java excel导出
1、 Excel导出的核心方法在ExportExcel类中,使用时请将该类完整的引入。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.io.OutputStream; 3 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 4 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; 5 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 7 import java.util.Collection; 8 import java.util.Date; 9 import java.util.Iterator; 10 import java.util.regex.Matcher; 11 import java.util.regex.Pattern; 12 13 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell; 14 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle; 15 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFClientAnchor; 16 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFComment; 17 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFont; 18 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFPatriarch; 19 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRichTextString; 20 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow; 21 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; 22 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; 23 import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.CellRangeAddress; 24 import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor; 25 import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.Region; 26 27 28 /** 29 * 利用开源组件POI3.10动态导出EXCEL文档 30 * 31 * @author dqz 32 * @version v1.0 33 * @param <T> 34 * 应用泛型,代表任意一个符合javabean风格的类 35 * 注意这里为了简单起见,boolean型的属性xxx的get器方式为getXxx(),而不是isXxx() 36 * byte[]表jpg格式的图片数据 37 */ 38 public class ExportExcel<T> { 39 public void exportExcel(Collection<T> dataset, OutputStream out) { 40 exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", null, dataset, out, "yyyy-MM-dd"); 41 } 42 43 public void exportExcel(String[] headers, Collection<T> dataset, 44 OutputStream out) { 45 exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", headers, dataset, out, "yyyy-MM-dd"); 46 } 47 48 public void exportExcel(String[] headers, Collection<T> dataset, 49 OutputStream out, String pattern) { 50 exportExcel("测试POI导出EXCEL文档", headers, dataset, out, pattern); 51 } 52 53 /** 54 * 这是一个通用的方法,利用了JAVA的反射机制,可以将放置在JAVA集合中并且符合一定条件的数据以EXCEL 的形式输出到指定IO设备上 55 * 56 * @param title 57 * 表格标题名 58 * @param headers 59 * 表格属性列名数组 60 * @param dataset 61 * 需要显示的数据集合,集合中一定要放置符合javabean风格的类的对象。此方法支持的 62 * javabean属性的数据类型有基本数据类型及String,Date,byte[](图片数据) 63 * @param out 64 * 与输出设备关联的流对象,可以将EXCEL文档导出到本地文件或者网络中 65 * @param pattern 66 * 如果有时间数据,设定输出格式。默认为"yyy-MM-dd" 67 */ 68 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 69 public void exportExcel(String title, String[] headers, 70 Collection<T> dataset, OutputStream out, String pattern) { 71 // 声明一个工作薄 72 HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); 73 // 生成一个表格 74 HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(title); 75 // 设置表格默认列宽度为15个字节 76 sheet.setDefaultColumnWidth((short) 15); 77 // 生成一个样式 78 HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle(); 79 // 设置这些样式 80 style.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.WHITE.index); 81 style.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND); 82 style.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 83 style.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 84 style.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 85 style.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 86 style.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); 87 // 生成一个字体 88 HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont(); 89 font.setColor(HSSFColor.BLACK.index); 90 font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12); 91 font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD); 92 // 把字体应用到当前的样式 93 style.setFont(font); 94 // 生成并设置另一个样式 95 HSSFCellStyle style2 = workbook.createCellStyle(); 96 style2.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.WHITE.index); 97 style2.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND); 98 style2.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 99 style2.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 100 style2.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 101 style2.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN); 102 style2.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); 103 style2.setVerticalAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER); 104 // 生成另一个字体 105 HSSFFont font2 = workbook.createFont(); 106 font2.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_NORMAL); 107 // 把字体应用到当前的样式 108 style2.setFont(font2); 109 110 // 声明一个画图的顶级管理器 111 HSSFPatriarch patriarch = sheet.createDrawingPatriarch(); 112 // 定义注释的大小和位置,详见文档 113 HSSFComment comment = patriarch.createComment(new HSSFClientAnchor(0, 114 0, 0, 0, (short) 4, 2, (short) 6, 5)); 115 // 设置注释内容 116 comment.setString(new HSSFRichTextString("可以在POI中添加注释!")); 117 // 设置注释作者,当鼠标移动到单元格上是可以在状态栏中看到该内容. 118 comment.setAuthor("leno"); 119 120 // 产生表格标题行 121 HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(0); 122 for (short i = 0; i < headers.length; i++) { 123 HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i); 124 cell.setCellStyle(style); 125 HSSFRichTextString text = new HSSFRichTextString(title); 126 cell.setCellValue(text); 127 } 128 sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0 , headers.length-1)); 129 row = sheet.createRow(1); 130 for (short i = 0; i < headers.length; i++) { 131 HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i); 132 cell.setCellStyle(style); 133 HSSFRichTextString text = new HSSFRichTextString(headers[i]); 134 cell.setCellValue(text); 135 } 136 137 // 遍历集合数据,产生数据行 138 Iterator<T> it = dataset.iterator(); 139 int index = 1; 140 while (it.hasNext()) { 141 index++; 142 row = sheet.createRow(index); 143 T t = (T) it.next(); 144 // 利用反射,根据javabean属性的先后顺序,动态调用getXxx()方法得到属性值 145 Field[] fields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); 146 for (short i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { 147 HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i); 148 cell.setCellStyle(style2); 149 Field field = fields[i]; 150 String fieldName = field.getName(); 151 String getMethodName = "get" 152 + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() 153 + fieldName.substring(1); 154 try { 155 Class tCls = t.getClass(); 156 Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName, 157 new Class[] {}); 158 Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[] {}); 159 // 判断值的类型后进行强制类型转换 160 String textValue = null; 161 // if (value instanceof Integer) { 162 // int intValue = (Integer) value; 163 // cell.setCellValue(intValue); 164 // } else if (value instanceof Float) { 165 // float fValue = (Float) value; 166 // textValue = new HSSFRichTextString( 167 // String.valueOf(fValue)); 168 // cell.setCellValue(textValue); 169 // } else if (value instanceof Double) { 170 // double dValue = (Double) value; 171 // textValue = new HSSFRichTextString( 172 // String.valueOf(dValue)); 173 // cell.setCellValue(textValue); 174 // } else if (value instanceof Long) { 175 // long longValue = (Long) value; 176 // cell.setCellValue(longValue); 177 // } 178 if (value instanceof Boolean) { 179 boolean bValue = (Boolean) value; 180 textValue = "男"; 181 if (!bValue) { 182 textValue = "女"; 183 } 184 } else if (value instanceof Date) { 185 Date date = (Date) value; 186 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern); 187 textValue = sdf.format(date); 188 } else if (value instanceof byte[]) { 189 // 有图片时,设置行高为60px; 190 row.setHeightInPoints(60); 191 // 设置图片所在列宽度为80px,注意这里单位的一个换算 192 sheet.setColumnWidth(i, (short) (35.7 * 80)); 193 // sheet.autoSizeColumn(i); 194 byte[] bsValue = (byte[]) value; 195 HSSFClientAnchor anchor = new HSSFClientAnchor(0, 0, 196 1023, 255, (short) 6, index, (short) 6, index); 197 anchor.setAnchorType(2); 198 patriarch.createPicture(anchor, workbook.addPicture( 199 bsValue, HSSFWorkbook.PICTURE_TYPE_JPEG)); 200 } else { 201 // 其它数据类型都当作字符串简单处理 202 textValue = value.toString(); 203 } 204 // 如果不是图片数据,就利用正则表达式判断textValue是否全部由数字组成 205 if (textValue != null) { 206 Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^//d+(//.//d+)?$"); 207 Matcher matcher = p.matcher(textValue); 208 if (matcher.matches()) { 209 // 是数字当作double处理 210 cell.setCellValue(Double.parseDouble(textValue)); 211 } else { 212 HSSFRichTextString richString = new HSSFRichTextString( 213 textValue); 214 HSSFFont font3 = workbook.createFont(); 215 font3.setColor(HSSFColor.BLACK.index); 216 richString.applyFont(font3); 217 cell.setCellValue(richString); 218 } 219 } 220 } catch (SecurityException e) { 221 e.printStackTrace(); 222 } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { 223 e.printStackTrace(); 224 } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { 225 e.printStackTrace(); 226 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 227 e.printStackTrace(); 228 } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { 229 e.printStackTrace(); 230 } finally { 231 // 清理资源 232 } 233 } 234 } 235 try { 236 workbook.write(out); 237 } catch (IOException e) { 238 e.printStackTrace(); 239 } 240 } 241 242 }
2、 创建ModelExcel数据模版类,该类用来记录所需导出到Excel的字段列,类中只包含字段属性及其get,set方法。
注:字段属性的先后顺序代表导出Excel中字段的先后顺序,get,set方法的先后顺序请与字段属性的先后顺序对应。
3、 构造导出方法,实现数据导出Excel。该方法中内容如下:

1 Public void ExportToExcel() 2 { 3 // 数据列表 4 List<ModelExcel> ds = new ArrayList<ModelExcel>(); 5 /* 6 *向ds中插入导出数据 7 */ 8 //创建ExportExcel对象 9 ExportExcel<ModelExcel> ex = new ExportExcel<ModelExcel>(); 10 //构造导出Excel的头标题,与ModelExcel类的字段属性一一对应 11 String[] headers = { "列1", "列2", "列3", "列4"}; 12 // 导出 13 try { 14 //获取xls文件存储路径 15 String filepath = “D:\textExcel.xls”; 16 OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filepath); 17 //导出Excel 18 ex.exportExcel("数据表单标题",headers, ds, out,"yyyy-MM-dd"); 19 out.close(); 20 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 }
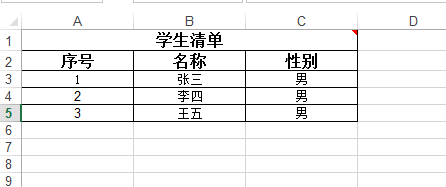
4、 应用举例
1)引入ExportExcel类
2)创建StudentExcel数据模版类

Public class StudentExcel { private int rowindex; //序号 private String name; //名称 private String sex; //性别 public void setRowindex(int rowindex) { this.rowindex = rowindex; } public int getRowindex() { return rowindex; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getSex() { return sex; } }
3)构造导出方法

Public void ExportToExcel() { // 数据列表 List<StudentExcel> ds = new ArrayList<StudentExcel>(); //向ds中插入导出数据 StudentExcel s1 = new StudentExcel(); s1. setRowindex(1); s1. setName(“张三”); s1. setSex(“男”); ds.add(s1); StudentExcel s2 = new StudentExcel(); s2. setRowindex(2); s2. setName(“李四”); s2. setSex(“男”); ds.add(s2); StudentExcel s3 = new StudentExcel(); s3. setRowindex(3); s3. setName(“王五”); s3. setSex(“男”); ds.add(s2); //创建ExportExcel对象 ExportExcel<StudentExcel> ex = new ExportExcel<SExcel>(); //构造导出Excel的头标题 String[] headers = { "序号", "名称", "性别"}; // 导出 try { //获取xls文件存储路径 String filepath = “D:\studentExcel.xls”; OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(filepath); //导出Excel ex.exportExcel("学生清单",headers, ds, out,"yyyy-MM-dd"); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
4)main函数调用运行

public static void main(String[] args) { ExportToExcel(); }
5)导出结果