第1章 绪论
1.3 抽象数据类型的表示与实现
将一些常用的头文件包含到一个头文件中,以后就只用调用这个头文件了:
1
 //
c1.h(程序名)
//
c1.h(程序名)
2
3 #include
<
string
.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
4 #include
<
ctype.h
>
#include
<
ctype.h
>
5 #include
<
malloc.h
>
//
malloc()等
#include
<
malloc.h
>
//
malloc()等
6 #include
<
limits.h
>
//
INT_MAX等
#include
<
limits.h
>
//
INT_MAX等
7 #include
<
stdio.h
>
//
EOF(=^Z或F6),NULL
#include
<
stdio.h
>
//
EOF(=^Z或F6),NULL
8 #include
<
stdlib.h
>
//
atoi()
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
//
atoi()
9 #include
<
io.h
>
#include
<
io.h
>
10 #include
<
math.h
>
#include
<
math.h
>
11 #include
<
process.h
>
#include
<
process.h
>
12 #include
<
iostream.h
>
#include
<
iostream.h
>
13
14 //
函数结果状态代码
//
函数结果状态代码
15 #define
TRUE 1
#define
TRUE 1
16 #define
FALSE 0
#define
FALSE 0
17 #define
OK 1
#define
OK 1
18 #define
ERROR 0
#define
ERROR 0
19 #define
INFEASIBLE -1
#define
INFEASIBLE -1
20
21 typedef
int
Status;
//
Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等
typedef
int
Status;
//
Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等
22 typedef
int
Boolean;
//
Boolean是布尔类型
typedef
int
Boolean;
//
Boolean是布尔类型
 //
c1.h(程序名)
//
c1.h(程序名)
2

3
 #include
<
string
.h
>
#include
<
string
.h
>
4
 #include
<
ctype.h
>
#include
<
ctype.h
>
5
 #include
<
malloc.h
>
//
malloc()等
#include
<
malloc.h
>
//
malloc()等
6
 #include
<
limits.h
>
//
INT_MAX等
#include
<
limits.h
>
//
INT_MAX等
7
 #include
<
stdio.h
>
//
EOF(=^Z或F6),NULL
#include
<
stdio.h
>
//
EOF(=^Z或F6),NULL
8
 #include
<
stdlib.h
>
//
atoi()
#include
<
stdlib.h
>
//
atoi()
9
 #include
<
io.h
>
#include
<
io.h
>
10
 #include
<
math.h
>
#include
<
math.h
>
11
 #include
<
process.h
>
#include
<
process.h
>
12
 #include
<
iostream.h
>
#include
<
iostream.h
>
13

14
 //
函数结果状态代码
//
函数结果状态代码
15
 #define
TRUE 1
#define
TRUE 1
16
 #define
FALSE 0
#define
FALSE 0
17
 #define
OK 1
#define
OK 1
18
 #define
ERROR 0
#define
ERROR 0
19
 #define
INFEASIBLE -1
#define
INFEASIBLE -1
20

21
 typedef
int
Status;
//
Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等
typedef
int
Status;
//
Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等
22
 typedef
int
Boolean;
//
Boolean是布尔类型
typedef
int
Boolean;
//
Boolean是布尔类型
采用动态分配的顺序存储结构
1
 //
c1-1.h 采用动态分配的顺序存储结构
//
c1-1.h 采用动态分配的顺序存储结构
2 typedef ElemType
*
Triplet;
//
由InitTriplet分配3个元素存储空间
typedef ElemType
*
Triplet;
//
由InitTriplet分配3个元素存储空间
3 //
Triplet类型是ElemType类型的指针,存放ElemType类型的地址
//
Triplet类型是ElemType类型的指针,存放ElemType类型的地址
 //
c1-1.h 采用动态分配的顺序存储结构
//
c1-1.h 采用动态分配的顺序存储结构
2
 typedef ElemType
*
Triplet;
//
由InitTriplet分配3个元素存储空间
typedef ElemType
*
Triplet;
//
由InitTriplet分配3个元素存储空间3
 //
Triplet类型是ElemType类型的指针,存放ElemType类型的地址
//
Triplet类型是ElemType类型的指针,存放ElemType类型的地址
有关抽象数据类型Triplet和ElemType的8个基本操作函数。
1
 //
bo1-1.cpp 抽象数据类型Triplet和ElemType(由c1-1.h定义)的基本操作(8个)
//
bo1-1.cpp 抽象数据类型Triplet和ElemType(由c1-1.h定义)的基本操作(8个)
2 Status InitTriplet(Triplet
&
T,ElemType v1,ElemType v2,ElemType v3)
Status InitTriplet(Triplet
&
T,ElemType v1,ElemType v2,ElemType v3)
3

 { // 操作结果:构造三元组T,依次置T的3个元素的初值为v1,v2和v3
{ // 操作结果:构造三元组T,依次置T的3个元素的初值为v1,v2和v3
4 if(!(T=(ElemType *)malloc(3*sizeof(ElemType))))
if(!(T=(ElemType *)malloc(3*sizeof(ElemType))))
5 exit(OVERFLOW);
exit(OVERFLOW);
6 T[0]=v1,T[1]=v2,T[2]=v3;
T[0]=v1,T[1]=v2,T[2]=v3;
7 return OK;
return OK;
8 }
}
9
10 Status DestroyTriplet(Triplet
&
T)
Status DestroyTriplet(Triplet
&
T)
11

 { // 操作结果:三元组T被销毁
{ // 操作结果:三元组T被销毁
12 free(T);
free(T);
13 T=NULL;
T=NULL;
14 return OK;
return OK;
15 }
}
16
17 Status Get(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType
&
e)
Status Get(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType
&
e)
18

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:用e返回T的第i元的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:用e返回T的第i元的值
19 if(i<1||i>3)
if(i<1||i>3)
20 return ERROR;
return ERROR;
21 e=T[i-1];
e=T[i-1];
22 return OK;
return OK;
23 }
}
24
25 Status Put(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType e)
Status Put(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType e)
26

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:改变T的第i元的值为e
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:改变T的第i元的值为e
27 if(i<1||i>3)
if(i<1||i>3)
28 return ERROR;
return ERROR;
29 T[i-1]=e;
T[i-1]=e;
30 return OK;
return OK;
31 }
}
32
33 Status IsAscending(Triplet T)
Status IsAscending(Triplet T)
34

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按升序排列,返回1,否则返回0
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按升序排列,返回1,否则返回0
35 return(T[0]<=T[1]&&T[1]<=T[2]);
return(T[0]<=T[1]&&T[1]<=T[2]);
36 }
}
37
38 Status IsDescending(Triplet T)
Status IsDescending(Triplet T)
39

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按降序排列,返回1,否则返回0
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按降序排列,返回1,否则返回0
40 return(T[0]>=T[1]&&T[1]>=T[2]);
return(T[0]>=T[1]&&T[1]>=T[2]);
41 }
}
42
43 Status Max(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
Status Max(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
44

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最大元素的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最大元素的值
45 e=T[0]>=T[1]?T[0]>=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]>=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
e=T[0]>=T[1]?T[0]>=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]>=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
46 return OK;
return OK;
47 }
}
48
49 Status Min(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
Status Min(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
50

 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最小元素的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最小元素的值
51 e=T[0]<=T[1]?T[0]<=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]<=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
e=T[0]<=T[1]?T[0]<=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]<=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
52 return OK;
return OK;
53 }
}
 //
bo1-1.cpp 抽象数据类型Triplet和ElemType(由c1-1.h定义)的基本操作(8个)
//
bo1-1.cpp 抽象数据类型Triplet和ElemType(由c1-1.h定义)的基本操作(8个)
2
 Status InitTriplet(Triplet
&
T,ElemType v1,ElemType v2,ElemType v3)
Status InitTriplet(Triplet
&
T,ElemType v1,ElemType v2,ElemType v3)3


 { // 操作结果:构造三元组T,依次置T的3个元素的初值为v1,v2和v3
{ // 操作结果:构造三元组T,依次置T的3个元素的初值为v1,v2和v34
 if(!(T=(ElemType *)malloc(3*sizeof(ElemType))))
if(!(T=(ElemType *)malloc(3*sizeof(ElemType))))5
 exit(OVERFLOW);
exit(OVERFLOW);6
 T[0]=v1,T[1]=v2,T[2]=v3;
T[0]=v1,T[1]=v2,T[2]=v3;7
 return OK;
return OK;8
 }
}
9

10
 Status DestroyTriplet(Triplet
&
T)
Status DestroyTriplet(Triplet
&
T)11


 { // 操作结果:三元组T被销毁
{ // 操作结果:三元组T被销毁12
 free(T);
free(T);13
 T=NULL;
T=NULL;14
 return OK;
return OK;15
 }
}
16

17
 Status Get(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType
&
e)
Status Get(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType
&
e)18


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:用e返回T的第i元的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:用e返回T的第i元的值19
 if(i<1||i>3)
if(i<1||i>3)20
 return ERROR;
return ERROR;21
 e=T[i-1];
e=T[i-1];22
 return OK;
return OK;23
 }
}
24

25
 Status Put(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType e)
Status Put(Triplet T,
int
i,ElemType e)26


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:改变T的第i元的值为e
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在,1≤i≤3。操作结果:改变T的第i元的值为e27
 if(i<1||i>3)
if(i<1||i>3)28
 return ERROR;
return ERROR;29
 T[i-1]=e;
T[i-1]=e;30
 return OK;
return OK;31
 }
}
32

33
 Status IsAscending(Triplet T)
Status IsAscending(Triplet T)34


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按升序排列,返回1,否则返回0
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按升序排列,返回1,否则返回035
 return(T[0]<=T[1]&&T[1]<=T[2]);
return(T[0]<=T[1]&&T[1]<=T[2]);36
 }
}
37

38
 Status IsDescending(Triplet T)
Status IsDescending(Triplet T)39


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按降序排列,返回1,否则返回0
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:如果T的3个元素按降序排列,返回1,否则返回040
 return(T[0]>=T[1]&&T[1]>=T[2]);
return(T[0]>=T[1]&&T[1]>=T[2]);41
 }
}
42

43
 Status Max(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
Status Max(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)44


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最大元素的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最大元素的值45
 e=T[0]>=T[1]?T[0]>=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]>=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
e=T[0]>=T[1]?T[0]>=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]>=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];46
 return OK;
return OK;47
 }
}
48

49
 Status Min(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)
Status Min(Triplet T,ElemType
&
e)50


 { // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最小元素的值
{ // 初始条件:三元组T已存在。操作结果:用e返回指向T的最小元素的值51
 e=T[0]<=T[1]?T[0]<=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]<=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];
e=T[0]<=T[1]?T[0]<=T[2]?T[0]:T[2]:T[1]<=T[2]?T[1]:T[2];52
 return OK;
return OK;53
 }
}
检查基本操作的主函数
1
 //
main1-1.cpp 检验基本操作bo1-1.cpp的主函数
//
main1-1.cpp 检验基本操作bo1-1.cpp的主函数
2 #include
"
c1.h
"
//
要将程序中所有#include命令所包含的文件拷贝到当前目录下
#include
"
c1.h
"
//
要将程序中所有#include命令所包含的文件拷贝到当前目录下
3
4 //
以下2行可根据需要选用一个(且只能选用一个),而不需改变基本操作bo1-1.cpp
//
以下2行可根据需要选用一个(且只能选用一个),而不需改变基本操作bo1-1.cpp
5 typedef
int
ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为整型
typedef
int
ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为整型
6 //
typedef double ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为双精度型
//
typedef double ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为双精度型
7
8 #include
"
c1_1.h
"
//
在此命令之前要定义ElemType的类型
#include
"
c1_1.h
"
//
在此命令之前要定义ElemType的类型
9 //
#include"bo1_1.cpp"
//
在此命令之前要包括c1-1.h文件(因为其中定义了Triplet)
//
#include"bo1_1.cpp"
//
在此命令之前要包括c1-1.h文件(因为其中定义了Triplet)
10
11 #include
"
bo1_1.h
"
#include
"
bo1_1.h
"
12
13 void
main()
void
main()
14

 {
{
15 Triplet T;
Triplet T;
16 ElemType m;
ElemType m;
17 Status i;
Status i;
18 i=InitTriplet(T,5,7,9); // 初始化三元组T,其3个元素依次为5,7,9
i=InitTriplet(T,5,7,9); // 初始化三元组T,其3个元素依次为5,7,9
19 //i=InitTriplet(T,5.0,7.1,9.3); // 当ElemType为双精度型时,可取代上句
//i=InitTriplet(T,5.0,7.1,9.3); // 当ElemType为双精度型时,可取代上句
20
21 printf("调用初始化函数后,i=%d(1:成功) T的3个值为:",i);
printf("调用初始化函数后,i=%d(1:成功) T的3个值为:",i);
22 cout<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
cout<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
23 // 为避免ElemType的类型变化的影响,用cout取代printf()。注意结尾要加endl
// 为避免ElemType的类型变化的影响,用cout取代printf()。注意结尾要加endl
24
25 i=Get(T,2,m); // 将三元组T的第2个值赋给m
i=Get(T,2,m); // 将三元组T的第2个值赋给m
26 if(i==OK) // 调用Get()成功
if(i==OK) // 调用Get()成功
27 cout<<"T的第2个值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T的第2个值为:"<<m<<endl;
28 i=Put(T,2,6); // 将三元组T的第2个值改为6
i=Put(T,2,6); // 将三元组T的第2个值改为6
29
30 if(i==OK) // 调用Put()成功
if(i==OK) // 调用Put()成功
31 cout<<"将T的第2个值改为6后,T的3个值为:"<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
cout<<"将T的第2个值改为6后,T的3个值为:"<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
32 i=IsAscending(T); // 此类函数实参与ElemType的类型无关,当ElemType的类型变化时,实参不需改变
i=IsAscending(T); // 此类函数实参与ElemType的类型无关,当ElemType的类型变化时,实参不需改变
33 printf("调用测试升序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
printf("调用测试升序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
34 i=IsDescending(T);
i=IsDescending(T);
35 printf("调用测试降序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
printf("调用测试降序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
36
37 if((i=Max(T,m))==OK) // 先赋值再比较
if((i=Max(T,m))==OK) // 先赋值再比较
38 cout<<"T中的最大值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T中的最大值为:"<<m<<endl;
39 if((i=Min(T,m))==OK)
if((i=Min(T,m))==OK)
40 cout<<"T中的最小值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T中的最小值为:"<<m<<endl;
41 DestroyTriplet(T); // 函数也可以不带回返回值
DestroyTriplet(T); // 函数也可以不带回返回值
42 cout<<"销毁T后,T="<<T<<"(NULL)"<<endl;
cout<<"销毁T后,T="<<T<<"(NULL)"<<endl;
43 }
}
 //
main1-1.cpp 检验基本操作bo1-1.cpp的主函数
//
main1-1.cpp 检验基本操作bo1-1.cpp的主函数
2
 #include
"
c1.h
"
//
要将程序中所有#include命令所包含的文件拷贝到当前目录下
#include
"
c1.h
"
//
要将程序中所有#include命令所包含的文件拷贝到当前目录下3

4
 //
以下2行可根据需要选用一个(且只能选用一个),而不需改变基本操作bo1-1.cpp
//
以下2行可根据需要选用一个(且只能选用一个),而不需改变基本操作bo1-1.cpp
5
 typedef
int
ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为整型
typedef
int
ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为整型6
 //
typedef double ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为双精度型
//
typedef double ElemType;
//
定义抽象数据类型ElemType在本程序中为双精度型
7

8
 #include
"
c1_1.h
"
//
在此命令之前要定义ElemType的类型
#include
"
c1_1.h
"
//
在此命令之前要定义ElemType的类型9
 //
#include"bo1_1.cpp"
//
在此命令之前要包括c1-1.h文件(因为其中定义了Triplet)
//
#include"bo1_1.cpp"
//
在此命令之前要包括c1-1.h文件(因为其中定义了Triplet)
10

11
 #include
"
bo1_1.h
"
#include
"
bo1_1.h
"
12

13
 void
main()
void
main()14


 {
{15
 Triplet T;
Triplet T;16
 ElemType m;
ElemType m;17
 Status i;
Status i;18
 i=InitTriplet(T,5,7,9); // 初始化三元组T,其3个元素依次为5,7,9
i=InitTriplet(T,5,7,9); // 初始化三元组T,其3个元素依次为5,7,919
 //i=InitTriplet(T,5.0,7.1,9.3); // 当ElemType为双精度型时,可取代上句
//i=InitTriplet(T,5.0,7.1,9.3); // 当ElemType为双精度型时,可取代上句20

21
 printf("调用初始化函数后,i=%d(1:成功) T的3个值为:",i);
printf("调用初始化函数后,i=%d(1:成功) T的3个值为:",i);22
 cout<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
cout<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;23
 // 为避免ElemType的类型变化的影响,用cout取代printf()。注意结尾要加endl
// 为避免ElemType的类型变化的影响,用cout取代printf()。注意结尾要加endl24

25
 i=Get(T,2,m); // 将三元组T的第2个值赋给m
i=Get(T,2,m); // 将三元组T的第2个值赋给m26
 if(i==OK) // 调用Get()成功
if(i==OK) // 调用Get()成功27
 cout<<"T的第2个值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T的第2个值为:"<<m<<endl;28
 i=Put(T,2,6); // 将三元组T的第2个值改为6
i=Put(T,2,6); // 将三元组T的第2个值改为629

30
 if(i==OK) // 调用Put()成功
if(i==OK) // 调用Put()成功31
 cout<<"将T的第2个值改为6后,T的3个值为:"<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;
cout<<"将T的第2个值改为6后,T的3个值为:"<<T[0]<<' '<<T[1]<<' '<<T[2]<<endl;32
 i=IsAscending(T); // 此类函数实参与ElemType的类型无关,当ElemType的类型变化时,实参不需改变
i=IsAscending(T); // 此类函数实参与ElemType的类型无关,当ElemType的类型变化时,实参不需改变33
 printf("调用测试升序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
printf("调用测试升序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);34
 i=IsDescending(T);
i=IsDescending(T);35
 printf("调用测试降序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);
printf("调用测试降序的函数后,i=%d(0:否 1:是)\n",i);36

37
 if((i=Max(T,m))==OK) // 先赋值再比较
if((i=Max(T,m))==OK) // 先赋值再比较38
 cout<<"T中的最大值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T中的最大值为:"<<m<<endl;39
 if((i=Min(T,m))==OK)
if((i=Min(T,m))==OK)40
 cout<<"T中的最小值为:"<<m<<endl;
cout<<"T中的最小值为:"<<m<<endl;41
 DestroyTriplet(T); // 函数也可以不带回返回值
DestroyTriplet(T); // 函数也可以不带回返回值42
 cout<<"销毁T后,T="<<T<<"(NULL)"<<endl;
cout<<"销毁T后,T="<<T<<"(NULL)"<<endl;43
 }
}
程序运行结果:

变量的引用类型和非引用类型的区别
1
 //
algo1-3.cpp 变量的引用类型和非引用类型的区别
//
algo1-3.cpp 变量的引用类型和非引用类型的区别
2 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3 void
fa(
int
a)
//
在函数中改变a,将不会带回主调函数(主调函数中的a仍是原值)
void
fa(
int
a)
//
在函数中改变a,将不会带回主调函数(主调函数中的a仍是原值)
4

 {
{
5 a++;
a++;
6 printf("在函数fa中:a=%d\n",a);
printf("在函数fa中:a=%d\n",a);
7 }
}
8
9 void
fb(
int
&
a)
//
由于a为引用类型,在函数中改变a,其值将带回主调函数
void
fb(
int
&
a)
//
由于a为引用类型,在函数中改变a,其值将带回主调函数
10

 {
{
11 a++;
a++;
12 printf("在函数fb中:a=%d\n",a);
printf("在函数fb中:a=%d\n",a);
13 }
}
14
15 void
main()
void
main()
16

 {
{
17 int n=1;
int n=1;
18 printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之前:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之前:n=%d\n",n);
19 fa(n);
fa(n);
20 printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之后,调用函数fb之前:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之后,调用函数fb之前:n=%d\n",n);
21 fb(n);
fb(n);
22 printf("在主程中,调用函数fb之后:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fb之后:n=%d\n",n);
23 }
}
 //
algo1-3.cpp 变量的引用类型和非引用类型的区别
//
algo1-3.cpp 变量的引用类型和非引用类型的区别
2
 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3
 void
fa(
int
a)
//
在函数中改变a,将不会带回主调函数(主调函数中的a仍是原值)
void
fa(
int
a)
//
在函数中改变a,将不会带回主调函数(主调函数中的a仍是原值)
4


 {
{5
 a++;
a++;6
 printf("在函数fa中:a=%d\n",a);
printf("在函数fa中:a=%d\n",a);7
 }
}
8

9
 void
fb(
int
&
a)
//
由于a为引用类型,在函数中改变a,其值将带回主调函数
void
fb(
int
&
a)
//
由于a为引用类型,在函数中改变a,其值将带回主调函数
10


 {
{11
 a++;
a++;12
 printf("在函数fb中:a=%d\n",a);
printf("在函数fb中:a=%d\n",a);13
 }
}
14

15
 void
main()
void
main()16


 {
{17
 int n=1;
int n=1;18
 printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之前:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之前:n=%d\n",n);19
 fa(n);
fa(n);20
 printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之后,调用函数fb之前:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fa之后,调用函数fb之前:n=%d\n",n);21
 fb(n);
fb(n);22
 printf("在主程中,调用函数fb之后:n=%d\n",n);
printf("在主程中,调用函数fb之后:n=%d\n",n);23
 }
}
程序运行结果:

1.4 算法和算法分析
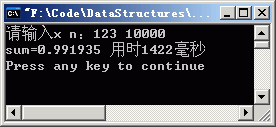
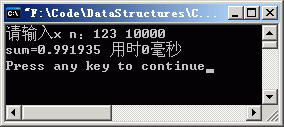
同样是计算:1-1/x+1/x*x-1/x*x*x+...,algo1_1.cpp的语句频度表达式为:(1+n)*n/2,它的时间复杂度T(n)=O(n*n);而algo1_2.cpp的语句频度表达式是n,时间复杂度T(n)=O(n)。
1
 //
algo1-1.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…
//
algo1-1.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…
2 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3 #include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
#include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
4 void
main()
void
main()
5

 {
{
6 timeb t1,t2;
timeb t1,t2;
7 long t;
long t;
8 double x,sum=1,sum1;
double x,sum=1,sum1;
9 int i,j,n;
int i,j,n;
10 printf("请输入x n:");
printf("请输入x n:");
11 scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
12 ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
13 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
14

 {
{
15 sum1=1;
sum1=1;
16 for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
17 sum1=sum1*(-1.0/x);
sum1=sum1*(-1.0/x);
18 sum+=sum1;
sum+=sum1;
19 }
}
20 ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
21 t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
22 printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
23 }
}
 //
algo1-1.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…
//
algo1-1.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…
2
 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3
 #include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
#include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
4
 void
main()
void
main()5


 {
{6
 timeb t1,t2;
timeb t1,t2;7
 long t;
long t;8
 double x,sum=1,sum1;
double x,sum=1,sum1;9
 int i,j,n;
int i,j,n;10
 printf("请输入x n:");
printf("请输入x n:");11
 scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);12
 ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间13
 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)14


 {
{15
 sum1=1;
sum1=1;16
 for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)17
 sum1=sum1*(-1.0/x);
sum1=sum1*(-1.0/x);18
 sum+=sum1;
sum+=sum1;19
 }
}20
 ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间21
 t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差22
 printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);23
 }
}
1
 //
algo1-2.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…的更快捷的算法
//
algo1-2.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…的更快捷的算法
2 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3 #include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
#include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
4 void
main()
void
main()
5

 {
{
6 timeb t1,t2;
timeb t1,t2;
7 long t;
long t;
8 double x,sum1=1,sum=1;
double x,sum1=1,sum=1;
9 int i,n;
int i,n;
10 printf("请输入x n: ");
printf("请输入x n: ");
11 scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
12 ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
13 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
14

 {
{
15 sum1*=-1.0/x;
sum1*=-1.0/x;
16 sum+=sum1;
sum+=sum1;
17 }
}
18 ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
19 t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
20 printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
21 }
}
 //
algo1-2.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…的更快捷的算法
//
algo1-2.cpp 计算1-1/x+1/x*x…的更快捷的算法
2
 #include
<
stdio.h
>
#include
<
stdio.h
>
3
 #include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
#include
<
sys
/
timeb.h
>
4
 void
main()
void
main()5


 {
{6
 timeb t1,t2;
timeb t1,t2;7
 long t;
long t;8
 double x,sum1=1,sum=1;
double x,sum1=1,sum=1;9
 int i,n;
int i,n;10
 printf("请输入x n: ");
printf("请输入x n: ");11
 scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);
scanf("%lf%d",&x,&n);12
 ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t1); // 求得当前时间13
 for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)14


 {
{15
 sum1*=-1.0/x;
sum1*=-1.0/x;16
 sum+=sum1;
sum+=sum1;17
 }
}18
 ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间
ftime(&t2); // 求得当前时间19
 t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差
t=(t2.time-t1.time)*1000+(t2.millitm-t1.millitm); // 计算时间差20
 printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);
printf("sum=%lf 用时%ld毫秒\n",sum,t);21
 }
}
程序运行结果:(左边的时间与计算机的配置有关)