Leetcode | Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.
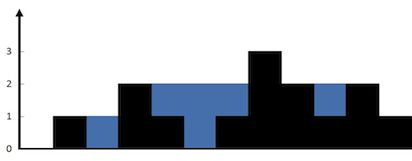
The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Thanks Marcos for contributing this image!
Method I
这道题用的和Largest Rectangle in Histogram类似的算法,都是用了一个栈。如果比栈顶小或者栈为空,就push进栈;如果比栈顶大,就计算围起来的面积。为了不重复计算面积,每次只计算,在栈顶以上,在栈顶的前一个数(pop之后的栈顶)和当前数围起来的长方形面积(Line 13)。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int trap(int A[], int n) { 4 int sum = 0; 5 stack<int> st; 6 7 for (int i = 0; i < n; ) { 8 if (st.empty()) { 9 st.push(i++); 10 } else if (A[i] >= A[st.top()]) { 11 int tmp = st.top(); 12 st.pop(); 13 if (!st.empty()) sum += (i - st.top() - 1) * (min(A[i], A[st.top()]) - A[tmp]); 14 } else { 15 st.push(i++); 16 } 17 } 18 return sum; 19 } 20 };
Method II
网上有另外一种算法,思路是算出每个位置可以存的雨量。就是把总雨量分摊到每个位置。当前位置的雨量由它的min(左边最大值,右边最大值)决定。照着思路重写了一遍。
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int trap(int A[], int n) { 4 if (n == 0) return 0; 5 int sum = 0; 6 vector<int> lfmost(n, 0); 7 8 lfmost[0] = A[0]; 9 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { 10 lfmost[i] = lfmost[i - 1] > A[i - 1] ? lfmost[i - 1] : A[i - 1]; 11 } 12 13 int max = A[n - 1]; 14 for (int j = n - 2; j >= 1; --j) { 15 if (A[j + 1] > max) max = A[j + 1]; 16 int s = min(lfmost[j], max) - A[j]; 17 if (s > 0) sum += s; 18 } 19 return sum; 20 } 21 };