看类的代码:http://hovertree.codeplex.com/SourceControl/latest#HoverTree.D
- SVG 教程 (三)圆形,椭圆,直线
天梯梦
svg
SVG <circle> SVG 圆形 - <circle>
<circle> 标签可用来创建一个圆:
下面是SVG代码:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<circle cx="100" c
- 链表栈
luyulong
java数据结构
public class Node {
private Object object;
private Node next;
public Node() {
this.next = null;
this.object = null;
}
public Object getObject() {
return object;
}
public
- 基础数据结构和算法十:2-3 search tree
sunwinner
Algorithm2-3 search tree
Binary search tree works well for a wide variety of applications, but they have poor worst-case performance. Now we introduce a type of binary search tree where costs are guaranteed to be loga
- spring配置定时任务
stunizhengjia
springtimer
最近因工作的需要,用到了spring的定时任务的功能,觉得spring还是很智能化的,只需要配置一下配置文件就可以了,在此记录一下,以便以后用到:
//------------------------定时任务调用的方法------------------------------
/**
* 存储过程定时器
*/
publi
- ITeye 8月技术图书有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
活动
ITeye携手博文视点举办的8月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。
8月试读活动回顾:
http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2102830
本次技术图书试读活动的优秀奖获奖名单及相应作品如下(优秀文章有很多,但名额有限,没获奖并不代表不优秀):
《跨终端Web》
gleams:http